Hydrothermal Synthesis and Structural Characterization of {Co(H2O)(phen)(C7H2O2 F2Br)2}n
JIANG Wei, NI Shengliang
(1. Tonglu Jiuxian Center School, Tonglu 311500, China;2. School of Life Sciences, Huzhou University, Huzhou 313000, China)
Abstract:Hydrothermal reaction of a freshly prepared CoCO3·xH2O, 4-bromo-2,6-difluorobenzoic acid and 1,10-phenanthroline(phen) in CH3OH/H2O (5∶1, V/V) yielded {Co(H2O)(phen)(C7H2O2F2Br)2}n . The cobalt coordination polymer was structurally characterized by single-crystal X-ray diffraction, it crystallizes in monoclinic system, space group P21/c , with a = 17.702(3) ?, b = 6.670(3) ?, c = 22.559(4) ?, β = 111.15(3)°, V = 2 484.2(8) ?3, C26H14O5N2F4Br2Co, Mr = 729.14, Z = 4, Dc = 1.950 g·cm-3, F(000) = 1 428, R1 = 0.053 8 and wR2 = 0.133 4 for 3 834 observed reflections(I≥ 2σ(I)) of 4 357 unique reflections. Within the complex, each Co(Ⅱ) atom has a distorted octahedral geometry which was six-coordinated by two N atoms and four O atoms. The chains bridged by 4-bromo-2,6-difluorobenzoato carboxylate anions extend in the b direction, the bc layers are assembled by inter-chains π-π packing interaction with aromatic rings.
Keywords:Cobalt(Ⅱ) coordination polymer; 4-bromo-2,6-difluorobenzoic acid; structural characterization
Cobalt complexes have potential application in medicine, catalytic oxidation, analytical chemistry, optical materials and magnetic materials[1]. Recently, much attention has been focused on the design and synthesis of cobalt complexes with carboxylic acid due to the large variety of architectures result from coordination versatility of the carboxylate ligands and variable coordination numbers of the metal centers.In recent years, polyhalogenated benzoic acid has been used as important ligands to obtain some supramolecular complexs[2-4]. In order to continue our studies on the cobalt complexes[5-6], we report herein the cobalt complex {Co(H2O)(phen)(C7H2O2F2Br)2}n, which was synthesized by using 4-bromo-2,6-difluorobenzoic acid as bridged ligand by hydrothermal method.
1 Experimental
1.1 Synthesis
In a typical synthesis[7], the fresh purple precipitate obtained by addition of 0.5 mL of 1 M NaCO3to a stirred aqueous solution of CoCl2·6H2O (0.119 0 g, 0.5 mmol) in 2 mL of H2O, CoCO3·yH2O, which was centrifuged and washed with water until no Cl-1ions were detected in the supernatant. The purple precipitate was added to a mixed solution of 4-bromo-2,6-difluorobenzoic acid (0.237 6 g, 1.0 mmol) and 1,10-phenanthroline (0.099 1 g, 0.5 mmol) in 12 mL CH3OH/H2O(5∶1,V/V). The mixture was stirred for 30 min, subsequently, was transferred into 20 cm3Teflon liner, which was sealed in a stainless autoclave, the reaction was carried out at 140 ℃ for 24 h under auto-geneous pressure, then cooled to room temperature, the resulting block crystals were obtained in 38% yield (0.138 7 g) based on initial CoCl2·6H2O.
