Diatomite Precoated Nonwoven Membrane Bioreactor for Domestic Wastewater Reclamation
HE Yue-ling (何月玲), RAO Pin-hua (饒品華)*, ZHANG Wen-qi (張文啟), JIN Peng (金 鵬)
1 College of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Shanghai University of Engineering Science, Shanghai 201620, China
Diatomite Precoated Nonwoven Membrane Bioreactor for Domestic Wastewater Reclamation
HE Yue-ling (何月玲)1, RAO Pin-hua (饒品華)1*, ZHANG Wen-qi (張文啟)1, JIN Peng (金 鵬)2
1CollegeofChemistryandChemicalEngineering,ShanghaiUniversityofEngineeringScience,Shanghai201620,China
2ChinaNortheastArchitecturalDesignandResearchInstituteCo.,Ltd.,Shenyang110006,China
diatomite;nonwoven;membranebioreactor(MBR);wastewaterreclamation
Introduction
Membrane bioreactor (MBR) has gained wide popularity in wastewater reclamation for its good effluent quality, complete solid-liquid separation, and small area occupied[1- 3]. Nevertheless, high membrane material cost and energy consumption limited its wide application. Thus, in developing countries like China, the MBR is still an expensive process.
To develop a more economical and simple MBR system, several low cost filter materials like mesh and fabric cloth were selected to replace conventional microporous (MF) or ultrafiltration (UF) membrane materials in submerged MBR system[4-7]. For the development and application of nonwoven MBR, Renetal.[8]used nonwoven fabric filter bag (NFFB) as the membrane bioreactor for activated sludge separation under gravity flow. Changetal.[9]investigated the performance and filtration characteristics of submerged nonwoven MBR. Results showed that the system could be operated until the mixed liquid suspended solids (MLSS) concentrations reached to 11 000 mg/L. However, cake layer was formed due to floc particles deposition, which gradually leads to membrane fouling. Thus, there was an urgent demand to develop anti-fouling methods for nonwoven membrane used in MBR system.
Common fouling control approaches in MBRs include operation parameters manipulation and surface chemical modification[10-13]. Recent studies reported that adding anti-fouling agents, like powered activated carbon (PAC) and coagulation of polymeric ferric chloride (PFC), could improve the mixed liquids properties and alleviate membrane fouling in some extent[14-15]. But, fresh materials were needed timely due to the gradual loss of operation effectiveness and thus large scale application was also limited.
Diatomite (SiO2·nH2O) has a series of characteristics including good hydrophilicity, high porosity, and good adsorptive properties[16-17]. Diatomite precoated on the surface of mesh support can form bio-diatomite, which has been proved to be an efficient surface modification method and showed good performance in MBR process for wastewater treatment[18-19]. However, diatomite precoated on the surface of nonwoven support in MBR system had not been reported.
In this paper, diatomite is selected as microorganism carriers to form diatomite dynamic membrane to substitute conventional PAC in submerged MBR process[18]. The main objective is to study the performance of diatomite precoated nonwoven used for wastewater reclamation and develop economical and practical wastewater treatment process.
1 Materials and Methods
1.1 Materials and chemicals
Synthetic wastewater was prepared with the following compositions and used as raw influent: starch (200 mg/L), NH4Cl (74.3 mg/L), KH2PO4(24.4 mg/L), CaCl2(60 mg/L), albumenflakes (15 mg/L), MgSO4·7H2O (60 mg/L), MnSO4·7H2O (1.5 mg/L) and FeSO4(0.2 mg/L).
Diatomite and other agents were chemical pure, purchased from Sinopharm Chemical Reagent Shanghai Co., Ltd., China. Nonwoven was obtained from Shanghai Zhihe Filtration Material Co., Ltd., China. The nonwoven parameter characteristics with different pore sizes were listed in Table 1.
