Detection and Quantification of Circulating Tumor Cells in Salvaged Blood in Surgical Osteosarcoma Patients:A Pilot Study from a Tertiary Medical Center
Ayixia NAWAN,ZHENG Shao Qiang,HE Xi Qiang,and WANG Geng
Osteosarcoma (OS) is a common primary malignant bone tumor that most commonly affects adolescents and children under 20.According to previous research,OS is distinguished by high-grade malignancy,rapid progression,distant metastasis,and a low long-term survival rate.Because of accurate diagnosis,pathological classification of biopsy,multiagent perioperative chemotherapy,and limb-salvage surgery,over-all survival rate of OS patients has significantly enhanced in recent years.According to previous research,nearly 90% of OS patients receive limb salvage treatment and respond well to chemotherapy[1].However,as limb salvage surgery has become more common,there has been an increase in perioperative allogeneic blood transfusion demand.Previous research has shown that allogeneic blood transfusion is significantly associated to tumor recurrence and mortality,varies patients’ immune states making them vulnerable to bacterial,viral,and tumor cell invasion,deeming it an independent and vital prognostic factor[2].Variance in inpatient costs between cell salvaged blood and allogeneic blood is only one unit[3].Intraoperative cell salvage (IOCS) effectively reduces allogeneic blood transfusion and retrieve cell salvage blood with high-quality fresh red blood cell(s) (RBCs)as per many studies.Although RBCs are essential components of perioperative care,autologous transfusion is not recommended in malignant tumor surgery due to the theoretical risk of spreading malignant tumor cells[3].Circulating tumor cells(CTCs) are epithelial cell adhesion molecules(EpCAM),expressing tumor cells that enter the peripheral blood circulation from primary tumors spontaneously or after tumor manipulation.Previous research has found that few CTCs have high activity and metastasis potential,implying important causes of tumor recurrence.CTC counts have important clinical implications in the occurrence,development,and early metastasis of various solid tumors along with drug efficacy,monitoring,prognosis,evaluation,and individualized treatment[4].An earlier study discovered CTCs in the blood of OS patients,CTCs greater than 2 indicated the presence of CTC in patients’ peripheral blood[5].Other previous study suggested that CTCs greater than 5 per 7.5 mL of blood are an independent predictor of poor outcome[6].
CTC isolation and detection are technically difficult due to their low number.Currently,there is no standard method for counting and quantifying CTCs from OS.Negative CTC enrichment technology which based on the antigen-antibody reaction principle was used in the current study to address this issue.As a result,despite their frequent mutations,the OS-derived CTCs were identified using fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH) with cluster of differentiation 45 (CD45) immunostaining markers (Chr7 and Chr8 with high copies) to exclude epithelial and the rest of the lymphocytic cells.Blood was filtered and collected in the current study using two types of IOCS-leucocyte depletion filter (LDF):SQ LDF and RC LDF;SQ LDF,a 40 μm filter aperture micro-molecule filter,filtered nucleated cells using zigzag and charge load filtration.RC LDF,a pure white blood cells (WBC) depletion filter with an 8 μm filter aperture,reliably and effectively reduced nucleated cells following filtration after gravity flow or high flow.
A total of 30 patients from the oncology department of Beijing JiShuiTan Hospital with American Society of Anesthesiologists (ASA) classes I-II were recruited.Patients were enrolled prospectively and pathologically diagnosed with OS.The study included patients between the ages of 10 and 65 who were scheduled for OS surgery.Those who had other malignant tumors or diseases within the previous five years of enrollment,on the other hand,were excluded from this study.Those with fever,infectious diseases,or on immunosuppressive therapy were also barred from participating in the study.Clinical characteristics of patients are outlined in Supplementary Table S1 (available in www.besjournal.com).Before the study,inclusive patients provided their written informed consent.
All patients were sedated using general anesthesia or a combination of epidural spinal and regional anesthesia.Cell Saver (CS) 5+(Haemon tics Corporation,MA 02184,USA) was used to retrieve blood from the operation field during surgery.According to the Institutional Review Board (IRB)protocol of Beijing JiShuiTan Hospital,the recovered blood was not transfused back to patients.Instead,blood samples were washed,centrifuged with CS 5+,and retrieved in a dedicated reservoir using standard operating procedures.After the cell salvage process,RC LDF (Haemon tics corporation,Massachusetts,USA) and SQ LDF (Haemon tics corporation,Massachusetts,USA) were used to filter blood.
Three 10-mL filtered blood samples were taken during surgery:10 mL cell salvaged blood from reservoir bag before filtration;10 mL blood sample after cell salvaged blood filtered with RC LDF,and 10 mL blood sample after cell salvaged blood filtered with RC LDF.Within 24 h,all samples were sent to the Cyttel biosciences laboratory for examination at room temperature.
Through a negative enrichment process,immunomagnetic beads conjugated with anti-CD45 antibodies were used to gradually remove plasma,RBCs,WBCs,and other components from blood samples.After that,the samples were fixed in slides.To identify,enumerate,and characterize rare CTCs,vimentin was immuno-stained and subjected to FISH.Counting the chromosome centromere probe(CEP) signal on smears was used as a criterion for identifying tumor cells and whereas cells with more than three hybridization signals per cell were classified as hyper diploid abnormal cells.Criteria to identify tumor cells was by using vimentin,DAPI(+),and CD45(-).OS-derived CTCs were found to be as DAPI+/CD45-/vimentin+/Chr7 or Chr8 multiploidy.(Figure 1).

