Effect of Cx32 over-expression on cell proliferation, migration, and invasion of hepatocellular carcinoma cell line Huh7 and its mechanism
JI Wen-bin, LV Zhen-yu, CHENG Qian-qian, ZHOU Xue-li, WANG Wei, YANG Yan
Department of Medical Oncology, The First Affiliated Hospital of Bengbu Medical College, Bengbu 233004, China
Keywords:
ABSTRACT
1.Introduction
Liver cancer is one of the most common malignant tumors in China, of which hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) accounts for about 75%~85%.Those patients have insidious early symptoms,and are usually diagnosed in the middle and advanced stages of the disease with a high mortality rate[1,2].Finding new targets for HCC and developing new drugs against these targets will provide help to improve the prognosis of HCC.Gap junction protein 32(Cx32) is also known as β1 connexin.As a major member of the gap junction (GJ) family, Cx32 is highly expressed in normal hepatocytes and forms GJ channels in the human liver, with GJs composed of Cx32 accounting for approximately 90% of total GJ function in the liver[3].Controversy remains regarding the role of Cx32 in the development of HCC.For example, Fujimoto et al.[4]suggested that Cx32 is a tumor suppressor gene, and its abnormal number and distribution may be associated with the development of HCC in humans.Previous studies by our team have also found that the carcinogenesis process of hepatocytes is closely related to the reduction or loss of Cx32, and restoring Cx32 expression may be a promising strategy for HCC treatment[5].However, there are some studies that suggest that Cx may play an important role in promoting tumor cell invasion and tumor metastasis.For example,accumulation of Cx32 protein in the cytoplasm of Huh7 promotes invasion and metastasis of HCC cells[6], and expands the cancer stem cell population in Huh7 cells by enhancing self-renewal capacity[7].Given that some controversial findings have mostly been found in Huh7 cells, and our team has previously successfully constructed Huh7 cell lines stably and highly expressing Cx32 mediated by lentiviruses[8], this study continues to carry out subsequent in vitro cytofunctional studies of Cx32 in Huh7 cell lines around this tool cell line.
Epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) is thought to be closely associated with invasion and metastasis of HCC[9].EMT is a biological process in which epithelial cells transform into a mesenchymal phenotype, and the expression of associated markers is altered during this particular transformation[10].However, the specific mechanisms regulating EMT initiation are still being explored.In this study, we focused on the effects of over-expression of Cx32 on the proliferation, migration and invasion of Huh7 cells and its role in the process of EMT, providing more experimental data and theoretical basis for further revealing the role, characteristics and potential mechanisms of Cx32 in the pathogenesis and progression of HCC.
2.Materials and methods
2.1 Materials and reagents
Human normal liver cell line LO2 and human HCC cell lines(Hep3B, Huh7, HepG2, SMMC-7721) were obtained from Nanjing Kaiji Biotechnology Development Co., Ltd.and Shanghai Cell Bank, Chinese Academy of Sciences, respectively; fetal bovine serum, DMEM basal medium and RPMI 1640 basal medium were purchased from Gibco; mouse monoclonal antibody Cx32 was purchased from Sigma; mouse monoclonal antibody E-cadherin,Vimentin, and polyclonal antibody Snail, were purchased from Abcam; mouse monoclonal antibody β-actin antibody was purchased from Santa Cruz, fluorescein isothiocyanate (FITC)-and Cy3-labeled secondary antibodies were purchased from Santa Cruz; BCA protein quantification kit was purchased from Bio-Rad;Matrigel gel was purchased from BD; ECL-plus chemiluminescence kit, and PVDF membrane were purchased from Millipore; lentiviral vectors were synthesized by Shanghai GenePharma Co., Ltd.
2.2 Cell culture
LO2, Hep3B, Huh7, HepG2 cell lines and SMMC-7721 cell line were cultured in DMEM medium and RPMI 1640 medium,respectively.Both media were composed of the corresponding basal medium, 10% fetal bovine serum and 1% penicillin-streptomycin.They were cultured daily in a constant temperature incubator, and digestion and subculture were used for subsequent experiments when the cells grew to the appropriate degree of fusion.