Table 1 Parameter characteristics of different pore sizes nonwoven
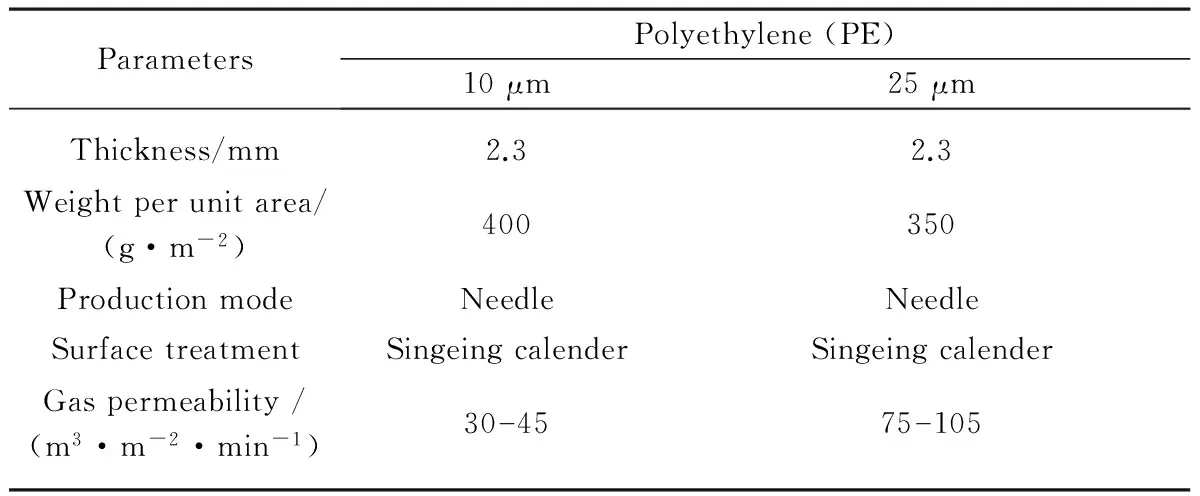
ParametersPolyethylene(PE)10μm25μmThickness/mm2.32.3Weightperunitarea/(g·m-2)400350ProductionmodeNeedleNeedleSurfacetreatmentSingeingcalenderSingeingcalenderGaspermeability/(m3·m-2·min-1)304575105
1.2 Experimental setup
The diagram of the MBR system for experimental study was shown in Fig.1. Synthetic wastewater was continuously pumped into the reactor. Flow rate of the system was maintained at 1 L/h. Stainless steel was used as nonwoven bag support module. The effluent was operated under gravity flow without a suction pump. The height of mixed liquid lever was controlled by the effluent lever in the operation. The total effective volume of membrane bioreactor was 5 L. The effective filtration area was 0.2 m2. The system of flux was operated at 5 L/(m2·h), corresponding to a hydraulic retention time (HRT) of 5 h. Air diffuser was placed at the bottom of the bag to mix the contents as well as provide oxygen to the aerobic microorganism. The characteristics of synthetic wastewater were listed in Table 2. Diatomite was added into MBR with a dose of 200 mg/L to form bio-diatomite dynamic membrane.
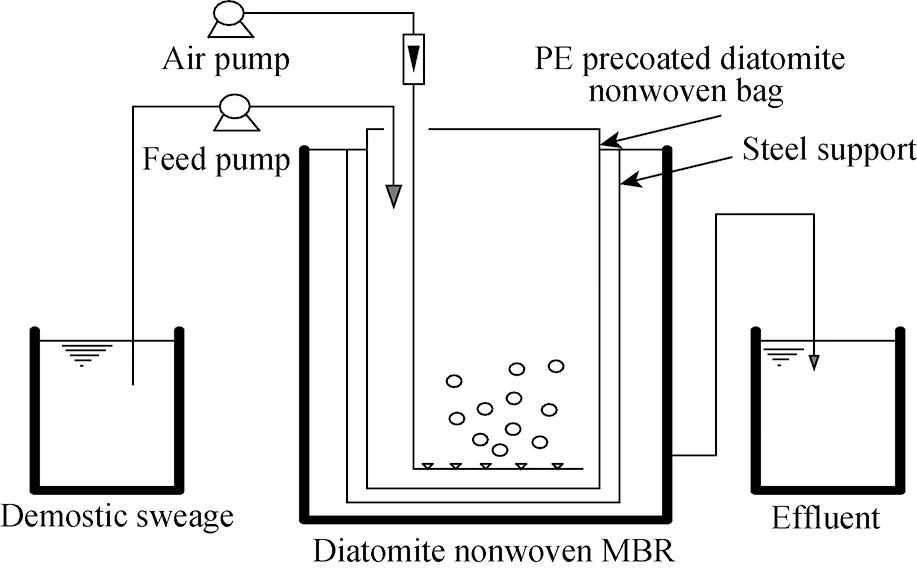
Fig.1 Schematic of the experimental setup
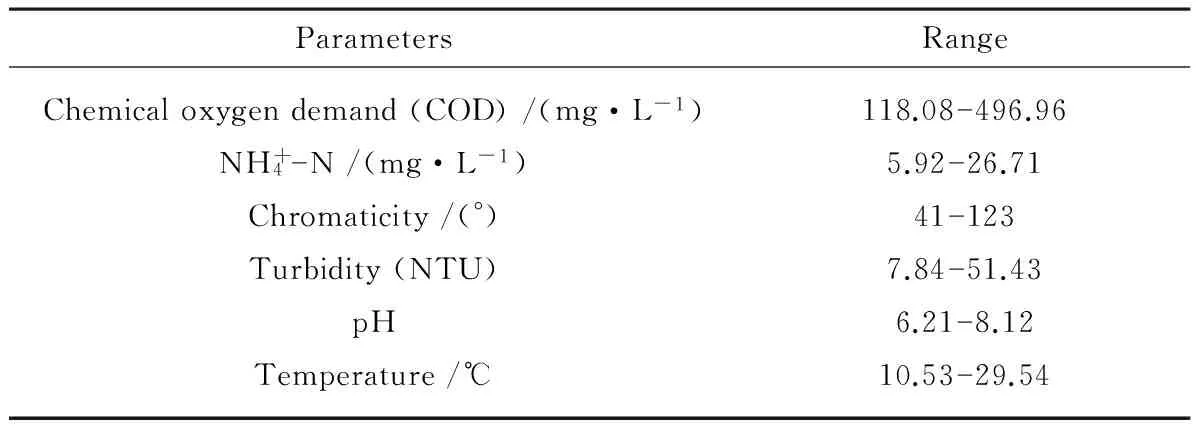
Table 2 Characteristics of the wastewater
1.3 Analytical methods

2 Results and Discussion
2.1 Diatomite precoating and nonwoven membrane selection
