BOUNDEDNESS FOR SOME SCHRDINGER TYPE OPERATORS ON MORREY SPACES WITH VARIABLE EXPONENT RELATED TO CERTAIN NONNEGATIVE POTENTIALS
WANG Min,SHU Li-sheng,QU Meng,CHENG Mei-fang
(School of Mathematics and Computer Science,Anhui Normal University,Wuhu 241003,China)
WANG Min,SHU Li-sheng,QU Meng,CHENG Mei-fang
(School of Mathematics and Computer Science,Anhui Normal University,Wuhu 241003,China)
In this paper,the boundedness of some Schrdinger type operators and the commutators is considered.Using the boundedness of them on Lpspace,we obtain the boundedness of some schrdinger type operators and the commutators on Morrey with variable exponents.
Morrey spaces;commutators;Schrdinger type operators;variable exponent
2010 MR Subject Classification:42B20;42B35
Document code:AArticle ID:0255-7797(2016)06-1149-11
1 Introduction
In this paper,we consider the schrdinger differential operator
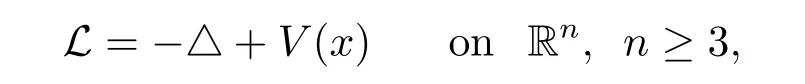
where V(x)is a nonnegative potential belonging to the reverse Hlder class Bqfor q≥
A nonnegative locally Lqintegrable function V(x)on Rnis said to belong to Bq(q>1) if there exists a constant C>0 such that the reverse Hlder inequality
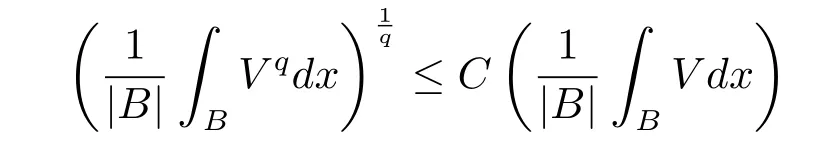
holds for every ball in Rn,see[1].
Shen[1]established Lpestimates for schrdinger type operators with certain potentials.Kurata,Nishigaki and Sugano[2]considered the boundedness of integral operators on generalized Morrey spaces and its application to Schrdinger operators.Recently,paper[3] by Tang and Dong proved the boundedness of some Schrdinger type operators on Morrey spaces related to certain nonnegative potentials.
It is well known that function spaces with variable exponents were intensively studied during the past 20 years,due to their applications to PDE with non-standard growth conditions and so on,we mention e.g.[4,5].A great deal of work was done to extend the theory of potential,singular type operators and their commutators on the classical Lebesgue spaces to the variable exponent case(see[6-8]).Also,many results about potential,singular type operators and their commutators were studied on Morrey Spaces with variable exponent(see [9-12]).Hence,it will be an interesting problem whether we can establish the boundedness of some schrdinger type operators on Morrey spaces with variable exponent related to certain nonnegative potentials.The main purpose of this paper is to answer the above problem.
To meet the requirements in the next sections,here,the basic elements of the theory of the Lebsegue spaces with variable exponent are briefly presented.
Let p(·):Rn→[1,∞)be a measurable function.The variable exponent Lebesgue space Lp(·)(Rn)is defined by
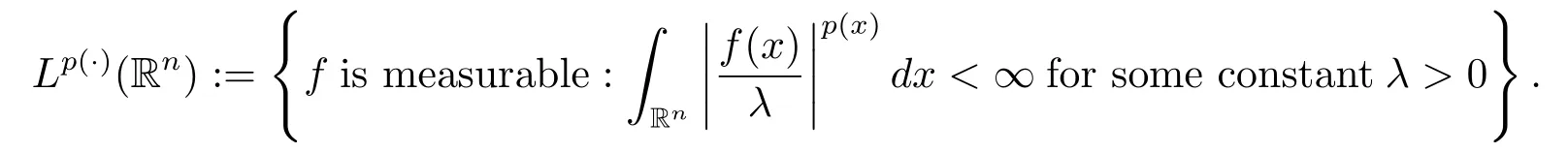
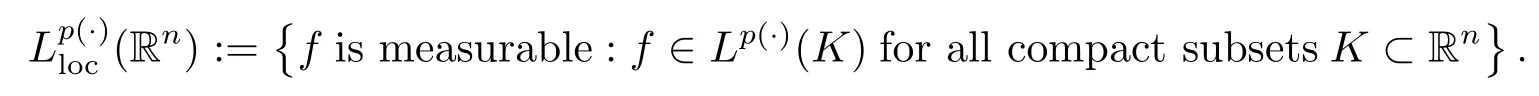
Lp(·)(Rn)is a Banach space with the norm defined by
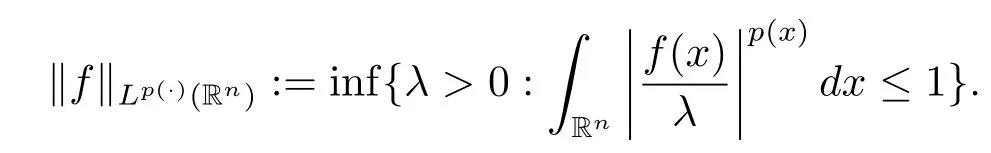
We denote p-:=ess
Let P(Rn)be the set of measurable function p(·)on Rnwith value in[1,∞)such that 1<p-≤p(·)≤p+<∞.
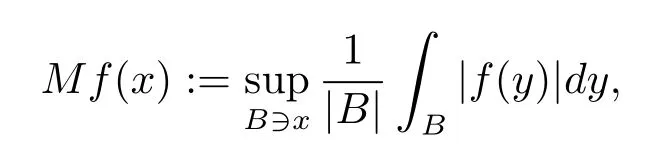
where the supremum is taken over all balls B containing x.B(Rn)is the set of p(·)∈P(Rn) satisfying the condition that M is bounded on Lp(·)(Rn).
We say a function p(·):Rn-→R is locally log-Hlder continuous at the origin,if there exists a constant C such that
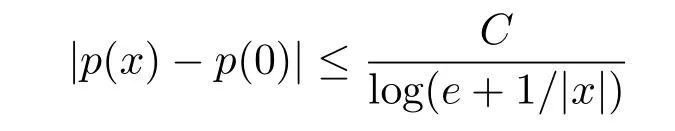
for all x∈Rn.If,for some p(∞)∈R and C>0,there holds
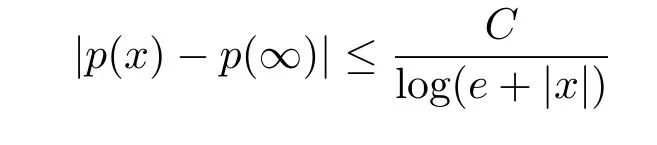
for all x∈Rn,then we say p(·)is log-Hlder continuous at infinity.