2.3 Establishment of lentiviral vector-mediated Cx32 stably over-expressed Huh7 cell line
Our group has previously constructed the lentiviral vector LV5-GFP-hCx32, which can stably infect Huh7 cells, leading to an overexpression of exogenous gene Cx32 in this cell line.The specific methods and identification of this lentiviral vector-mediated Cx32 stably over-expressed Huh7 cell line were described in our previous study[8].We aimed to carry out subsequent in vitro functional studies on this tool cell line in this study.
2.4 Western blot
Upon getting confluent, cells were lysed and proteins were then extracted; protein concentration was determined; samples were loaded for electrophoresis, electrotransferred to PVDF membranes,and blocked in blocking solution for 15 minutes before hatching the primary antibody (dilution ratios: Cx32 1:500, Vimentin 1:1 000,E-cadherin 1:1 000, Snail 1:1 000, β-actin 1:500) overnight at 4℃.The next day, after washing the membrane, it was incubated with the secondary antibody (dilution ratio: Cx32:1 000; remaining indicators:1:5 000) at room temperature for 2 hours.Protein expression levels were normalized to those of the internal control(β-actin).
2.5 Immunofluorescence assay
Cells in the logarithmic growth phase were mounted, fixed with 4%paraformaldehyde for 30 min and incubated with primary antibodies at room temperature for 3 h; fluorescent secondary antibodies were incubated at room temperature in the dark for 2 h, and coincubated with DAPI for 5 min.They were then rinsed, mounted, and examined under an inverted fluorescence microscope.
2.6 MTT assay
After adjusting the cell density to 3 000 cells/well, cells were plated in 96-well plates and placed in the incubator for 24 h.Ten microliters of MTT solution at a concentration of 5 mg/mL was added to each well, the culture was continued for 4 h and the supernatant was discarded after centrifugation; DMSO was added to each well and shaken on a shaker for 10 min to determine the OD490 value of the cells using a microplate reader.
2.7 Wound-healing assay
Adjusting the cell density to 1.5×106cells/well in 6-well plates,and when the cells were observed to fuse into a monolayer state under a microscope, they were evenly scratched in the wells with a sterile microtip and continued to be cultured in an incubator.After that, an inverted microscope was used to measure the scratch width at 0 and 24 hours, and the wound closure rate was then calculated.Cell wound closure rate (%)=[(scratch area at 0 h - scratch area at 24 h)/scratch area at 0 h] × 100%.
2.8 Transwell invasion assay
Matrigel solution was added to the culture medium to fully mix well and then added to the upper compartment of the transwell chambers; cells in each group were plated at a density of 1.0×105cells/well and cultured in 800 μL complete culture medium in the lower chamber for 24 h.Non-invasive cells in the upper layer of the insert were removed and treated with 4% paraformaldehyde solution and 0.1% crystal violet for 20 min each, and after washing with PBS and drying, photographs were taken and cells were counted under a microscope.
2.9 Statistical processing
Statistical analysis were performed with Prism 9.0 (Graphpad Software) software.The experimental data were shown as (x±s).t test was used to compare the measurement data between the two groups, and one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) was used to compare the measurement data between multiple groups.Differences with P<0.05 were considered significant.
3.Results
3.1 Bioinformatics analysis of Cx32 mRNA and protein expression in HCC tissues and normal liver tissues
TCGA database download data and analysis showed that the expression level of Cx32 mRNA in HCC tissues was lower than that in adjacent normal liver tissues (Figure 1A), and its expression level would decrease with the progression of T stage, histological grade and clinical stage of HCC patients (P<0.05, Figure 1B, D, E),showing a negative correlation trend with N stage (P>0.05, Figure 1C); CPTAC database showed that Cx32 protein expression in normal liver tissues was higher than that in HCC tissues (P<0.01,Figure 1F).