Diatomite has uneven shapes with small particles[21]. Two different nonwovens, with pore size of 10 μm and 25 μm, were investigated with diatomite precoated on the support module to form dynamic membrane. Choosing the right nonwoven pore size is important. The precoating stage was conducted when the nonwoven module was placed in the bioreactor. The permeate effluent from the tube was measured every 15 min. The variation characteristics of membrane flux and effluent turbidity were shown in Figs.2 and 3. The nonwoven with diatomite precoated on the surface showed good filterability.
Figure 2 showed that dynamic membrane could be formed rapidly due to relatively high flux. Water flux dropped quickly from about 2044 L/(m2·h) (10 μm) and 3303 L/(m2·h) (25 μm) to 106 L/(m2·h) (10 μm) and 183 L/(m2·h) (25 μm) in the first 45 min and then kept stable. The corresponding effluent turbidity was also dropped to 4 NTU and 34 NTU (Fig.3), respectively. To obtain the same turbidity, the time needed for the 25 μm nonwoven was longer than the time needed for 10 μm nonwoven. Nonwoven with pore size of 10 μm was more suitable in the following MBR system for wastewater reclamation.
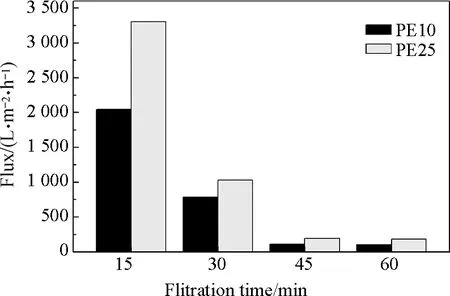
Fig.2 Water flux variation in the precoating stage
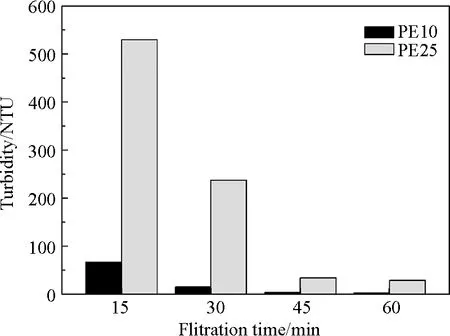
Fig.3 Variations of the effluent turbidity in the precoating stage
2.2 Operation of the system
In the operation process, the MBR system was operated steadily under gravity flow and there was basically no water head. The activated sludge had good growth and settling properties. Some microorganisms that represent good water quality like vorticella and rotifers were detected by microscope. The variation of SV (3%-24%) showed a gradual rise with increasing temperature (from 10.5 ℃ to 29.5℃) and improving operation conditions in the MBR system (Fig.4).
