Impact of the mass isotope on plasma confinement and transport properties in the HL-2A tokamak
Yu HE (何鈺), Jun CHENG (程鈞), Yuhong XU (許宇鴻),*, Qian FANG (方茜), Yucai LI (栗鈺彩), Jianqiang XU (許健強(qiáng)), Weice WANG (王威策),Longwen YAN (嚴(yán)龍文), Zhihui HUANG (黃治輝), Na WU (吳娜),Min JIANG (蔣敏), Zhongbing SHI (石中兵), Yi LIU (劉儀), Wulyu ZHONG(鐘武律) and Min XU (許敏)
1 Institute of Fusion Science, School of Physical Science and Technology, Southwest Jiaotong University,Chengdu 610031, People's Republic of China
2 Southwestern Institute of Physics, Chengdu 610041, People's Republic of China
Abstract The impact of the mass isotope on plasma confinement and transport properties has been investigated in Ohmically-heated hydrogen and deuterium plasmas in the HL-2A tokamak.Experimental results show that under similar discharge parameters the deuterium plasma has better confinement and lower turbulent transport than the hydrogen one,and concomitantly,it is found that the magnitude of geodesic acoustic mode zonal flows, the tilting angle of the Reynolds stress tensor and the turbulence correlation lengths are all larger in the edge region of the deuterium plasma.The results provide direct experimental evidence on the importance of the nonlinear energy coupling between ambient turbulence and zonal flows for governing the isotope effects in fusion plasmas.
Keywords: isotope effect, confinement and transport, turbulence and zonal flows
1. Introduction
The influence of the isotope mass on plasma confinement properties has been a longstanding issue in magnetically confined plasmas.According to gyro-Bohm scaling[1,2],the plasma transport diffusivity scales asω*∝k⊥V*∝(ρi, ω*, V*, and k⊥represent the ion Larmor radius, diamagnetic drift frequency, diamagnetic drift velocity and perpendicular wavenumber of turbulence, respectively).Therefore, it is expected that the plasma confinement should be degraded with increasing ion mass mi. However, in the past decades, there have been a significant amount of experiments showing strong deviations from the gyro-Bohm expectation in both tokamaks [3-12] and stellarators [13-16]under comparable hydrogen(H)and deuterium(D)discharge conditions. Meanwhile, theoretical and numerical efforts[17-26] have been made to unveil the physical mechanisms behind the isotope effects, among which the possible impact by isotopic mass on shear flow rates [25] and zonal flows[17, 23, 24] has been proposed.
The first experimental observation in the TEXTOR tokamak has demonstrated that the amplitude of geodesic acoustic mode (GAM) zonal flows substantially increases during the transition from H to D dominated plasmas [9],which is qualitatively consistent with the GKV simulation[17]. However, up to date, there has been little evidence showing the increase of nonlinear interplay between ambient turbulence and zonal flows in heavier mass isotope plasmas.
In this paper, we present direct experimental evidence to expose the fact that in D majority plasmas,the nonlinear energy transfer plays a dominant role in exciting larger GAM zonal flows by extracting more energy from ambient turbulence,which results in lower turbulent transport and better confinement compared to H majority plasmas.The results provide additional proof for understanding the isotope effects in fusion plasmas.
2. Experimental setup