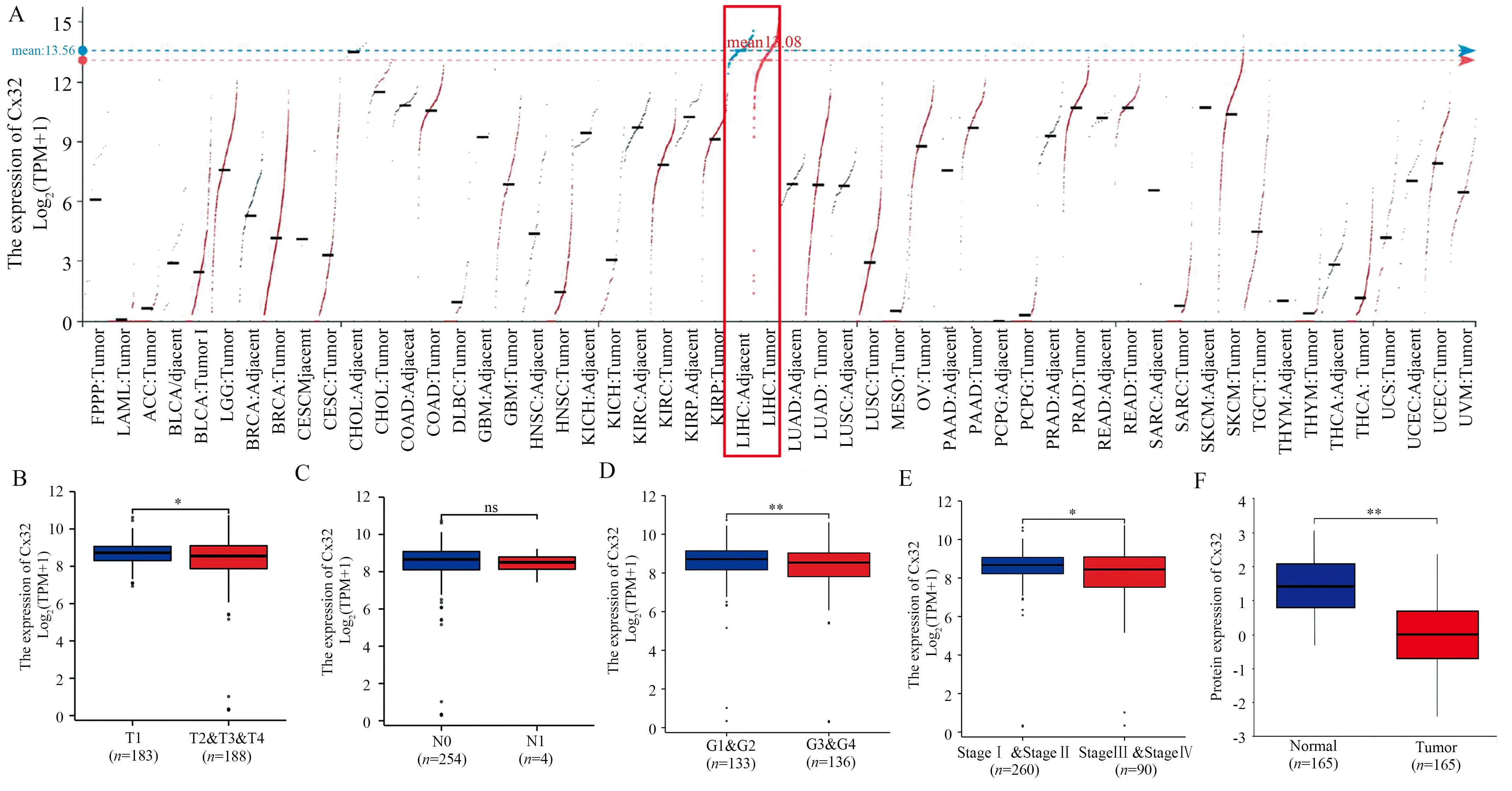
Fig1 Expression of Cx32 mRNA and protein in different public databases
3.2 Expression of Cx32 in HCC cells and construction of Cx32 OE cell line
To identify the expression of Cx32 in HCC cells, we found that Cx32 protein expression in several HCC cells such as Hep3B, Huh7,HepG2, and SMMC-7721 was significantly decreased compared with normal liver epithelial cells LO2 by Western blot (P<0.05, Table 1, Figure 2A).
Following the discovery of low Cx32 expression in the Huh7 cell line, we conducted additional experiments using a previously successful Huh cell model stably overexpressing Cx32[8], which consistently confirmed the presence of Cx32 protein over-expression in this model cell by Western blot and IF (P<0.05, Table 2-3, Figures 2B, C).