Definition 1.1[9]For any p(·)∈B(Rn),let kp(·)denote the supremum of those q>1 such that p(·)/q∈B(Rn).Let ep(·)be the conjugate of kp'(·).
Definition 1.2[9]Let p(·)∈L∞(Rn)and 1<p(x)<∞.A Lebesgue measurable function u(x,r):Rn×(0,∞)→(0,∞)is said to be a Morrey weight function for Lp(·)(Rn) if there exists a constant C>0 such that for any x∈Rnand r>0,u fulfills
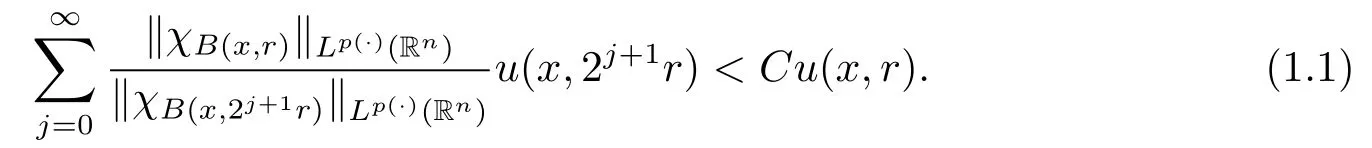
We denote the class of Morrey weight functions by Wp(·).
Next we define the Morrey spaces with variable exponent related to the nonnegative potential V.
For x∈Rn,the function mV(x)is defined by
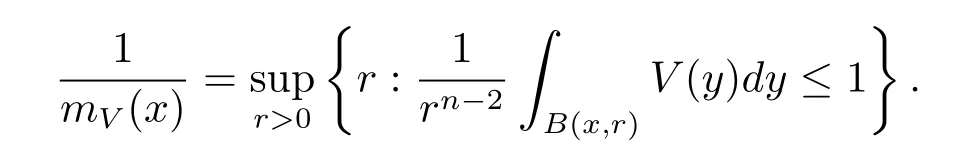
Definition 1.3 Let p(·)∈B(Rn),u(x,r)∈Wp(·)and-∞<α<∞.For f∈(Rn)and V∈Bq(q>1),we say the Morrey spaces with variable exponent related to the nonnegative potential V is the collection of all function f satisfying
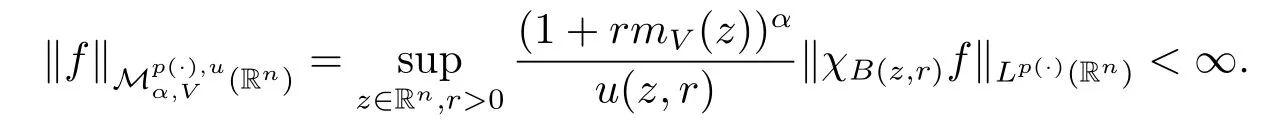
In particular,when α=0 or V=0,the spaces(Rn)is the Morrey spaces with variable exponent Mp(·),u(Rn)introduced in[9].It is easy to see thatMp(·),u(Rn)for α>0 and Mp(·),u(Rn)?(Rn)for α<0.If p(x)is a constant, u(x,r)=rλand λ∈[0,n/p),we have
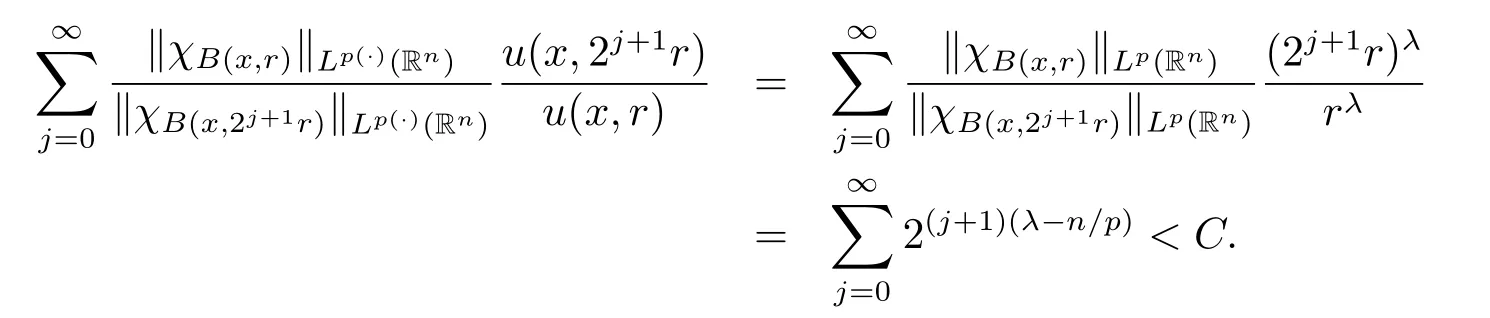
Now it is in this position to state our results.
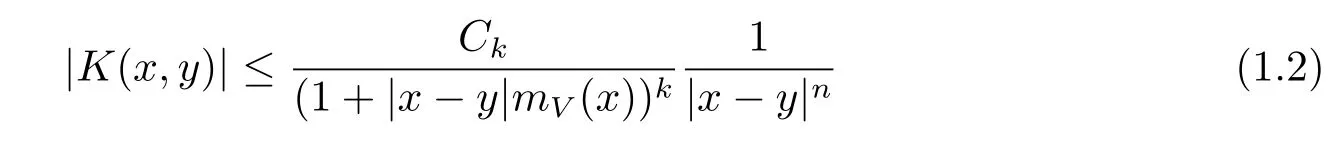
for any k∈N,where Ckdenotes a positive constant depend on k.In the rest of this paper, we always assume that T is one of the schrdinger type operators?(-△+V)-1?,?(-△+ V)-1/2and(-△+V)-1/2?with V∈Bn.