3. Experimental results and discussion


Figure 1.Time traces of discharge waveforms in H (black curves)and D (red curves) majority plasmas. (a) Plasma current, (b) loop voltage, (c) central line-averaged density, (d) plasmas stored energy and (e) radial position of the reciprocating probes.
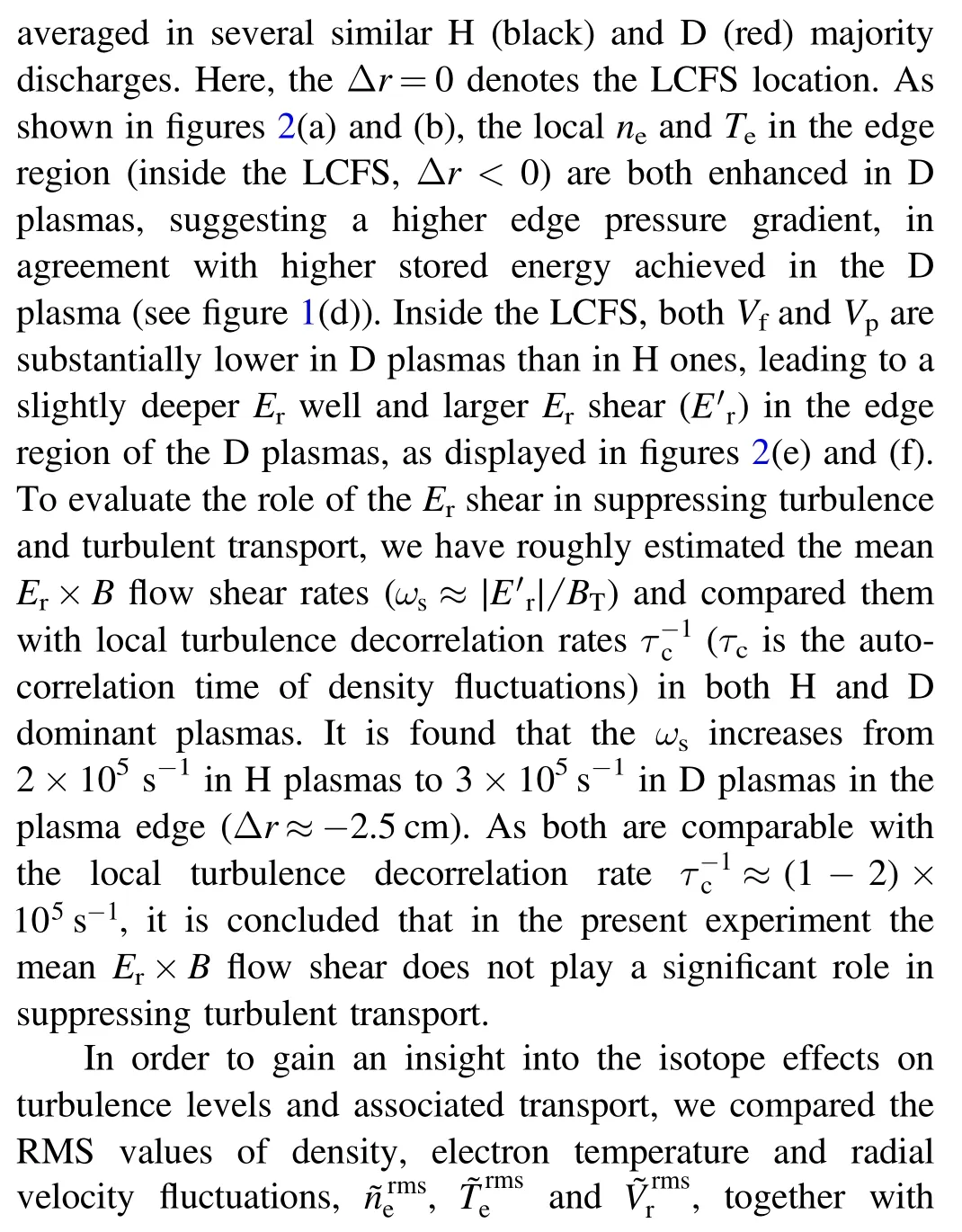

Figure 2.Radial profiles of edge plasma parameters in H(black curves)and D(red curves)majority plasmas.(a)Plasma density,(b)electron temperature, (c) floating potential, (d) plasma potential, (e) radial electric field Er and (f) Er shear. The error bars indicate the standard deviation about the mean estimated in similar discharges.

To understand the mechanisms responsible for the reduction of turbulent transport in the isotope deuterium plasmas, we analyzed the spectrum characteristics of edge turbulence and zonal flows in H and D plasmas.In HL-2A,a low frequency coherent mode with long-range toroidal correlations, namely GAM zonal flows, has been routinely observed in floating potential signals [32, 33]. Theories predict that the GAM zonal flow has poloidally symmetric (m/n=0/0) potential and asymmetric (m/n=1/0) density perturbations[34,35].In the present experiments,it is found that the maximum GAM amplitude presents at Δr ≈-3 cm inside the LCFS[36].Plotted in figure 4 are the frequency spectra of floating potential(?Vf)and density(?ne)fluctuations detected at Δr ≈-3 cm in H and D majority plasmas averaged over several similar shots.As shown in figure 4(a),the ?Vfspectrum exhibits a sharp peak at f ≈8-10 kHz in both H and D plasmas, whereas the ?nespectrum displays quasi-coherent modes in higher frequency ranges.
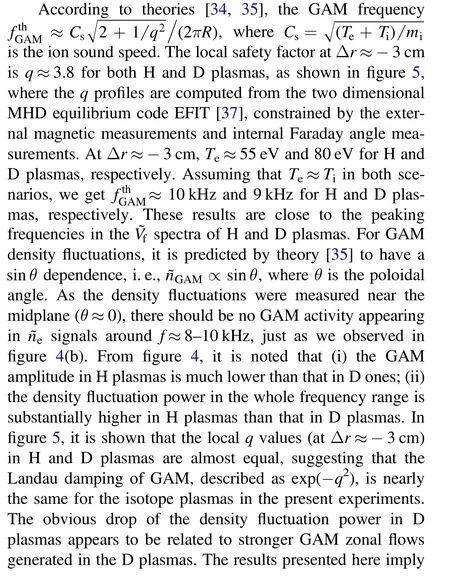