Figure 1.Identification of CTCs using CD45-FISH and vimentin.Micrographs of CTCs isolated from OS patients shown by immunofluorescence staining (vimentin — green;CD45 — dark red),CEP8:light orange;DAPI:blue.DAPI:4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole;CD45:cluster of differentiation 45;CEP:Centromere Probe.OS:Osteosarcoma.(Magnification:100x).
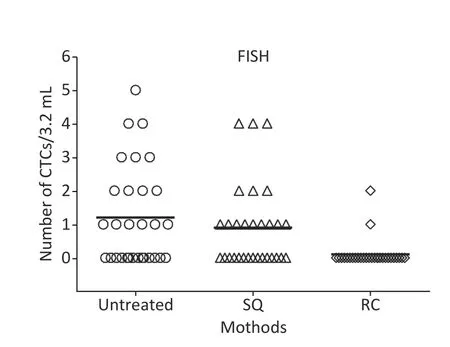
Figure 2.Comparison of CTCs detection using CD45?FISH pre-and post-filtration by two LDF.Data are (untreated) before SQ and RC LDF,(SQ) post-filtration by SQ-LDF,(RC) postfiltration by RC-LDF.No significant difference was detected in untreated SQ (P= 0.3969);A statistically significant difference was found between untreated and RC (P=0.0002),also SQ and RC (P=0.0014).(Independent samples t-test).FISH,fluorescence in situ hybridization;CTCs,circulating tumor cells;LDF,leucocyte depletion filter.
SPSS 22.0 software (IBM Corp.,Armonk,NY,USA) was used to analyze the data.The independent samplet-test and rank sum test were used to compare measurement data of groups.P<0.05 values were considered statistically significant.The ratios of the two different CTCs detection methods are presented in Supplementary Table S2 (available in www.besjournal.com).
Reliable detection methods and CTC markers are critical in determining the proliferative capacity of CTCs after filtration and the filtration efficiencies of appropriate LDF.In this study to enumerate technique for CTCs,FISH and microscopic analysis on OS patients were performed to improve detection rates based on tumor cell sizes.We assessed a negative CTCs enrichment technology founded on the principle of antigen-antibody reaction,with successive multiplex CD45 staining and FISH for the depletion of CD45+cells and subsequent quantification of CTCs of epithelial origin.In this study,at cut-off of vimentin+CTC ≥ 1/2 × 107WBC,CTCs were perceived in 20 (66.7%) patients,where CTC counts ranged from 0 and 81 CTCs/mL (median=7 CTCs/mL,mean=14.2 CTCs/mL).Vimentin is overexpressed in various tumor types and associated to epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT)[7].As representative EMT marker,high countenance of vimentin is positively linked with tumor metastasis,even with the potential to accelerate OS occurrence and metastasis rate[8].
In the said study,a high proportion of leukocytes,platelets,and plasma were removed from the blood collected from the operation field after the IOCS process to obtain concentrated RBCs.CTC counts from patients’ peripheral blood and surgical tumor removal determine the number of tumor cells in the reservoir bag.Previous research has found that most patients receive systemic preoperative chemotherapy to lessen solid tumors,reducing peripheral blood CTCs in patients with advanced cancer[3].CTC counts did not differ significantly between patients who had received chemotherapy and those who had not received chemotherapy before surgery.Prior to filtration,CTCs were detected in 16 (53%) of the patients at cut-off of CD45-FISH (-) CTC ≥ 1/2 × 107WBC,with CTC counts ranging from 0 to 5 CTCs/mL (median=1 CTCs/mL,mean=1.2 CTCs/mL).Results of this study revealed that CTCs still over-expressed even after IOCS LDF in few of the patients who received first-line chemotherapy before surgery,but the CTCs counts reduced after IOCS LDF compared to OS patients without chemotherapy.There were two plausible explanations available.The first is that combination chemotherapy reduced CTCs counts,derived from systemic circulation and solid tumors.Secondly,fragile tumor cells after chemotherapy have been disrupted during IOCS centrifugation and LDF filtration.Unfortunately,we did not compare the pre-operation peripheral CTCs counts of the patients in this study.
Previous research has suggested that tumor cells are destroyed during the IOCS and filtration processes[9],this is also consistent with findings of current study.Chen H et al.previously stated that filters with smaller pore sizes had good sensitivity in filtering rare CTCs after comparing varying pore sizes ranging from 5 to 18 μm[10].Diameters of both SQ and RC LDF filters in the current study were sufficient for the passage of RBCs with diameters ranging from 6 to 9 μm.For CTCs filtering there were no significant differences in vimentin (+) cell counts between pre-and post-filtration processes using SQ LDF (P=0.4742),in CD45(-) CTC counts between using SQ LDF (P=0.3969).On the other hand,there were statistically significant differences in vimentin(+) cell counts between the pre-and post-filtration steps using RC LDF (P=0.0002),in CD45(-) CTC counts between the pre-and post-filtering steps using RC LDF (P=0.0002).Furthermore,statistically significant differences between SQ and RC LDF(P=0.0002) in vimentin (+) in CD45(-) and were observed.(Figures 2 &3).This established that an RC filter consistently barred most nucleated cells transient through elongated passagewaysviagravity flow or high flow.Nonetheless,the current study confirms that it is impossible to efficiently remove malignant tumor cells following the IOCS procedure.Further more,CTC counts between patients who had received chemotherapy and those who had no chemotherapy treatment before surgery were not significantly different (Supplementary Table S3 available in www.besjournal.com).