1.2 Crystal structure determination
Suitable orange single crystals was selected under a polarizing microscope and fixed with epoxy cement on respective fine glass fibers, which were then mounted on a Rigaku R-Axis Rapid IP X-ray diffractometer with graphite-monochromated MoKradiation (λ= 0.710 73 ?) for cell determination and subsequent data collection. The reflection intensities in the θ range 3.20°~25.00° were collected at 298 K using the scan technique. The employed single crystals exhibit no detectable decay during the data collection. The data were corrected forLpand absorption effects. The SHELXS-97[8]and SHELXL-97[9]programs were used for structure solution and refinement. The structures were solved by using direct methods. Subsequent difference Fourier syntheses enabled all non-hydrogen atoms to be located. After several cycles of refinement, all hydrogen atoms associated with carbon atoms were geometrically generated, and the rest of the hydrogen atoms were located from the successive difference Fourier syntheses. Finally, all non-hydrogen atoms were refined with anisotropic displacement parameters by the full-matrix least-squares technique and hydrogen atoms with isotropic displacement parameters set to 1.2 times of the values for the associated heavier atoms. Detailed information about the crystal data and structure determination is summarized in Tab.1.
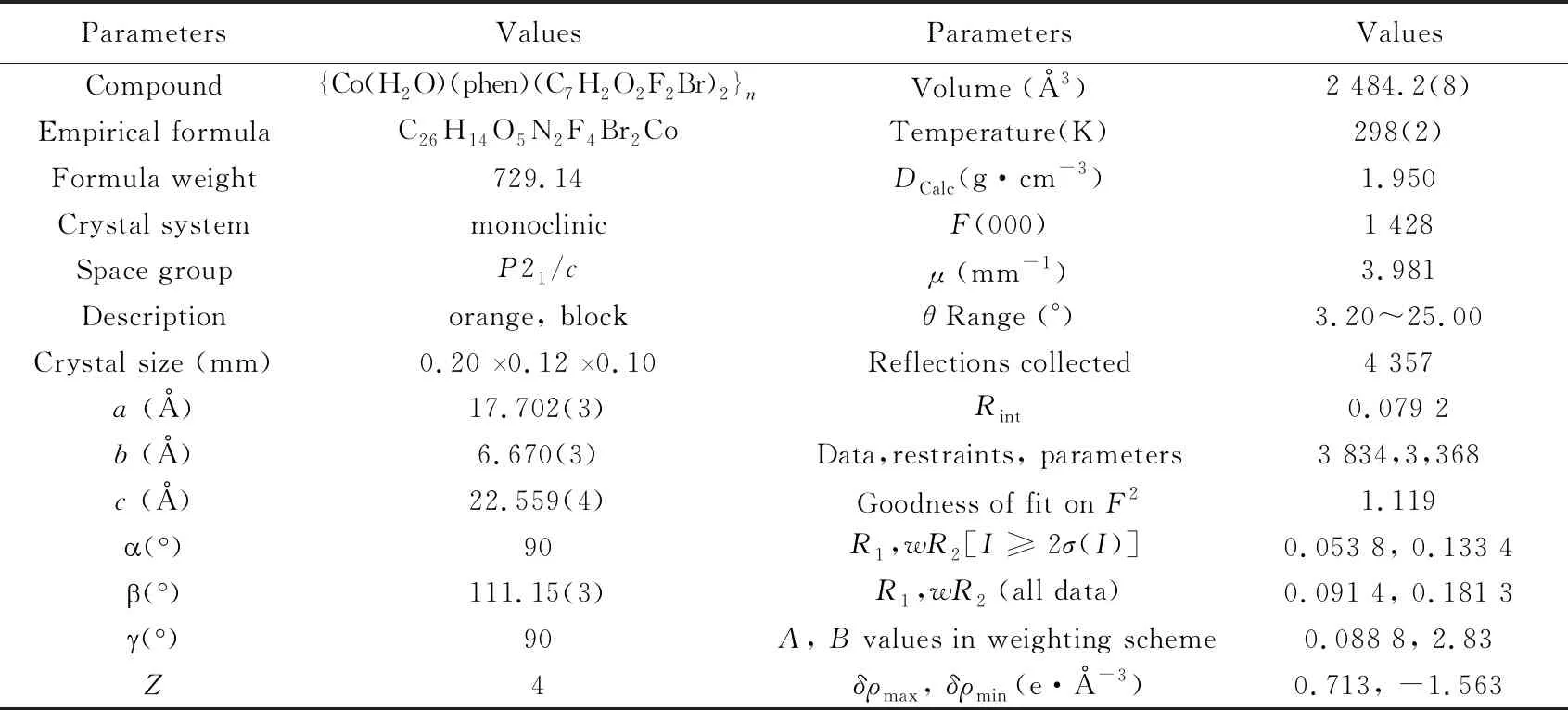
Tab.1 Crystallographic data for {Co(H2O)(phen)(C7H2O2F2Br)2}n
whereR1=∑(Fo-Fc)/∑Fo,
2 Results and Discussions
2.1 Crystal structure
The cobalt complex, {Co(H2O)(phen)(C7H2O2F2Br)2}n, its asymmetric unit consisting of one Co(Ⅱ) ion, one phen ligand,two different coordinated 4-bromo-2,6-difluorobenzoate anions with significant plane torsional angles (O1-C1-O2 angle = 31.5°, O3-C8-O4 angle = 75.5°), and one coordinated water. As shown in Fig. 1,the Co(Ⅱ) ion lie in a distorted octahedral coordination environment with an N2O4donor set. The Co-O/N bond length of Co(Ⅱ) ion in the basal plane vary between 2.087 ~ 2.247 ?, and the axial position bond bridged-coordinated carboxylate oxygen atoms are 2.227 ? and 2.278 ?. The cisoid angles subtended