Figure 3.Radial profiles of (a) rms level of density fluctuations, (b)rms level of electron temperature fluctuations,(c)rms level of radial velocity fluctuations, (d) fluctuation-driven particle flux and (e)fluctuation-driven energy flux measured by the fast reciprocating probe array in H(black curves)and D(red curves)majority plasmas.

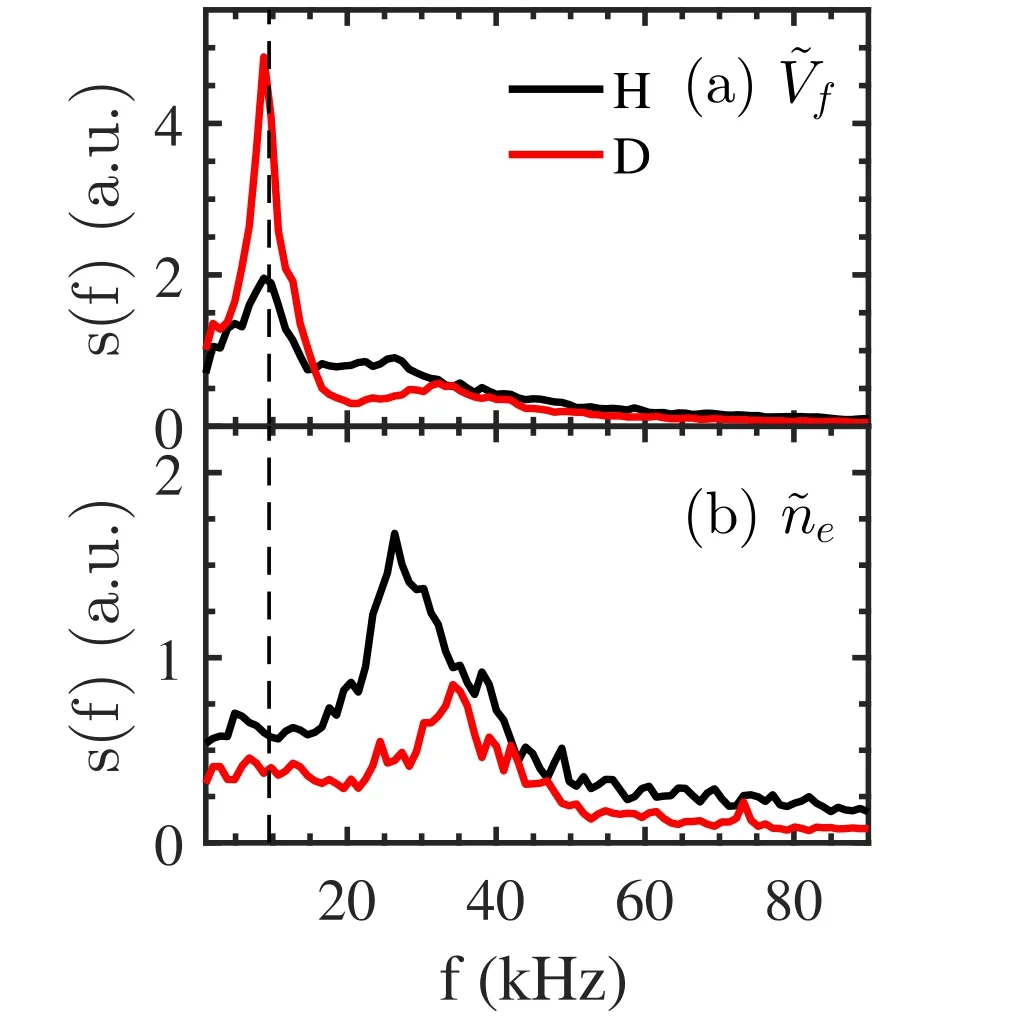
Figure 4.Frequency spectra of(a)floating potential fluctuations and(b)density fluctuations measured at Δr ≈-3 cm in H(black curves)and D (red curves) plasmas averaged over several similar shots.
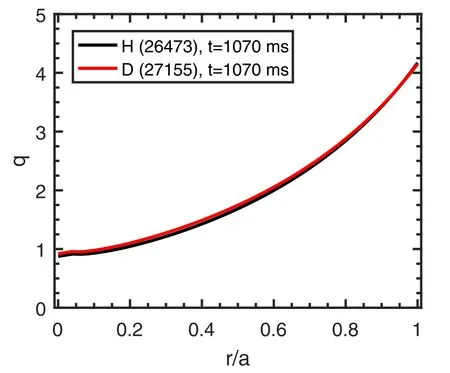
Figure 5.Radial dependence of the safety factor calculated from the two dimensional MHD equilibrium code EFIT as a function of the radial position normalized by a.