Tab1 Cx32 protein expression in human normal hepatic epithelial cell line and different HCC cell lines(n=3,)

Tab1 Cx32 protein expression in human normal hepatic epithelial cell line and different HCC cell lines(n=3,)
Note: Compared to LO2 cells, *P<0.05.
Group Cx32 LO2 0.99±0.11 Hep3B 0.19±0.09*Huh7 0.20±0.16*HepG2 0.27±0.76*SMMC-7721 0.63±0.08*F 40.31 P 0.00

Fig2 Expression of Cx32 in different HCC cell lines and identification of Huh7 cell line of stably over-expressed Cx32
Tab2 Cx32 protein expression in different groups of Huh7 cells (n=3, )

Tab2 Cx32 protein expression in different groups of Huh7 cells (n=3, )
Note: Compared to Control Group, *P<0.05; Compared to NC Group,#P<0.05.
Group Cx32 Control 1.02±0.10 NC 1.02±0.13 Cx32 OE 1.56±0.20*F 13.39 P 0.00#
Tab3 Fluorescence intensity of Cx32 in different groups of Huh7 cells(n=3,)

Tab3 Fluorescence intensity of Cx32 in different groups of Huh7 cells(n=3,)
Note:Compared to Control Group, *P<0.05; Compared to NC Group,#P<0.05.
Group Cx32 Control 1.01±0.11 NC 1.12±0.15 Cx32 OE 1.71±0.09*F 29.32 P 0.00#
3.3 Over-expression of Cx32 decreased the proliferation,invasion and migration capacities of Huh7 cell line
MTT colorimetric assays revealed that OD490 values in the Cx32 OE group were significantly lower than in the Control or NC groups(P<0.01, Table4, Figure 3A).
The results of cell scratch assay showed that the cell scratch healing rate at 24 h in Cx32 OE group (29.09±2.88)% was significantly lower compared with NC group (55.27±2.89)% (P<0.01, Table 5, Figure 3B).The results of transwell assay further revealed that the number of cells invaded in the Cx32 OE group (44.67 ± 0.88)was less than that in the control group (63.00±1.15) or NC group(62.00±0.57) (P<0.05,Table 6, Figure 3C).The above results showed that Cx32 over-expression inhibited the proliferation, migration and invasion of Huh7 cells.
Tab4 Effect of Cx32 over-expression on the proliferative ability of Huh7 cells(n=3, )

Tab4 Effect of Cx32 over-expression on the proliferative ability of Huh7 cells(n=3, )
Note: Compared to Control Group, *P<0.05; Compared to NC Group,#P<0.05.
Group Cell viability Control 1.49±0.06 NC 1.59±0.05 Cx32 OE 0.43±0.04*#F 509.30 P 0.00
Tab5 Effect of Cx32 over-expression on the migration ability of Huh7 cells(n=3,)

Tab5 Effect of Cx32 over-expression on the migration ability of Huh7 cells(n=3,)
Note: Compared to NC Group, *P<0.05.
?
Tab6 Effect of Cx32 over-expression on the invasive ability of Huh7 cells (n=3,)

Tab6 Effect of Cx32 over-expression on the invasive ability of Huh7 cells (n=3,)
Note: Compared to Control Group, *P<0.05; Compared to NC Group,#P<0.05.
Group Number of invasive cells Control 63.67±3.51 NC 62.00±5.00 Cx32 OE 43.00±4.00*#F 22.24 P 0.00
3.4 Over-expression of Cx32 inhibited EMT process in Huh7 cells
Since EMT is an important biological mechanism of tumor cell migration and invasion[10,11], we further investigated the effect of over-expression of Cx32 on EMT progression in Huh7 cells.Western blot and IF experiments consistently showed up-regulation of E-cadherin protein, an epithelial marker, and down-regulation of Snail and vimentin protein, mesenchymal markers, in the Cx32 OE group compared with the Control or NC groups (Table 7-8, Figure 4A).This result suggests that over-expression of Cx32 can inhibit EMT progression in Huh7 cells.