Theorem 1.1 Suppose V∈Bn,-∞<α<∞,p(x)∈B(Rn).If u∈Wp(·),then
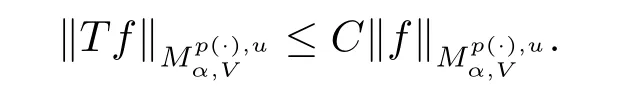
Let b∈BMO(see its definition in[14]),we define the commutator of T by
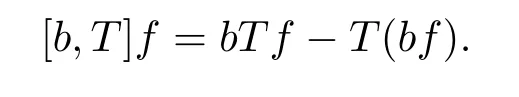
Theorem 1.2 Suppose V∈Bn,b∈BMO,-∞<α<∞,p(x)∈B(Rn).If
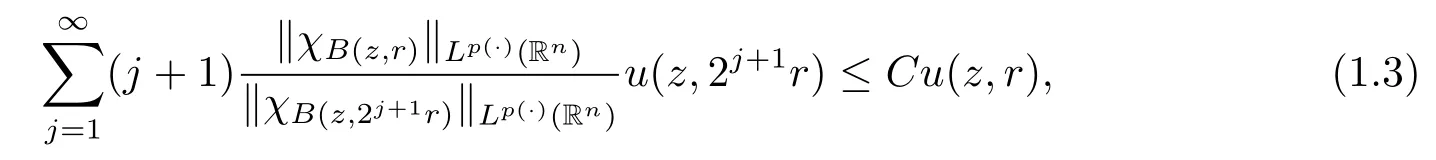
then
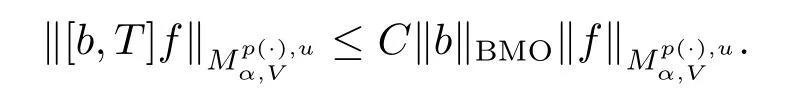
Remark 1 We can easily show that u fulfills(1.3)implies u∈Wp(·)
Next,we consider the boundedness of fractional integrals related to schrdinger operators.
The L-fractional integral operator is defined by
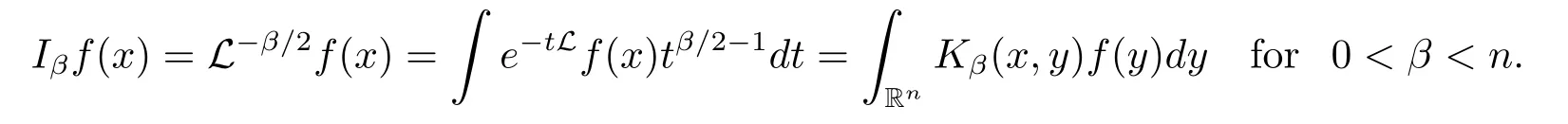
By Lemma 3.3 in[15],one can get the kernel Kβ(x,y)of Iβsatisfy the following inequality
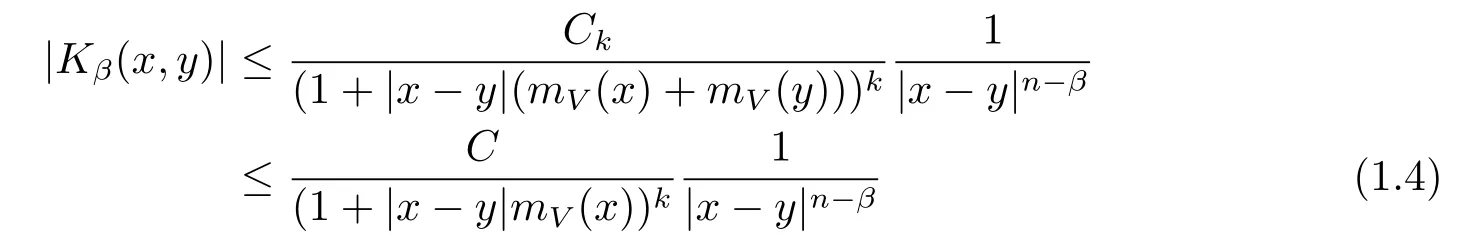
for any k∈N and 0<β<n.
Theorem 1.3 Suppose V∈Bn/2,-∞<α<∞,p(x),q(x)∈B(Rn)satisfy p+<If exists q0satisfying
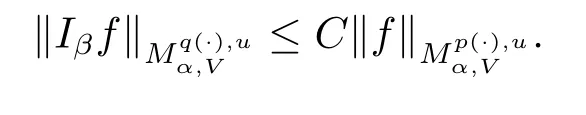
Remark 2 Wq(·)?Wp(·).Indeed,for j≥0,by inequality(2.3)in the next section,we have
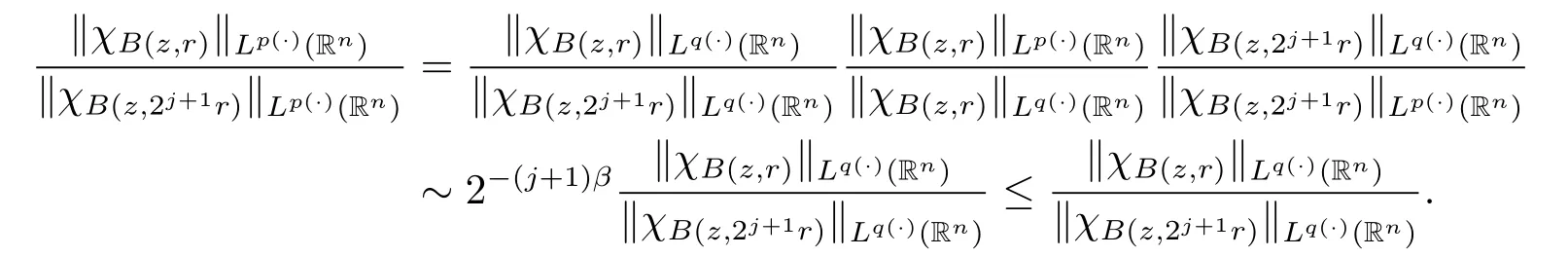
Therefore,using inequality(1.1),we obtain Wq(·)?Wp(·).
Let b∈BMO,we define the commutator of Iβby[b,Iβ]f=bIβf-Iβ(bf).
