Wooden stick penetration from the perineal region up to the thorax
V.C.S.G.Government Medical Sciences & Research Institute, Srinagar Garhwal, Pauri Garhwal, Uttarakhand, India
Case Report
Wooden stick penetration from the perineal region up to the thorax
Khem Pal Singh, Anil Kumar Joshi, Mohit Kumar Joshi, Chitra Joshi, Mridu Singh, Vikram Singh
V.C.S.G.Government Medical Sciences & Research Institute, Srinagar Garhwal, Pauri Garhwal, Uttarakhand, India
BACKGROUND:Penetrating injuries of the perineum are rare but very dangerous. Since the genitourinary and colorectal organs may be injured, how to evaluate surgical management of the injury is very important.
METHODS:The present report presents a case of penetrating injury of the perineum by a wooden stick when the patient fell on the upright wooden stick from a tree. The three feet long stick entered the perineal region just left lateral to the anal opening. Upon reaching the thoracic cavity, it broke and only a foot stick was left in the subcutaneous plane. These injuries are potentially serious with risk of damage to multiple organs. Exploratory laprotomy was done, and bladder injury was repaired. The entry wound and the track of stick was thoroughly washed and allowed for secondary intention healing.
RESULTS:The post operative period was uneventful and the patient recovered fully.
CONCLUSION:Meticulous evaluation and surgical management of perineal injuries are the key to prevent devastating complications.
Penetrating injury; Perineal region; Perineal injuries
INTRODUCTION
Penetrating injuries of the perineum are rare. These types of injuries, depending upon the extent of penetration, can be devastating. They can involve multiple organ damage which needs meticulous evaluation and operative planning.
CASE REPORT
A 17-year-old boy reported in the emergency department with low grade fever, pain in the perineal region, abdomen and thorax, hypotension, hematuria and bleeding from the perineal region 8 hours after injury. The patient had a history of fall from a tree, and he was injured by a wooden stick 3 feet long and 5 cm in diameter after falling. He came with a broken part of the stick, about 1 foot of which was found in the thorax in the subcutaneous plane. The patient bled from the perianal region and emergency management was done according to the advanced trauma life support (ATLS) guidelines. The cervical spine of the patient was stabilized and the patient was investigated. Nasogastric intubation was done and intravenous fluids were given. On urinary catheterization, blood stained urine came out, suggesting the probability of urethral or bladder injury. Rectal examination was done to rule out rectal injury. Blood was sent for routine hemogram and blood grouping. Lateral radiograph of the cervical spine and dorsal spine was performed to rule out spinal injury. The spine was normal. Chest radiograph in erect posture was normal. Computed tomography (CT) of the head, abdomen and pelvis was done. Head CT showed nothing abnormal. Abdomen CT showed a foreign body extraperitoneally in the anterior abdominal wall and anterior chest wall(Figure 1). There was no diaphragmatic injury. CT showed rupture of the posterior urinary bladder wall. Proctosigmoidoscopy and cystography were performed. Broad spectrum antibiotics with aerobic (gram positive and negative) and aerobic coverage were given. On local examination, the stick entered the perineal region about 3 cm lateral to the anal opening on the left side (Figure 2). The stick while entering through the perineal region damaged the posterior wall of the urinary bladder on the left side and perforated the anterior bladder at dome, with a 3–4 cm defect. Free f uid was present in the peritoneal cavity due to intraperitoneal rupture of the bladder. The stick track was found in a pre-peritoneal plane on the left side up to the umbilicus then observed in the subcutaneous plane. In the subcutaneous plane, the tip of the stick was accompanied with green leaves at the level of the anterior end of the 12th rib in the left mid axillary line. The anterior end of the f oating ribs posed resistance for further progression of the stick. The stick was broken below the thorax after injury. The bladder was repaired by Vicryl No. 1 and subcutaneous track was thoroughly washed. Suprapubic cystostomy was done for bladder injury. Exploratory laparotomy was done and the stick was removed from the anterior abdominal wall and the anterior chest wall by a small separate incision (Figures 3 and 4). The perineal entry wound was allowed to heal secondarily. The post operative period was uneventful and the patient recovered fully.
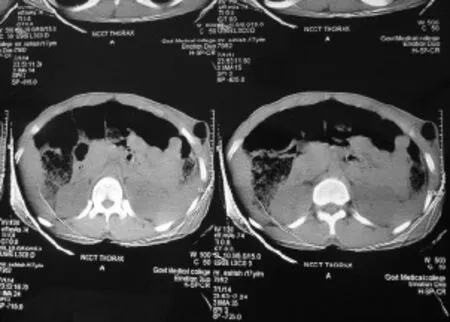
Figure 1. CT scan showing a defect in the anterior abdominal wall due to a wooden stick.
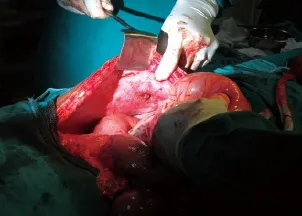
Figure 3. Laprotomy showing the path of a wooden stick in the anterior abdominal wall.