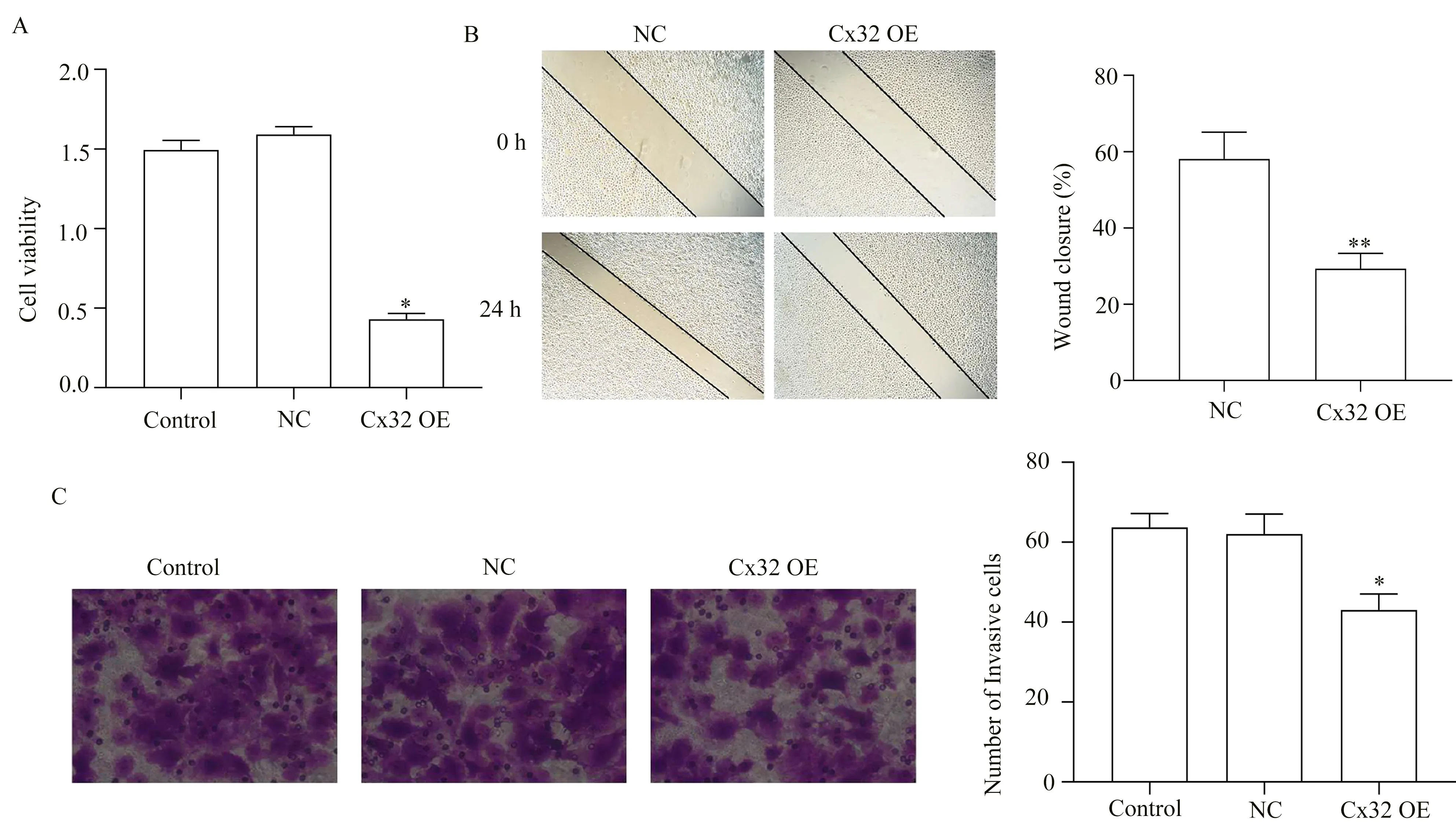
Fig3 Effect of Cx32 over-expression on the proliferation, migration and invasion of Huh7 cells
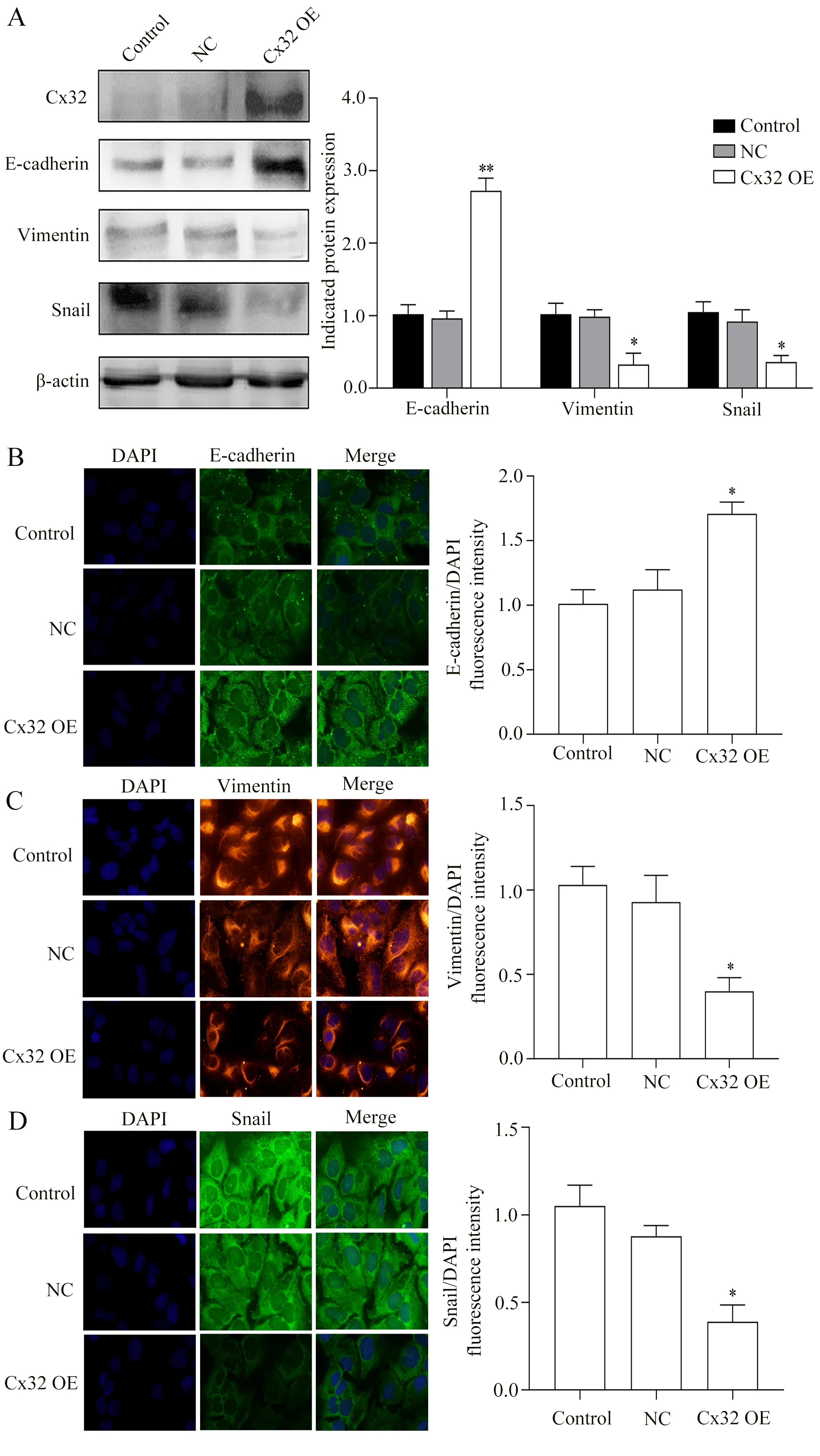
Fig4 Effect of Cx32 over-expression on protein levels of EMT markers in Huh7 cells