Theorem 1.4 Suppose V∈Bn/2,b∈BMO,-∞<α<∞,p(·)∈
If p+<and
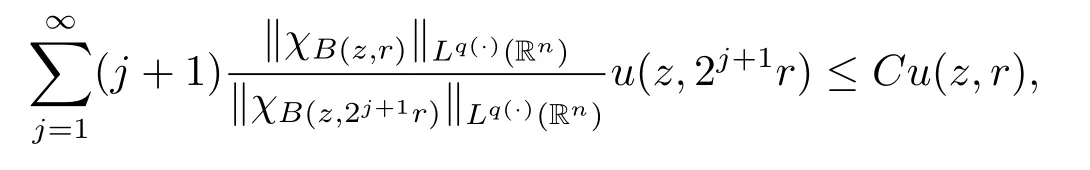
then
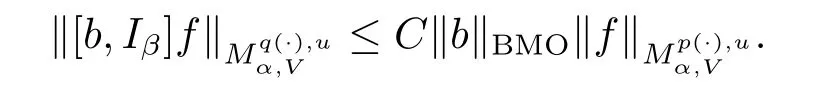
For brevity,C always means a positive constant independent of the main parameters and may change from one occurrence to another.B(x,r)={y∈Rn:|x-y|<r},χBkbe the characteristic function of the set Bkfor k∈Z.|S|denotes the Lebesgue measure of S.The exponent p'(x)means the conjugate of p(x),that is,1/p'(x)+1/p(x)=1.
2 Proofs of Theorems
In order to prove our result,we need some conclusions as follows.
Lemma 2.1[16]Let p(·)∈P(Rn).Then the following conditions are equivalent:
(1)p(·)∈B(Rn);
(2)p'(·)∈B(Rn);
(3)p(·)/q∈B(Rn)for some 1<q<p-;
(4)(p(·)/q)'∈B(Rn)for some 1<q<p-.
Lemma 2.1 ensures that kp(·)is well-defined and satisfies 1<kp(·)≤p-.Moreover, p+≥ep(·).
Lemma 2.2[17]If p(·)∈P(Rn),then for all f∈Lp(·)(Rn)and all g∈Lp'(·)(Rn)we have
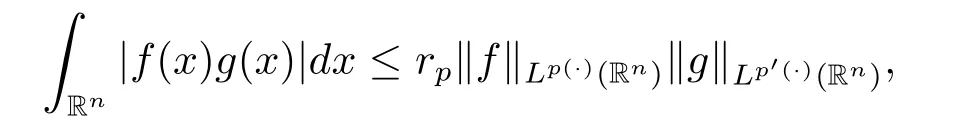
where rp:=1+1/p--1/p+.
Lemma 2.3[6]If p(·)∈B(Rn),then there exists C>0 such that for all balls B in Rn,
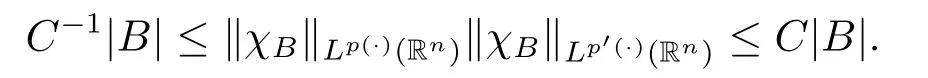
Lemma 2.4[9]Let p(x)∈B(Rn)and 1<p-≤p+<∞.There exist C1,C2>0 such that for any B∈B,
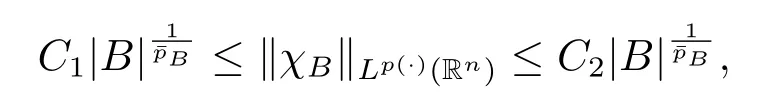
Lemma 2.5[9]Let p(x)∈B(Rn).For any 1<q<kp(·)and 1<s<kp'(·),there exist constants C1,C2>0 such that for any x0∈Rnand r>0,we have
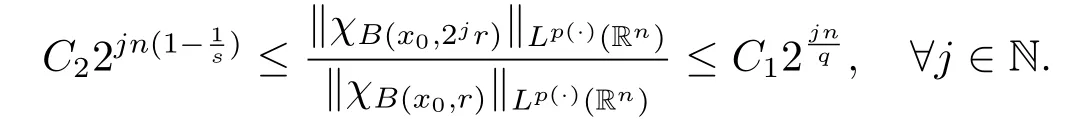
The next lemma can be get by inequality(1.4)and Corollary 2.12 in[6].
Lemma 2.6[6]Let β>0,p(x),q(x)∈P(Rn)satisfy p+<.If exists q0satisfyingfor some C>0.
Theorem 1 in[8]and inequality(1.4)are rewrited as the following lemma.
Lemma 2.7 Suppose that p(·)∈.then we have
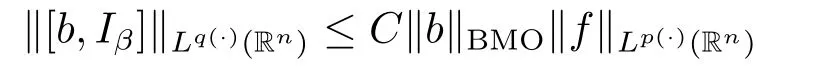
for f∈Lp(·)(Rn)and b∈BMO(Rn).
Using Corollary 2.5 and Corollary 2.10 in[6]and the inequality(1.2),we can get the following result.
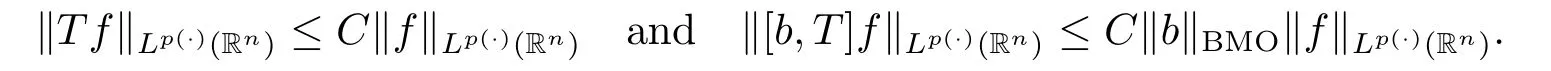
Lemma 2.9[18]Let k be a positive integer.Then we have that for all b∈BMO(Rn) and all i,j∈Z with i>j,
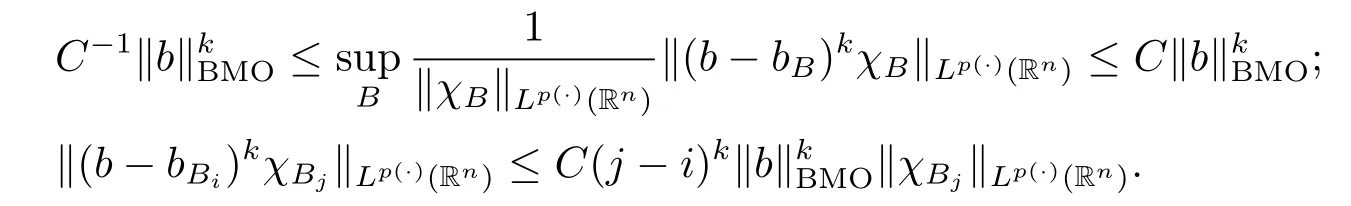
Lemma 2.10[1,3]Suppose V∈Bqwith q≥n/2.Then there exist positive constants C and k0such that
(1)mV(x)~mV(y)if|x-y|≤
(2)mV(y)≤C(1+|x-y|mV(x))kOmV(x);
(3)mV(y)≥
We will give the proofs of Theorems 1.3 and 1.4 below.The arguments for Theorems 1.1 and 1.2 are similar,we omit the details here.