at the Co(Ⅱ) ion fall in the ranges of 74.1°~ 100.7°, and transoid ones range from 169.1° to 174.6°, exhibitinging significant deviation from the ideal values. Bond distances and angles of the benzoate anions and phen ligand fall in usual range[10-11]. Selected inter-atomic distances and bond angles are given in Tab.2.
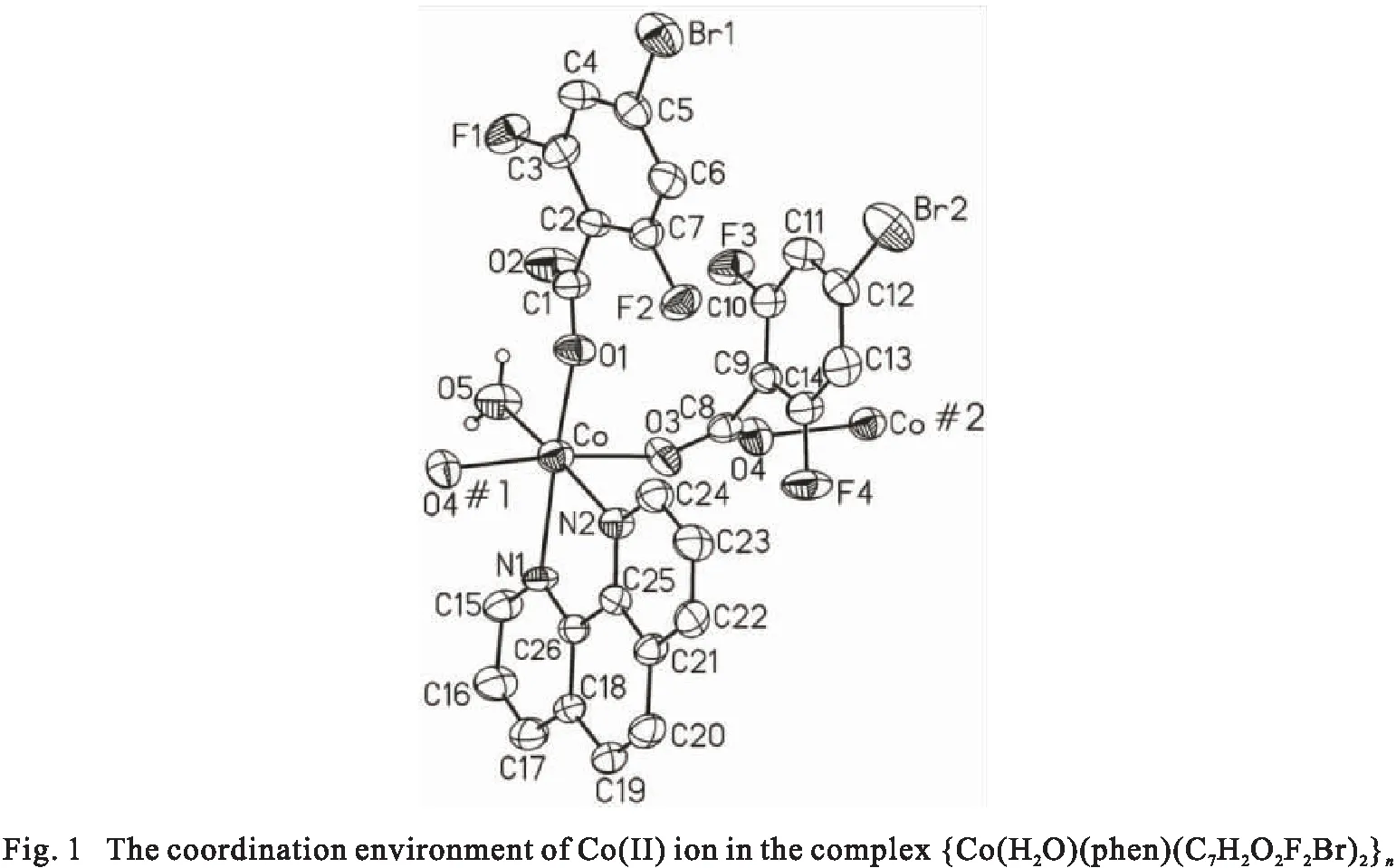
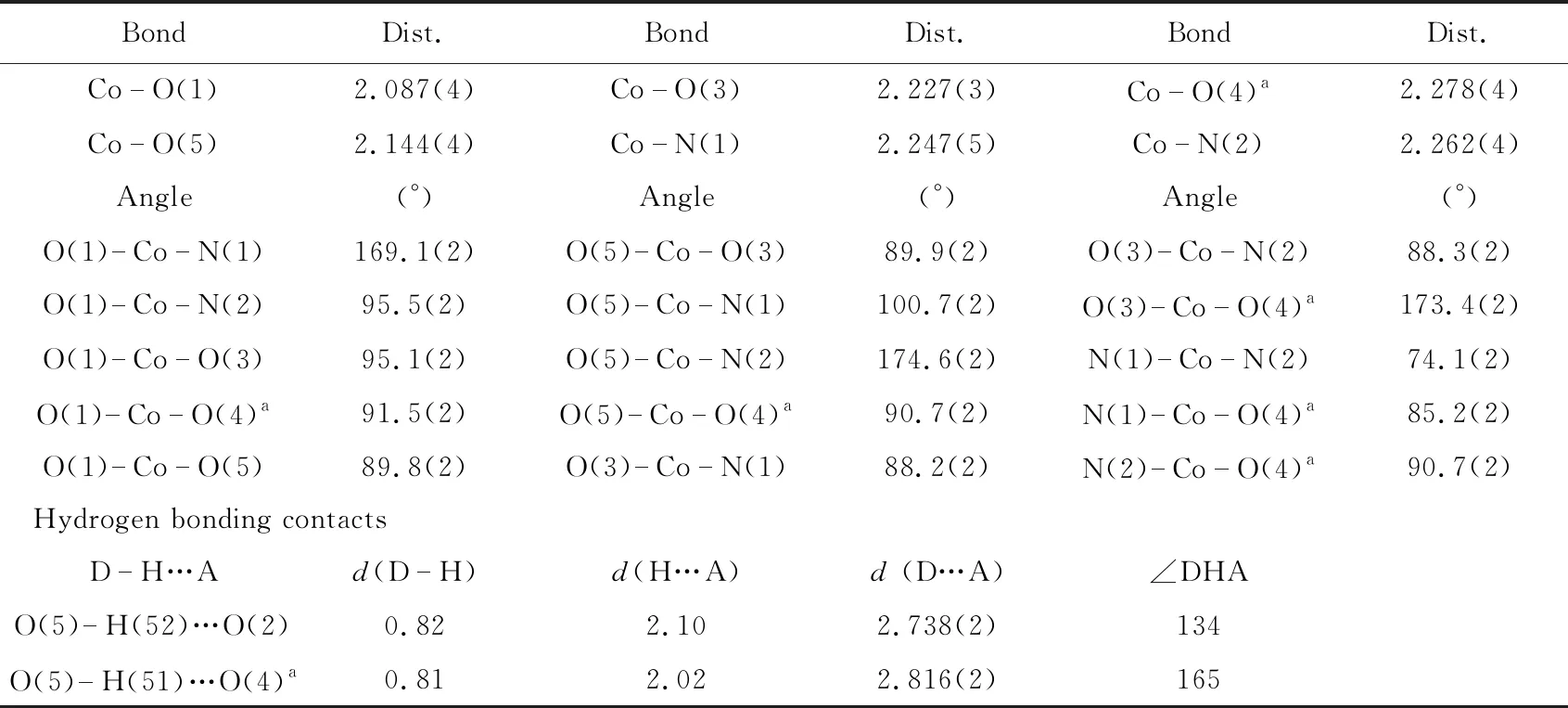
Tab.2 Selected bond and hydrogen bond lengths (?) and bond angles (°) for the complex {Co(H2O)(phen)(C7H2O2F2Br)2}n
Symmetry codes:a=-x, -y+1, -z+1.
The complex asymmetric units bridged by benzoate anions are assembled into one-dimension chains extending along thebdirection, as shown in Fig. 2. Two neighboring 1D chains held together byπ-πaromatic ring packing interactions with centroid-centroid distances of 3.556 ?, as shown in Fig. 3. The former double chains interlinkedbclayers structure and 3D framework via Van der Waals forces.
2.2 IR spectra
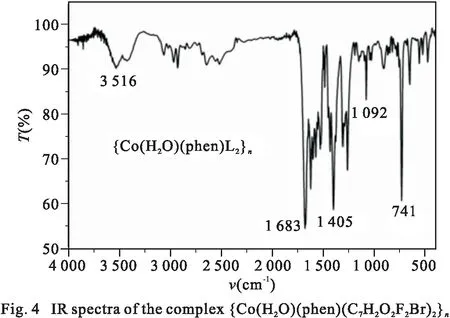
Infrared(IR) spectra was recorded with KBr discs in the range of 4 000~ 400 cm-1, as shown in Fig. 4. The result shows a strong and broad peak at 3 516 cm-1, which indicates the presence of water molecules. The disappearance of a characteristic peak of the cobalt complex near 1 700 cm-1indicates that the carboxyl group has been completely deprotonated. The strong peaks at 1 683 cm-1and 1 405cm-1are attributed to the asymmetric and symmetric vibrations of carboxylate groups, Δν=νas(COO-)-νs(COO-) = 278 cm-1shows that the carboxyl in complex adopt monodentate coordinate mode[12]. The above result is consistent with the X-ray diffraction study.
3 Conclusion
In conclusion, a novel cobalt(Ⅱ) coordination polymer, {Co(H2O)(phen)(C7H2O2F2Br)2}n, was synthesized by hydrothermal reaction and characterized by single-crystal X-ray diffraction and infrared spectrum. The single-crystal X-ray diffraction reveals that the center Co(Ⅱ) atom is in six-coordination distorted octahedral geometry. The chains bridged by 4-bromo-2,6-difluorobenzoato carboxylate anions extend in thebdirection, thebclayers are assembled by inter-chainsπ-πpacking interaction with aromatic rings.