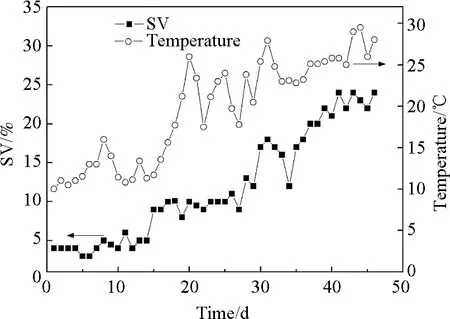
Fig.4 Temperature and sludge SV in MBR system
The experiment was conducted for 46 d without serious membrane fouling. Figure 5 showed the results of SEM analysis of nonwoven surface from the MBR. Figure 5(a) presented the random arrangement of nonwoven fabrics, which were partly clogged by pollutants. Image of Fig.5(b), which was 15 times of Fig.5(a), showed a clear combination between diatomite and activated sludge. The flux might be declined owing to partial membrane fouling. However, the set flux was relatively low and membrane fouling rate is slow. So it could be assumed that the system could be operated over three months. After that, membrane backwash and renew precoating were needed in MBR process.
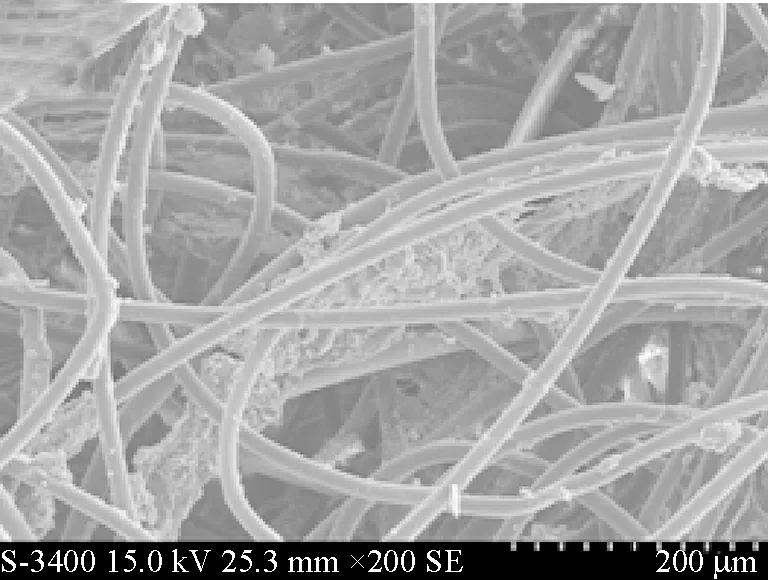

(a) Part fouling nonwoven
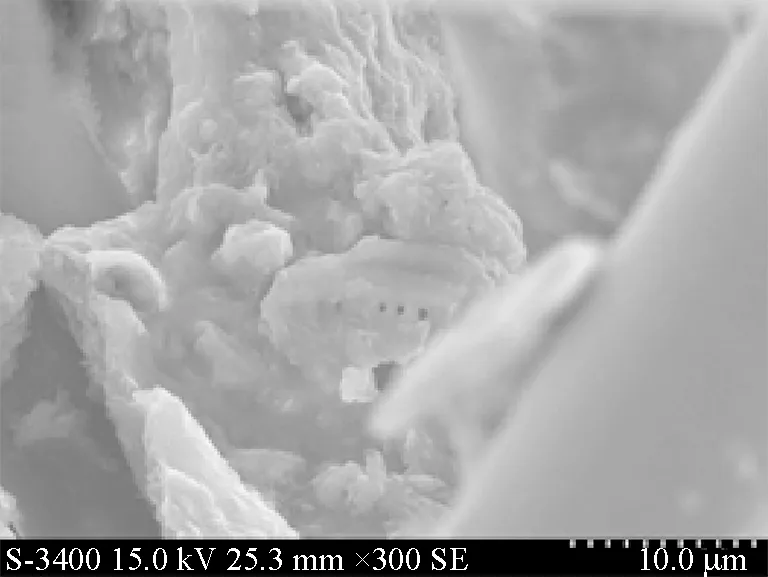

(b) Bio-diatomite pollutantsFig.5 SEM images of the nonwoven in MBR system
2.3 Performance of MBR
Performance of the MBR system was studied as shown in Figs.6-8.According to Fig.6, the system was able to obtain stable effluent COD concentration (34.3 mg/L), corresponding to an average removal efficiency of 86%. The result also showed that the effluent COD of MBR system was irrelevant to the influent COD variation.