Proof of Theorem 1.3 Without loss of generality,we may assume that α<0.Let f∈Mp(·),u.For any z∈Rnand r>0,we write f(x)=f0(x)+fj(x),where f0= fχB(z,2r),fj=fχB(z,2j+1r)B(z,2jr)for j≥1.Hence we have
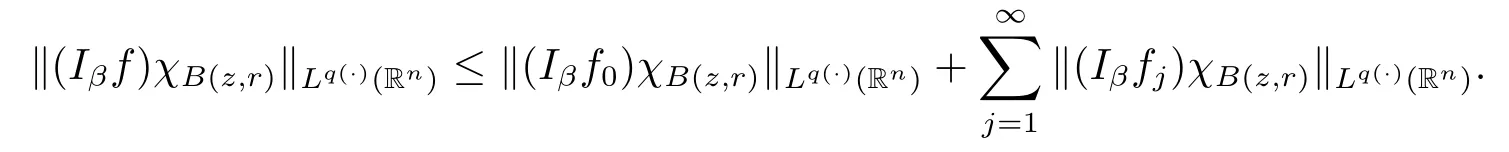
By Lemma 2.6,we obtain
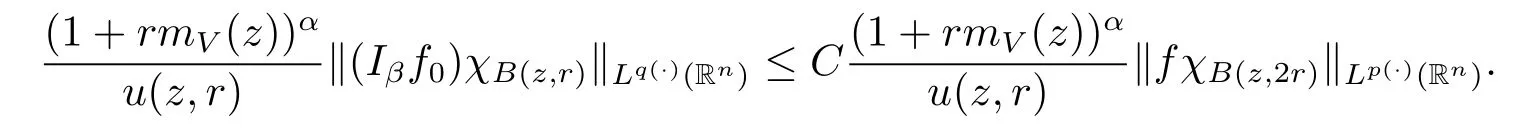
Because inequality(1.1)and Lemma 2.5 imply that u(x,r)≥Cu(x,2r).Therefore,we obtain
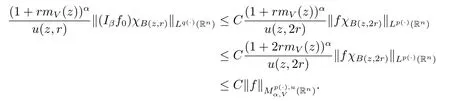
Furthermore,for any j≥1,x∈B(z,r)and y∈B(z,2j+1r)B(z,2jr),we note that |x-y|≥|y-z|-|x-z|>C2jr.Thus we get
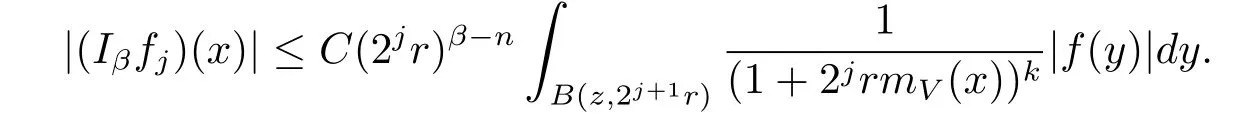
Using Lemma 2.10,we derive the estimate
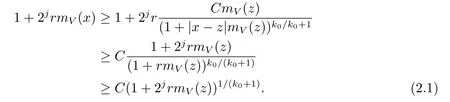
Thus we get that
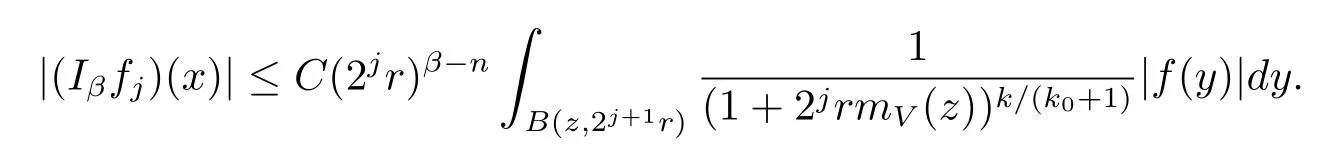
Lemma 2.2 ensures that
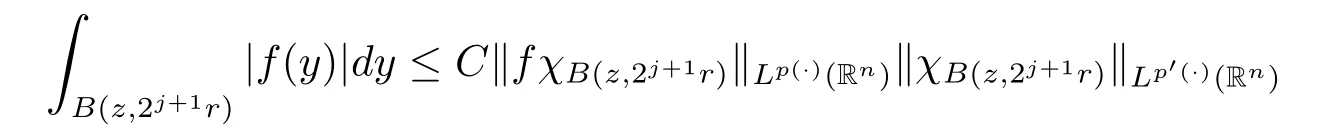
for some constant C>0.
Subsequently,taking the norm‖·‖Lq(·)(Rn),we have
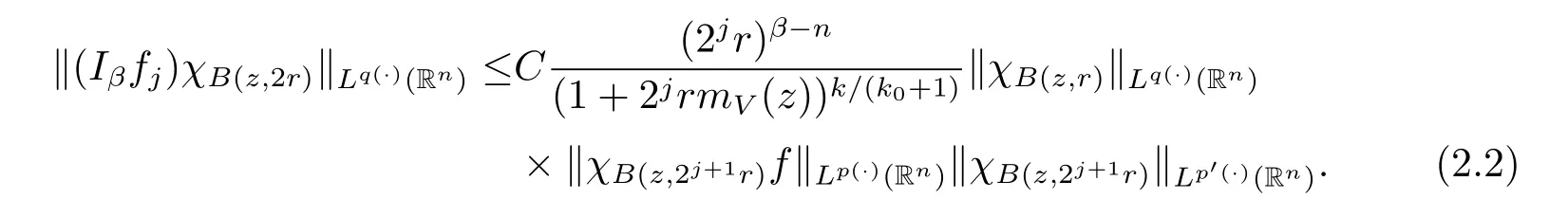
Applying Lemma 2.3 with B=B(z,2j+1r),we obtain
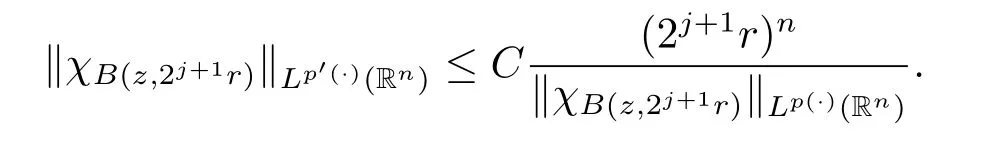
Using the above inequality on(2.2),we obtain
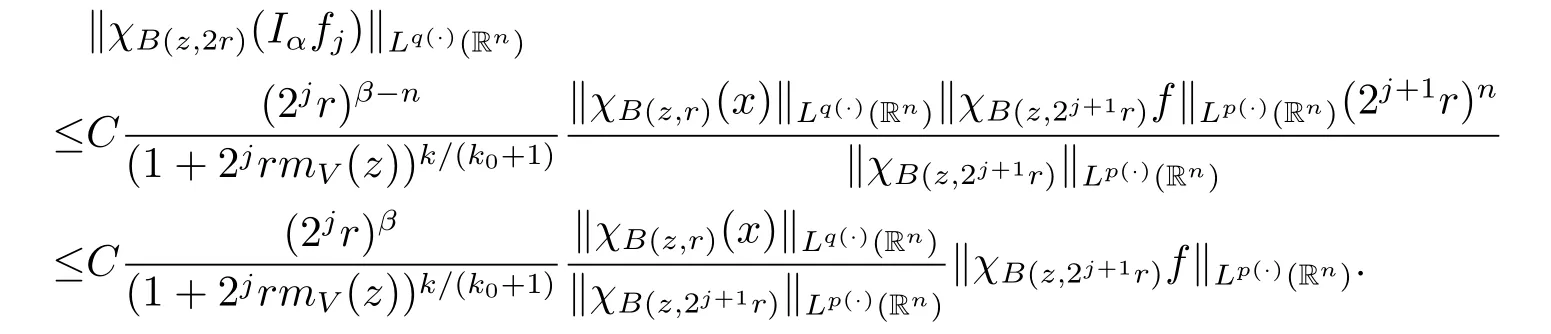
In view of the fact that for any ball B,we have
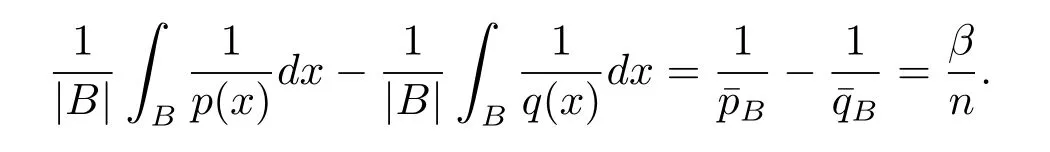
Lemma 2.4 implies that
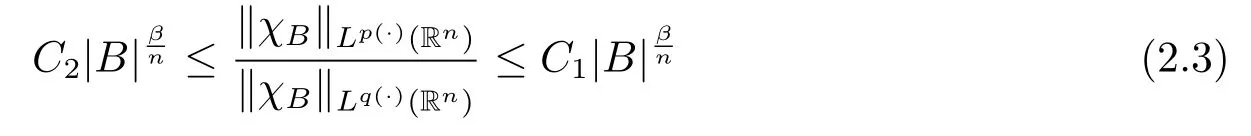
for some constants C1>C2>0 independent of B.
Hence using(2.3)with B=B(z,2j+1r),we have
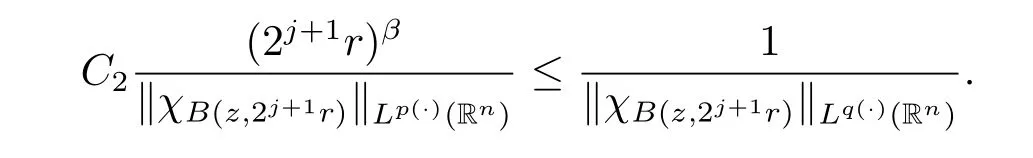
Therefore