Tab7 Effect of Cx32 over-expression on protein levels of E-cadherin, Vimentin and Snail in Huh7 cells(n=3,)
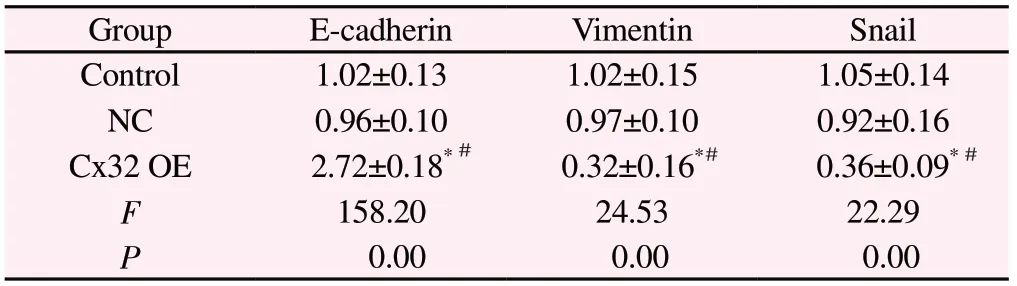
Tab7 Effect of Cx32 over-expression on protein levels of E-cadherin, Vimentin and Snail in Huh7 cells(n=3,)
Note: Compared to Control Group, *P<0.05; Compared to NC Group,#P<0.05.