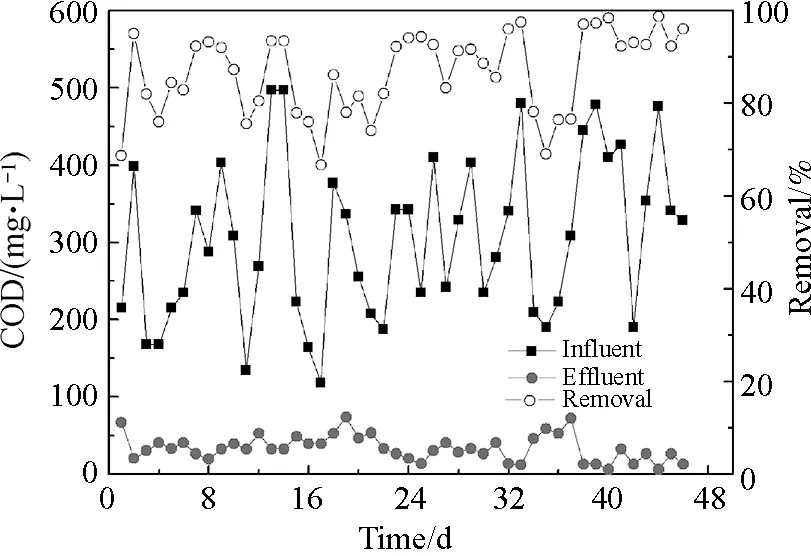
Fig.6 Removal of COD in the MBR system
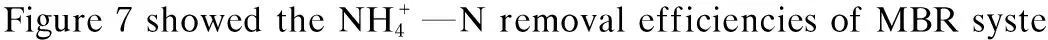
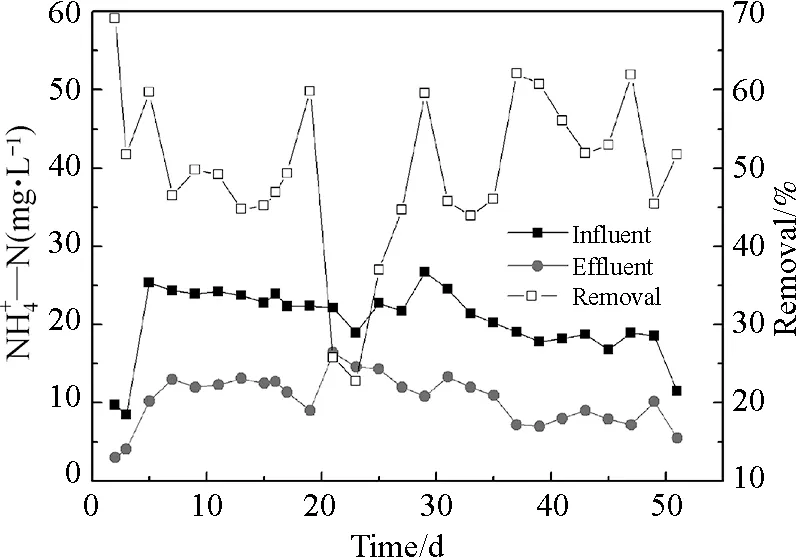
Fig.