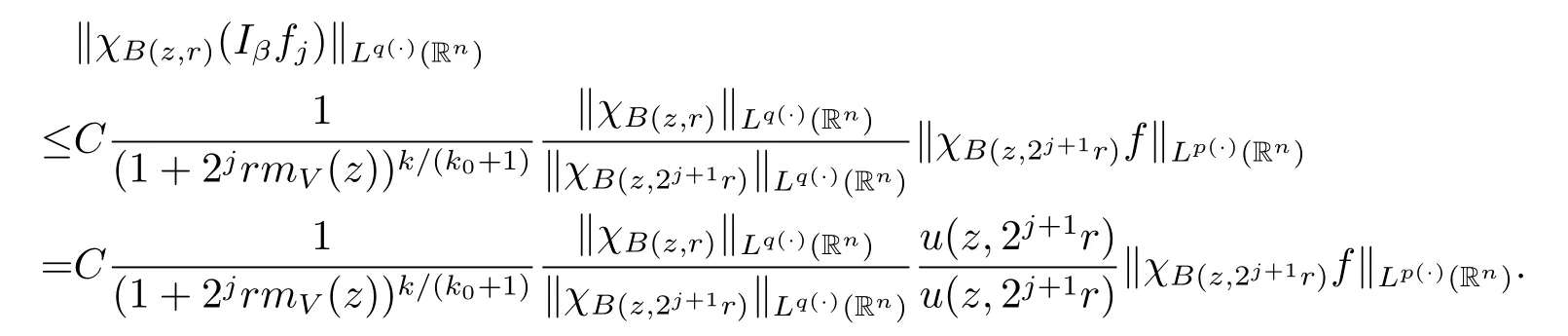
Thus we arrive at the inequality
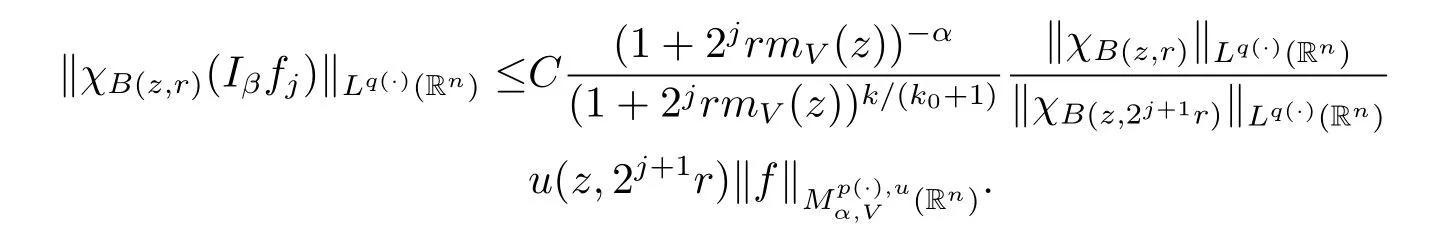
Taking k=(-[α]+1)(k0+1),we obtain
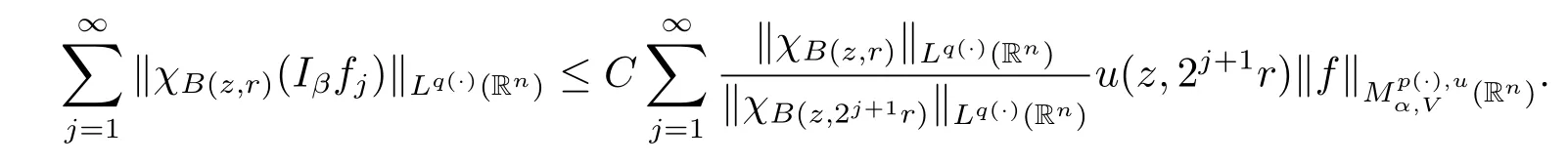
As u∈Wq(·)and α<0,we have
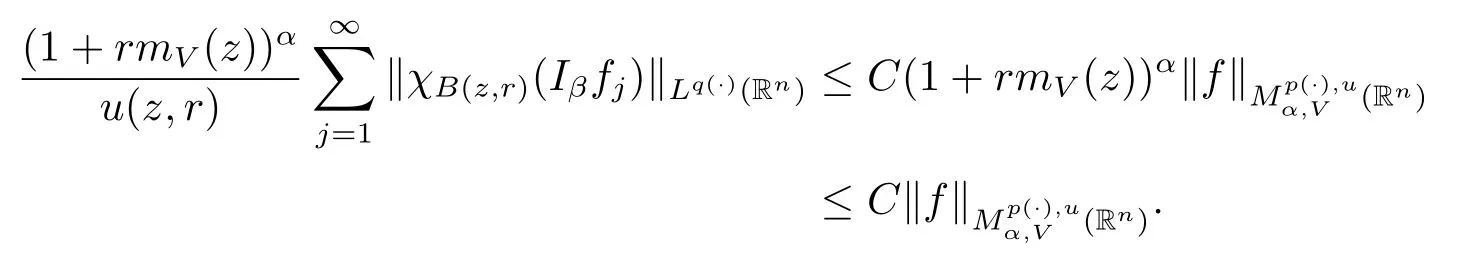
Proof of Theorem 1.4 Without loss of generality,we may assume that α<0.Let f∈Mp(·),u.For any z∈Rnand r>0,write f(x)=f0(x)+fj(x),where f0=fχB(z,2r), fj=fχB(z,2j+1r)B(z,2jr)for j≥1.Hence we have
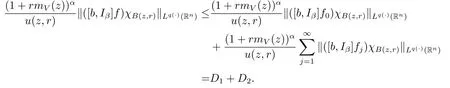
First,we estimate D1.
Lemma 2.7 shows that‖[b,Iβ]f0‖Lq(·)(Rn)≤C‖b‖BMO‖f0‖Lp(·)(Rn).Thus,we find that
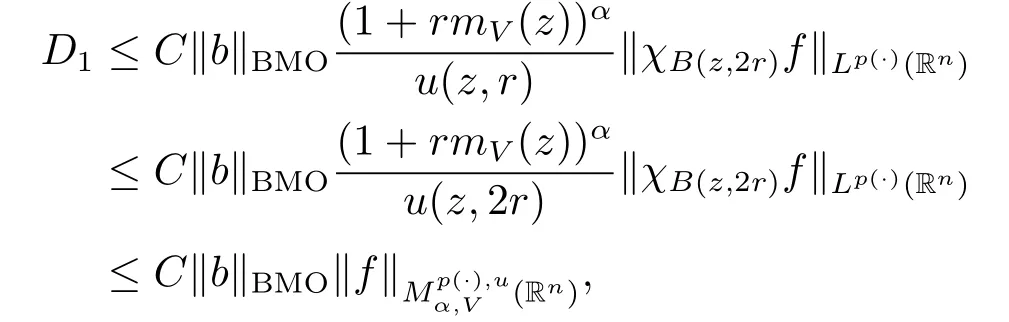
because inequality(1.1)and Lemma 2.5 imply that u(z,2r)≤Cu(z,r).
Next,we estimate D2.
For any j≥1,x∈B(z,r)and y∈B(z,2j1r)B(z,2jr),we note that|x-y|≥|y-z|-|x-z|>C2jr.Using inequality(2.1)and Lemma 2.2,we obtain
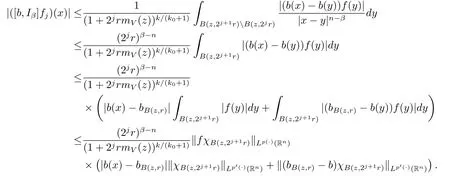
Subsequently,taking the norm‖·‖Lq(·)(Rn)and using Lemma 2.9,we have
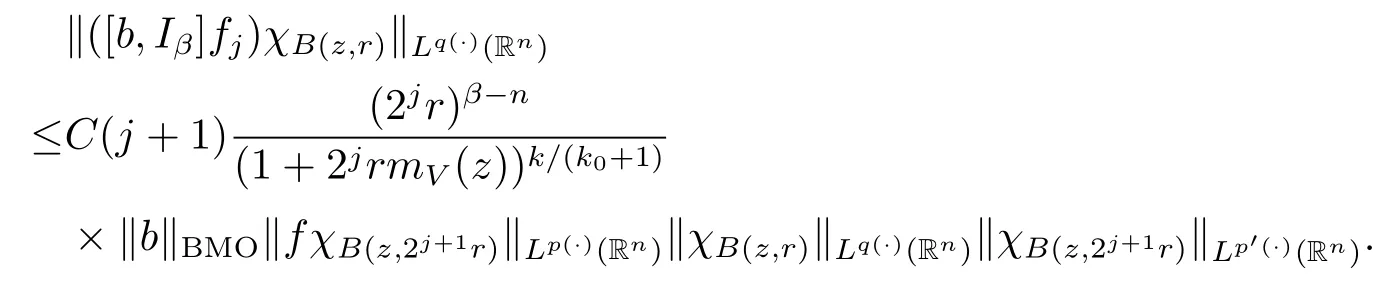
The arguments here are quite similar to the proof of Theorem 1.3,so we have
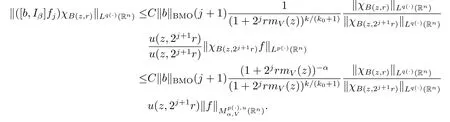
Taking k=(-[α]+1)(k0+1),we obtain
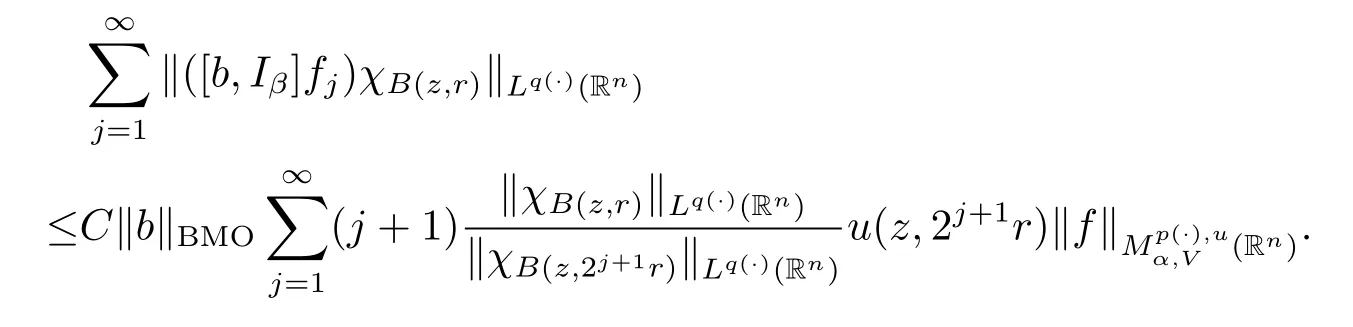
As u fulfills(1.3)and α<0,we obtain
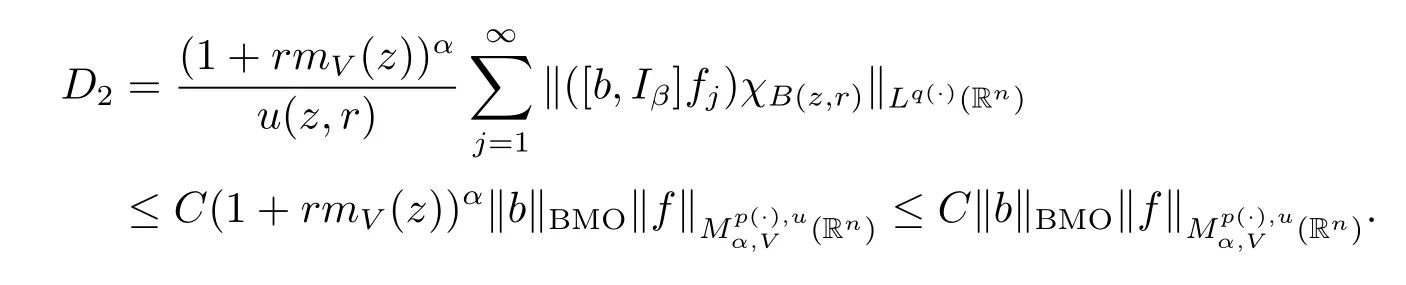
Consequently we have proved Theorem 1.4.
References
