Bilateral calcified Macroplastique? after 12 years
Dear editor,
In recent years,endoscopic subureteral transurethral injection(STING)has become the first-line therapy for children with vesicoureteral reflux(VUR)owing its diffusion in clinical practice to a high success rate and minimum complications[1].Macroplastique?(Uroplasty,Inc.,Minnetonka,MN,USA)is an efficient and safe bulking agent commonly used in VUR,being non-migratory,non-antigenic,and biocompatible.Moreover,its stability over time,with a virtual no-reabsorption phenomenon,has allowed its application in wider medical fields[2].The main postoperative complications,defined in scientific literature,are the obstruction of the ipsilateral ureter(1%),bladder mucosal erosions(0.6%),and occurrence of contralateral VUR(2.1%)[3].Despite a low rate of complications,a long-term follow-up is required to promptly identify and eventually resolve such eventualities.In this study,we report a rare case of two bladder and ureteral calcifications originating from the extrusion of a previously implanted STING Macroplastique? 12 years before,the longest interval reported between implantation and occurrence of complications.Patient’s parents and patient herself provided informed written consent to procedures and publication.
A 17-year-old female patient was referred in October 2018 to our urological department with a recent history(1-2 months)of right flank pain,nausea,and recurrent fever>37.5°C.An outpatient ultrasound scan(US)performed a week before the urological visit reported the presence of distal bilateral ureteral stones near the ostia with no signs of hydronephrosis.Medical history and previous documentations reported a first-degree and a thirddegree VUR to the left and to the right respectively,treated endoscopically with Macroplastique? STING 12 years before.Consequently,due to the absence of symptoms at the time of the visit,a kidney-ureter-bladder X-ray was prescribed,confirming the previously reported calcifications(Fig.1A-D).In order to properly assess the condition and evaluate a successive treatment,a further computed tomography(CT)urography scan was prescribed 2 months later which reported:regular kidneys for shape,position,and size,with a slightly smaller right kidney compared to the contralateral,conserved excretory functionality,and no evidence of hydronephrosis;regular ureters up to the bladder,where two racemose stones of 18 mm and 6 mm,apparently wedged in the ostia of left and right ureter,respectively,were identified,with no upstream ectasia reported.Aside from a small accessory spleen(<2 cm),belonging to the upper pole of the spleen,no relevant findings were reported.In the same month,renal scintigraphy was prescribed,reporting a glomerular filtration rate of 65.64%and 34.36%for left and right kidney,respectively.As for US and CT urography findings,no hydronephrosis was reported.Considering the past medical history and the instrumental findings,in order to fully rule out the origin of the calcifications and evaluate a possible extrusion of Macroplastique?,a diagnostic cystoscopy was performed.At the exam,mucosal erosions and peri-ostial calcifications compatible with extruded and calcified Macroplastique?were reported.Holmium ureteroscopic laser lithotripsy was programmed to remove those calcifications.The surgery was performed 2 months after the CT urography,which permitted the successful removal of both calcifications without complications(Fig.1E).The postoperative was uneventful and the patient was discharged after 4 days with antibiotic therapy.Follow-up US at 1 month did not report any pathological findings.A successive follow-up cystoscopy was performed in 4 months after the surgery reporting the complete healing of mucosal erosions and the absence of residual extruded Macroplastique?,with ostia identifiable and completely recovered.US and blood tests were performed 6 months later at successive follow-up visit,reporting no pathological findings.The patient is currently in follow-up with an US every 6 months and blood tests annually.Previous symptoms such as flank pain,nausea,and fever did not ever reoccur to date.