Figure 8 showed the characteristics of effluent turbidity and chromaticity of MBR system. The results showed good solid-liquid separation capacity of nonwoven membrane. The system had good treatment efficiency on effluent turbidity, which was generally below 5 NTU. This phenomenon could probably be attributed to surface adsorption of the cake layer on the membrane surface[19]. Comparing with effluent turbidity, the chromaticity varied greatly. But, effluent chromaticity was generally below 25°. From the result of this work, diatomite precoated nonwoven MBR may be a promising technology.
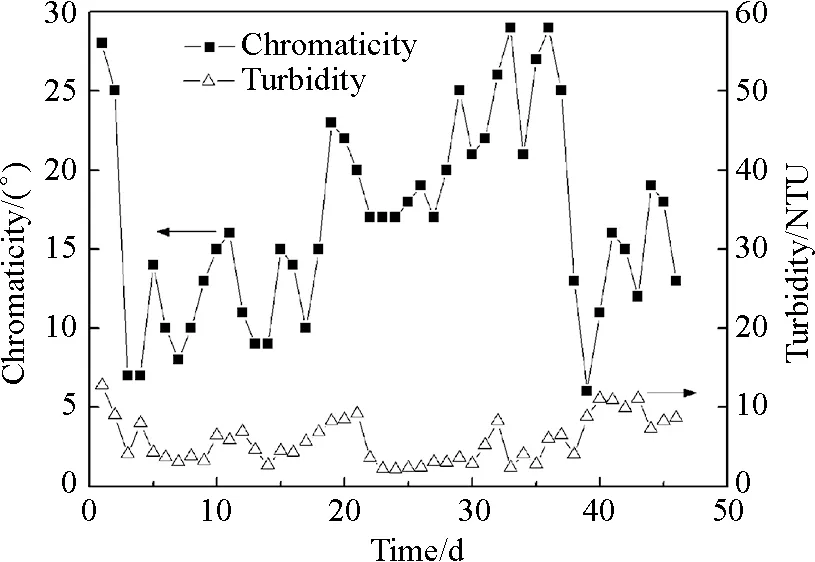
Fig.8 Effluent turbidity and chromaticity in the MBR system
3 Conclusions
[1] Judd S. The Status of Membrane Bioreactor Technology [J].TrendsinBiotechnology, 2008, 26(2): 109-116.
[2] Yang W, Cicek N, Ilg J. State-of-the-art of Membrane Bioreactors: Worldwide Research and Commercial Applications in North America [J].JournalofMembraneScience, 2010, 270(1): 201-211.
[3] Seo G T, Moon B H, Park Y M,etal. Filtration Characteristics of Immersed Coarse Pore Filters in an Activated Sludge System for Domestic Wastewater Reclamation [J].WaterScienceandTechnology, 2007, 55(1/2): 51-58.
[4] Ferraris M, Innella C, Spagni A. Start-up a Pilot-Scale Membrane Bioreactor to Treat Municipal Wastewater [J].Desalination, 2009, 237(1/2/3): 190-200.
[5] Satyawali Y, Balakrishnan M. Treatment of Distillery Effluent in a Membrane Bioreactor (MBR) Equipped With Mesh Filter [J].SeparationandPurificationTechnology, 2008, 63(2): 278-286.
[6] Fuchs W, Resch C, Kernstock M,etal. Influence of Operational Conditions on the Performance of a Mesh Filter Activated Sludge Process [J].WaterResearch, 2005, 39(5): 803-810.
[7] Seo G T, Moon B H, Lee T S,etal. Nonwoven Fabric Filter Separation Activated Sludge Reactor for Domestic Wastewater Reclamation [J].WaterScienceandTechnology, 2003, 47(1): 133-138.
[8] Ren X H, Shon H K, Jang N J,etal. Novel Membrane Bioreactor (MBR) Coupled with a Nonwoven Fabric Filter for Household Wastewater Treatment [J].WaterResearch, 2010, 44(3): 751-760.
[9] Chang M C, Horng R Y, Shao H S,etal. Performance and Filtration Characteristics of Non-woven Membranes Used in a Submerged Membrane Bioreactor for Synthetic Wastewater Treatment [J].Desalination, 2006, 191(1/2/3): 8-15.