[1]Shen Z.Lpestimates for Schrdinger operators with certain potentials[J].Ann.Inst.Fourier(Grenoble),1995,45(2):513-546.
[2]Kurata K,Nishigaki S,Sugano S.Boundedness of integral operators on generalized Morrey spaces and its application to Schrdinger operators[J].Proc.Amer.Math.Soc.,2000,128(4):1125-1134.
[3]Tang L,Dong J.Boundedness for some Schrdinger type operators on Morrey spaces related to certain nonnegative potentials[J].J.Math.Anal.Appl.,2009,355(1):101-109.
[4]Chen Y,Levine S,Rao M.Variable exponent,linear growth functionals in image restoration[J]. SIAM J.Appl.Math.,2006,66(4):1383-1406.
[6]Cruz-Uribe D,Fiorenza A,Martell J M,et al.The boundedness of classical operators on variable Lpspaces[J].Ann.Acad.Sci.Fenn.Math.,2006,31(1):239-264.
[7]Huang A,Xu J.Multilinear singular integrals and commutators in variable exponent Lebesgue spaces[J].Appl.Math.J.Chin.Univ.,2010,25(1):69-77.
[8]Izuki M.Commutators of fractional integrals on Lebesgue and Herz spaces with variable exponent[J]. Rend.Circ.Mat.Palermo.,2010,59(3):461-472.
[9]Ho K P.The fractional integral operators on Morrey spaces with variable exponent on unbounded domains[J].Math.Inequal.Appl.,2013,16:363-373,.
[10]Almeida A,Hasanov J,Samko S.Maximal and potential operators in variable exponent Morrey spaces[J].Geor.Math.J.,2008,15:195-208.