Group E-cadherin Vimentin Snail Control 1.02±0.13 1.02±0.15 1.05±0.14 NC 0.96±0.10 0.97±0.10 0.92±0.16 Cx32 OE 2.72±0.18*0.32±0.16*0.36±0.09*F 158.20 24.53 22.29 P 0.00 0.00 0.00###
Tab8 Effect of Cx32 over-expression on fluorescence intensity of E-cadherin,Vimentin and Snail in Huh7 cells(n=3,)
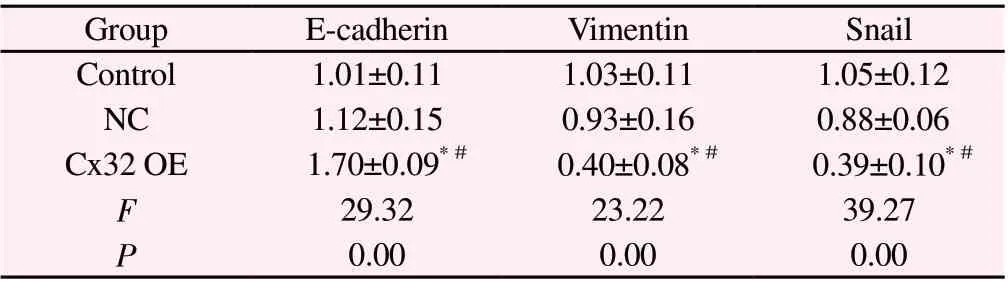
Tab8 Effect of Cx32 over-expression on fluorescence intensity of E-cadherin,Vimentin and Snail in Huh7 cells(n=3,)
Note:Compared to Control Group, *P<0.05; Compared to NC Group,#P<0.05.
Group E-cadherin Vimentin Snail Control 1.01±0.11 1.03±0.11 1.05±0.12 NC 1.12±0.15 0.93±0.16 0.88±0.06 Cx32 OE 1.70±0.09*0.40±0.08*0.39±0.10*F 29.32 23.22 39.27 P 0.00 0.00 0.00###
4.Discussion
Cx32 is an important component of GJ in liver tissue and maintains the communication function between normal hepatocytes mediated by GJ[12].GJ is a kind of protein channel which widely exists between neighboring cells, regulates the transmission of substances and signal transduction between cells, and plays a key regulatory role in the growth and development of the body and the proliferation, differentiation and apoptosis of cells.Previous studies have shown that down-regulation or loss of GJ is often linked to the growth of tumors[13,14], and Cx proteins were thought to be tumor suppressors[15], for example, study has found that Cx37 can inhibit tumor growth by decreasing angiogenesis[16], and Cx31 can inhibit the proliferation, migration, and invasion of thyroid cancer cells[17].Studies, including ours, have confirmed that Cx32 expression decreases continuously as HCC progresses, and that over-expression of Cx32 helps to suppress or reverse the malignant phenotype of HCC[5,6].These results support the traditional view that Cx proteins act as tumor suppressors by maintaining cellular homeostasis through GJs.Of course, Cx32 itself, as a unique protein,cannot be excluded from its GJ-independent effects[18].However, it has also been found that the mRNA and protein levels of Cx32 in HCC have not changed significantly, but abnormal localization in the cytoplasm has emerged[19].When Cx32 protein cannot precisely localize to Huh7 cell membranes, its abnormal accumulation in HCC cytoplasm will promote invasion and metastasis of Huh7 cells[6,7,20].The differences in the effects and characteristics of Cx32 in different HCC cell lines suggest that further studies are needed.