[10] Wang Z W, Wu Z C, Xing Y,etal. Membrane Fouling in a Submerged Membrane Bioreactor (MBR) under Sub-critical Flux Operation: Membrane Foulant and Gel Layer Characterization [J].JournalofMembraneScience, 2008, 325(1): 238-244.
[11] Wu J, He C. Effect of Cyclic Aeration on Fouling in Submerged Membrane Bioreactor for Wastewater Treatment [J].WaterResearch, 2012, 46(11): 3507-3515.
[12] Yu Z X, Chu H Q, Cao D W,etal. Pilot-scale Hybrid Bio-diatomite/dynamic Membrane Reactor for Slightly Polluted Raw Water Purification [J].Desalination, 2012, 285: 73-82.
[13] Zhang C H, Yang F L, Wang W J,etal. Preparation and Characterization of Hydrophilic Modification of Polypropylene Non-woven Fabric by Dip-Coating PVA (polyvinyl alcohol) [J].SeparationandPurificationTechnology, 2008, 61(3): 276-286.
[14] Satyawalia Y, Balakrishnan M. Effect of PAC Addition on Sludge Properties in an MBR Treating High Strength Wastewater [J].WaterResearch, 2009, 43(6): 1577-1588.
[15] Yang X L, Song H L, Chen M,etal. Characterizing Membrane Foulants in MBR with Addition of Polyferric Chloride to Enhance Phosphorus Removal [J].BioresourceTechnology, 2011, 102: 9490-9496.
[16] Osmanlioglu A E. Natural Diatomite Process for Removal of Radioactivity from Liquid Waste [J].AppliedRadiationandIsotopes, 2007, 65(1): 17-20.
[17] Zhang W Q, Ma J, Yang S D,etal. Pretreatment of Coal Gasification Wastewater by Acidification Demulsion [J].ChineseJournalofChemicalEngineering, 2006, 14(3): 398-401. (in Chinese)
[18] Zhao Y, Cao D, Liu L,etal. Municipal Wastewater Treatment by Moving Bed-biofilm Reactor with Diatomaceous Earth as Carriers [J].WaterEnvironmentResearch, 2006, 78(4): 392-396.
[19] Chu H Q, Cao D W, Jin W,etal. Characteristics of Bio-diatomite Dynamic Membrane Process for Municipal Wastewater Treatment [J].JournalofMembraneScience, 2008, 325(1): 271-276.
[20] Wei F S, Qi W Q. Water and Wastewater Monitoring and Analysis Methods Fourth Edition [M]. Beijing: China Environmental Science Press, 2002: 211-284. (in Chinese)
[21] Zhang W Q, Rao P H, Zhang H,etal. The Role of Diatomite Particles in the Activated Sludge System for Treating Coal Gasification Wastewater [J].ChineseJournalofChemicalEngineering, 2009, 17(1): 167-170. (in Chinese)
Foundation items: China State Construction Innovation Project (No. CSCEC-2012-Z-14); Shanghai Education Research and Innovation Project, China (Nos.11ZZ176, 12YZ153, and ZZGJD12052)
X703 Document code: A
1672-5220(2015)01-0109-04
Received date: 2014-01-24
* Correspondence should be address to RAO Pin-hua, E-mail: raopinhua@hotmail.com
 Journal of Donghua University(English Edition)2015年1期
Journal of Donghua University(English Edition)2015年1期
- Journal of Donghua University(English Edition)的其它文章
- Mechanical Property and Crystal Structure of Poly(p-phenylene terephthalamide) (PPTA) Fibers during Heat Treatment under Tension
- Supported Manganese Oxide on Graphite Oxide: Catalytic Oxidation of Nitrogen Oxide in Waste Gas
- Preparation and Properties of Polylactic Acid (PLA)/Nano-SiO2 Composite Master Batch with Good Thermal Properties
- Scheduling Rules Based on Gene Expression Programming for Resource-Constrained Project Scheduling Problem
- Dynamic Analysis of Some Impulsive Fractional-Order Neural Network with Mixed Delay
- Software Maintainability Evaluation Based on Quantitive Model