Figure 6.Contour-plot of the squared auto-bicoherence of Vf fluctuations(a)in H plasmas and(b)in D plasmas.Shown in(c)is the summed squared auto-bicoherence in H (black curves) and D (red curves) plasmas. The horizontal dotted line indicates the statistical noise level.

Figure 7. Contour-plot of the joint-PDF of the Reynolds stress tensor between poloidal velocity fluctuations ( θ?V) and radial velocity fluctuations (?Vr) in H (left side) and D (right side) dominant plasmas. The PDF values are normalized by the maximum one.

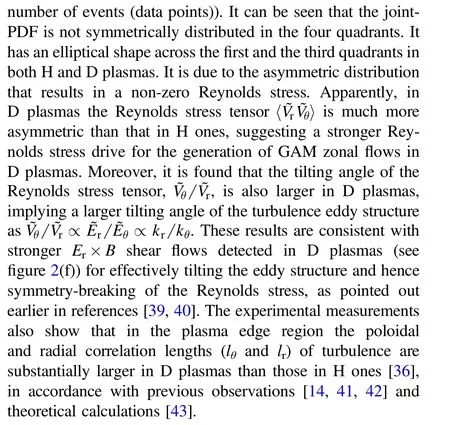
4. Summary
In summary,the isotope effects on plasma confinement,edge turbulence and turbulent transport as well as GAM zonal flows have been studied using a two-step Langmuir probe array in H and D majority plasmas in the HL-2A tokamak.Evidence shows that under similar discharge parameters the D plasma has better confinement and lower turbulent transport than the H plasma. Meanwhile, it is observed that the magnitude of GAM zonal flows,the tilting angle of the Reynolds stress tensor, and the turbulence correlation lengths are all larger in the edge region of the D plasma.The results provide direct experimental proof on the importance of the nonlinear energy transfer between turbulence and zonal flows for governing the isotope effects in fusion plasmas.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank to the HL-2A team for their operational assistance in the experiment.This work was partially supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos.11 820 101 004, 11 875 017, 12 075 079 and 51 821 005) and partially supported by the National Key R&D Program of China(No.2019YFE03020000), the National Magnetic Confinement Fusion Science Program of China(No.2018YFE0310300),the Science and Technology Plan Project in Sichuan Province of China(No.2020YFSY0047)and Sichuan International Science and Technology Innovation Cooperation Project (No.2021YFH0066).
 Plasma Science and Technology2022年9期
Plasma Science and Technology2022年9期
- Plasma Science and Technology的其它文章
- Implementation and application of PyNE sub-voxel R2S for shutdown dose rate analysis
- Microchannel cooling technique for dissipating high heat flux on W/Cu flat-type mock-up for EAST divertor
- Development of the pellet injection system on the J-TEXT tokamak
- Degradation of tiamulin by a packed bed dielectric barrier plasma combined with TiO2 catalyst
- Experimental study on surface arc plasma actuation-based hypersonic boundary layer transition flow control
- Efficient direction-independent fog harvesting using a corona discharge device with a multi-electrode structure