In this study, we firstly started from bioinformatics data mining and found that Cx32 mRNA and protein were lowly expressed in HCC tissues, and their expression levels decreased with the progression of T stage, histological grade and clinical stage of HCC patients.In addition, there was a negative correlation between N-stage and Cx32 mRNA expression level.The results of in vitro experiments showed that the expression of this protein in HCC cells was generally lower than that in normal liver epithelial cells LO2, which was consistent with the results obtained by bioinformatics techniques and together supported the presence of Cx32 down-regulation during HCC carcinogenesis or progression.We then used previously constructed cells and designed a series of experiments to reveal the role of over-expression of Cx32 in Huh7, a cell line.The construction and identification of Huh cell models stably overexpressing Cx32 have been reported in detail in our previous literature[8].According to this study, only a small proportion of the overexpressed Cx32 molecules were found at the cell membrane, with the majority found in the cytoplasm[8].We also confirmed the localization of Cx32 by IF assay in this study, and we speculated that some Cx32 protein present in the cell membrane may be associated with GJ formation,but the majority of it was localized in the cytoplasm, which is more conducive to observing the effect caused by Cx32 accumulation in the cytoplasm.
According to the MTT assay results, Cx32 could effectively reduce the proliferation, migration and invasion of Huh7 cells when overexpressed.The inhibitory effect of specific over-expression of Cx32 on the biological function of Huh7 cells has been reported in previous studies[21], but comprehensive studies on Cx32 in Huh7 cells have found that the exact role of Cx32 varies in different literatures.This study still supports the role of traditional tumor suppressors, and we speculate that this difference may be related to the culture conditions of the cell line, changes in cell characteristics during passage, and spatiotemporal heterogeneity.EMT is one of the important mechanisms by which tumor cells acquire invasiveness and undergo metastasis[10,11], and activation of EMT is also an important manifestation of malignant phenotype acquisition in HCC[22].It has been documented that the invasive ability of HCC cells will decrease with the expression of E-cadherin, an epithelial cell-derived marker, and increase the expression of Snail and vimentin, mesenchymal cell-derived markers[23].In this study, overexpression of Cx32 upregulated E-cadherin protein expression and downregulated vimentin protein and Snail protein expression while exerting the above effects.Based on this, we speculated that the possible reason for the reduced migration and invasion of Huh7 cells was that over-expression of Cx32 suppressed the EMT progression of Huh7 cells.This is consistent with our previous findings on HepG2 and SMMC-7721 cell lines[5].Given the localization of overexpressed Cx32 in Huh7 cells, the comprehensive effects of GJdependent and GJ-independent may exist in this machinery.
In summary, the present study found that the inhibition of EMT process may be one of the mechanisms that lead to inhibition of cell proliferation, migration and invasion mediated by Cx32 overexpression.Combined with the series studies on Cx and HCC carried out by our research team, we have a more comprehensive understanding of the role and characteristics of Cx32 in different HCC cell lines, and provide more experimental data for revealing the biological effect of Cx32 in HCC.Together the results of this study further support that Cx32 can be an important target for HCC,and any methods or strategies to up-regulate or increase Cx32 is promising for treatment against advanced HCC.
Author’s contribution:
Ji Wen-bin: main experimental execution, data analysis and paper writing; Lv Zhen-yu, Cheng Qian-qian, Zhou Xue-li and Wang Wei:assisted with experimental execution, data collation and analysis;Yang Yan: experimental design and manuscript revision.All authors declare no conflict of interest.
 Journal of Hainan Medical College2023年2期
Journal of Hainan Medical College2023年2期
- Journal of Hainan Medical College的其它文章
- Research progress of modern pharmacological effects of Pueraria lobata and its compound clinical application
- A systemaic review and meta-analysis of traditional Chinese medicine in the treatment of chronic cough
- Research progress on sensitive genes related to ferroptosis
- Identification of key genes underlying clinical features of hepatocellular carcinoma based on weighted gene co-expression network analysis and bioinformatics analysis
- METTL14 upregulates m6A modification of pri-miR-141 inhibiting ZEB1 to promote proliferation and inflammation of lung fibroblasts
- Serum anti-blood type IgG/IgM binding and cytotoxicity to pig PBMC and RBC