[11]Xuan Z,Shu L.Boundedness for commutators of Caldern-Zygmund operator on morrey spaces with variable exponent[J].Anal.The.Appl.,2013,29(2):128-134.
[12]Kokilashvili V,Meskhi A.Boundedness of maxmial and singular operators in Morrey spaces with variable exponent[J].Armenian Math.J.,2008,1:18-28.
[13]Nekvinda A.Hardy-Littlewood maximal operator on Lp(x)(Rn)[J].Math.Inequal.Appl.,2004,7: 255-265.
[14]Stein E M.Harmonic analysis:real-variable methods,orthogonality,and oscillatory integrals[M]. Princeton,NJ:Princeton Univ.Press,1993.
[15]Tang L.Weighted norm inequalities for Schrdinger type operators[J].Forum Math.:2013,27(4): 2491-2532.
[16]Diening L.Maximal function on Musielak-Orlicz spaces and generalized Lebesgue spaces[J].Bulletin des Sci.Math.,2005,129(8):657-700.
[18]Izuki M.Boundedness of commutators on Herz spaces with variable exponent[J].Rend.Circ.Mat. Palermo,2010,59(2):199-213.
王敏,束立生,瞿萌,程美芳
(安徽師范大學(xué)數(shù)學(xué)計(jì)算機(jī)科學(xué)學(xué)院,安徽蕪湖241003)
本文考慮了一類Schrdinger型算子和其交換子的有界性問題.利用其在Lp空有界性間上的,獲得了一類Schrdinger型算子和其交換子在變指數(shù)Morrey空間上的有界性.
Morrey空間;交換子;Schrdinger型算子;變指數(shù)
MR(2010)主題分類號(hào):42B20;42B35O174.2
?date:2014-04-15Accepted date:2014-09-15
Supported by NSFC(11201003);University NSR Project of Anhui Province (KJ2014A087)and Anhui Provincial Natural Science Foundation(1408085MA01).
Biography:Wang Min(1990-),male,born at Wuwei,Anhui,postgraduate,major in harmonic analysis.