DISCUSSION
In all penetrating perineal injuries it is mandatory to diagnose urinary bladder and colorectal injuries. In all patients with penetrating injury of the perineum with hematuria, colorectal and bladder injury should be suspected.[1]Cystogram and proctoscopy are mandatory in these cases.[2]A majority of the patients with penetrating injury to the perineum present with hemodynamic instability and are at the risk of septicemia. A variety of management strategies have been described in the literature for the patients with penetrating pelvic injury such as primary repair, divertingcolostomies and selective non-operative management (SNOM).[3,4]The approach for a patient should be judiciously tailored. All patients should be thoroughly investigated by CECT scan of the abdomen and pelvis. Although a majority of patients with penetrating perineal injuries require operative intervention, a small subset of hemodynamically stable patients with normal abdominal f ndings may be managed by serial physical examinations alone with appropriate investigations.
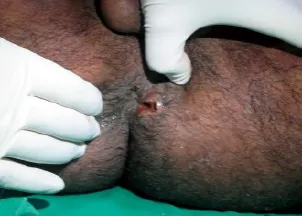
Figure 2. Clinical photograph showing an entry wound lateral to the anal opening.
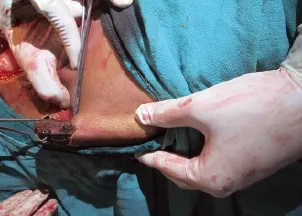
Figure 4. Removal of the wooden stick from the anterior abdominal wall.
Chest radiograph in erect posture can identify subdiaphragmatic air. The clinical approach for evaluation of a patient with penetrating perineal injury includes physical examination (recommended sequence of examination at 1, 4, 12, and 24 hours for hemodynamic stability and signs of peritonitis) and local wound exploration (wound extended under local anesthesia and track followed through tissue layers). The diagnostic modalities include diagnostic peritoneal lavage (DPL), focused assessment with sonography in trauma (FAST), CT scan, laproscopy, and exploratory laparotomy. CT cystography is more accurate than conventional cystography.[5]The complications of penetrating injuries of the perineum include pelvic, suprapubic or subphrenic abscesses in 18%, rectourethral or rectovesical fistulae in 24%, chronic urinary tract infections in 18%, urolithiasis in 12%, and urethral strictures in 12% cases. These complications can be decreased by meticulous presacral drainage, distal rectal wash, and rectal wound repair. Moreover, it is further prevented by prolonged suprapubic drainage and isolating rectal and urinary tract wounds. It is very important to thoroughly debride necrotic tissues with stretch-free tissue closure and to place a drainage tube. To prevent formation of rectourethral and rectovesical fistulae, the sites of rectovesical injuries are isolated by the omentum, gracilis and myocutaneous f aps.[6,7]
Funding:There was no funding in any form or from inside or outside the institute.
Ethical approval:The institute adheres to the basic principles of the Declaration of Helsinki of the World Medical Association. The study was approved by institutional review board (IRB) and informed consent was obtained from the patient.
Conflicts of interest:There is no conflict of interest relevant to this report.
Contributors:All authors approved the entirety of the submitted material and contributed actively to the study.
1 Painuly GP, Negi DS. Combined penetrating injury of the perineum and abdominal viscera. BMJ Case Rep 2009; 1892: 6.
2 Carroll PR, McAninch JW. Major bladder trauma: the accuracy of cystography. J Urol 1983; 130: 887–888.
3 Stawicki SP. Trends in non operative management of traumatic injuries. A synopsis. OPUS 12 Scientist 2007; 1: 19–35.
4 Schwab CW. Selection of nonoperative management candidates. World J Surg 2001; 25: 1389–1392.
5 Klein FA, Texter Jr. JH, Snoddy WJ. Urologic injuries associated with penetrating wounds to the buttock. Va Med 1980; 107: 375–377.
6 Kupelian AS, Tincello DG. Penetrating glass injury to the perineum. J Obstet Gynaecol 2004; 24: 713–714.
7 Franko ER, Ivatury RR, Schwalb DM. Combined penetrating rectal and genitourinary injuries: a challenge in management. J Trauma 1993; 34: 347–353.
Received November 12, 2014
Accepted after revision April 8, 2015
Anil Kumar Joshi, Email: aniljoshi11@gmail.com
World J Emerg Med 2015;6(4):305–307
10.5847/wjem.j.1920–8642.2015.04.010
 World journal of emergency medicine2015年4期
World journal of emergency medicine2015年4期
- World journal of emergency medicine的其它文章
- Subject index WJEM 2015
- Author index WJEM 2015
- Antidotes for patients taking novel oral anti-coagulants
- Bottle gourd (Lagenaria siceraria) juice poisoning
- Instructions for Authors
- Expression of phosphatidylinositol-3 kinase and effects of inhibitor Wortmannin on expression of tumor necrosis factor-α in severe acute pancreatitis associated with acute lung injury