The endoscopic treatment of VUR is based on the creation of solid support behind the intravesical ureter with the elongation of the intramural length of the ureter[1].The effectiveness and safety of Macroplastique? STING as first-line therapy for VUR treatment was well reported inthe literature,with success rates ranging from 70% to 90%and complications rates between 1.0% and 1.5%[3-5].However,in some cases,the presence of late calcifications in the site of previous Macroplastique? injections was detected,as described in three patients with submucosal bladder calcifications at 5 years,7 years,and 9 years following the initial injection,presenting lower urinary tract symptoms,hydronephrosis,and haematuria[6].Similarly,another case reported symptomatic bladder calcification in a 10-year-old patient with a history of Macroplastique? STING 6 years before,resolved with cystolitholapaxy[7].Analogously,a symptomatic 15-year-old female patient,who underwent Macroplastique?injection 7 years before,reported a 5 mm stone that required lithotripsy and ureteral reimplantation,while in a 39-year-old male patient,a bladder stone developed from the previous site of Macroplastique? STING(7 years before)was resolved with ureteroscopic lithotripsy[8,9].Finally,a recent case in a 5-year-old male patient described a calcified Macroplastique? implanted 4 years before and successfully removed with Holmium laser[10].The rationale which could explain the development of calcifications from previously implanted Macroplastique? is related to the intrinsic property of this material which is nonbiodegradable and virtually permanent.Its potential exposition into the bladder,due to mucosal erosions or extrusion could act as a nidus for the development of calcifications and stones through Randall’s plaques-like mechanism.To our knowledge,there are fewer than 10 cases in the literature describing ureteral or bladder calcifications due to previous Macroplastique? injection.In addition to increasing the reported cases in literature,this case is characterized by the longest time between Macroplastique? injection and onset of symptoms and by the bilateral localization of the condition.
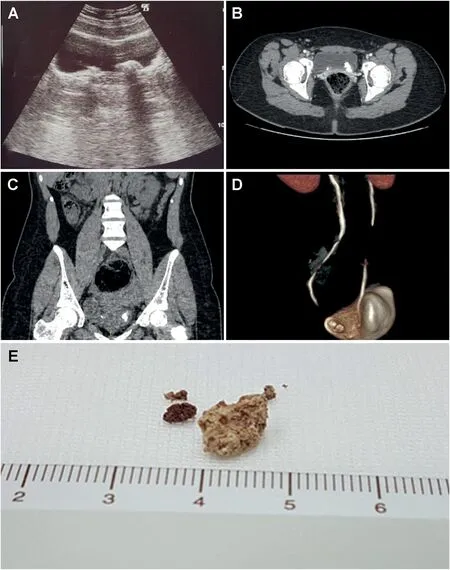
Figure 1 Presence of bilateral calcifications and fragments retrieved.(A)Echographic appearance;(B)Computed tomography scan appearance(transverse);(C)Computed tomography scan appearance(coronal);(D)Three-dimensional reconstruction;(E)Fragments retrieved.
Endoscopic subureteral injection of bulking agents has become first-line therapy for the treatment of VUR and for this reason,it is important for physicians to recognize late complications of those practices,especially in patients complaining of recurrent urinary tract infection or lower urinary tract symptoms.As described,bladder and ureteral calcifications,although rare,could occur even after 12 years,therefore,requiring longer follow-up in order to avoid misdiagnosis and overtreatment in young patients with suspicious and recurrent urinary symptoms.
Author contributions
Study concept and design:Biagio Barone,Luigi De Luca.
Data acquisition:Biagio Barone,Mariano Marsicano,Gennaro Cancelmo.
Data analysis:Biagio Barone,Luigi De Luca,Luigi Napolitano,Vincenzo Francesco Caputo.
Drafting of manuscript:Biagio Barone,Vincenzo Francesco Caputo.
Critical revision of the manuscript:Massimiliano Creta,Ferdinando Fusco.
Conflicts of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Biagio Barone*Luigi De Luca Luigi Napolitano Vincenzo Francesco Caputo Mariano Marsicano Gennaro Cancelmo Massimiliano Creta
Department of Neuroscience,Reproductive Sciences and Dentistry,University of Naples Federico II,Naples,Italy
Ferdinando Fusco
Department of Woman,Child and General and Specialized Surgery,University of Campania Luigi Vanvitelli,Naples,Italy
*Corresponding author.
E-mail address:biagio.barone@unina.it(B.Barone)
19 August 2021
 Asian Journal of Urology2022年3期
Asian Journal of Urology2022年3期
- Asian Journal of Urology的其它文章
- Burned-out testicular seminoma with retroperitoneal metastasis and contralateral sertoli cell-only syndrome
- Endoscopic management of adolescent closed Cowper’s gland syringocele with holmium:YAG laser
- Transcutaneous dorsal penile nerve stimulation for the treatment of premature ejaculation:A novel technique
- Culture-positive urinary tract infection following micturating cystourethrogram in children
- A phase II study of neoadjuvant chemotherapy followed by organ preservation in patients with muscle-invasive bladder cancer
- Augmentation cystoplasty in children with stages III and IV chronic kidney disease secondary to neurogenic bladder