Supplementary Table S1. Patient demographics,medical history,and disease characteristics

Supplementary Table S2. Pre-and post-filtration ratios of two different CTC detection methods using two leucocyte depletion filters in OS

Supplementary Table S3. Patient ratios and comparisons who received and did not receive preoperative chemotherapy,n (%)

Figure 3.Characteristics of CTCs detection using vimentin pre-and post-filtration by two LDF.Data are (untreated) before SQ and RC LDF,(SQ) post-filtration by SQ-LDF,(RC) postfiltration by RC-LDF.No significant difference was detected in untreated SQ (P=0.4742);A statistically significant difference was found between untreated and RC (P=0.0002),also SQ and RC (P=0.0002) (Independent samples t-test).CTCs,circulating tumor cells;LDF,leucocyte depletion filter.
CTCs derived from OS can travel through the bloodstream,and that distant metastasis is the leading cause of treatment failure[11].However,some researchers found only certain genomic regions and phenotypes of CTCs can subsist in the bloodstream and form distant metastasis lesions through interaction with a new microenvironment[12].The ability of CTCs to withstand circulation patterns,spillover blood vessel barriers,and reach and survive at the target site determines their dissemination potential.As a result,only a few CTCs can form metastasis lesions[12,13]and CTC counts and removal efficiency are important factors influencing the prognosis of patients with metastatic OS[14].Since Vimentin is also found in the nuclei of labeled CTCs,the value of vimentin as an accurate biomarker for OS is demonstrated.Hence,low vimentin expression in these neoplasms may be justified as a favorable prognosis in cancer treatment.
The current study’s findings revealed significant potential for detecting and enumerating OS-derived CTCs.These findings may confirm the role of vimentin as a conventional biomarker for OS and suggest that it could be used as a target for OS treatment.However,because this was a singlecenter cohort with small sample size,more patients are needed in future studies to validate the findings.
Finally,reliable detection methods are critical in determining the filtration efficiency of LDF and the proliferative capacity of CTCs after filtration.Our approach was to quantify CTCs in the IOCS reservoir bag of OS patients and can detect rare CTCs.In spite of well-documented risks of allogeneic blood transfusion,the presence of viable,nucleated malignant cells in the final filtered samples suggests that using cell salvage during OS surgery would risk re-transfusion of such cells,with unknown risk of causing metastatic disease spread.We wanted to establish if total clearance of all labeled malignant CTCs was possible in all cases.
This study has been registered at the Chinese Clinical Trial Registry (ChiCTR2000037773).Registered 1 September 2020 -Retrospectively registered,https://www.chictr.org.cn/edit.aspx?pid=33441&htm=4.
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
This research was carried out at Beijing Jishuitan Hospital.This work was supported by Beijing LAIR biological laboratory of CYTTEL BIOSCIENCES INC.
Ayixia NAWAN (M.D.) performed the trial and contributed to data collection.ZHENG Shao Qiang(M.D.) contributed to data collection,HE Xi Qiang(M.D.) and WANG Geng (M.D.) contributed to the study design.All authors have read and approved the final manuscript.
#Correspondence should be addressed to WANG Geng,professor,PhD,Tel:86-10-58516907,E-mail:w_geng@163.com
Biographical note of the first author:Ayixia NAWAN,female,born in 1985,PhD Candidate,majoring in blood conservation and bone tumor.
 Biomedical and Environmental Sciences2022年4期
Biomedical and Environmental Sciences2022年4期
- Biomedical and Environmental Sciences的其它文章
- Correction
- Nicotine Weakens the Osteogenic Differentiation and lmmune Regulation Capabilities of Periodontal Ligament Stem Cells*
- Relationship between Road Network Density and Cognitive Function:Results from a Cross-Sectional Study among Adults Aged 60 Years and Older in Liaoning,China*
- Study of Migration and Safety Assessment of Manganese (Mn)from Food Contact Stainless-Steel Products in China*
- N-terminal 5-mer Peptide Analog P165 of Amyloid Precursor Protein Exert Antioxidant,Anti-Inflammatory and Anti-Apoptotic Effects on UVB-Irradiated HaCaT Cells
- Dose-Dependent,Frequency-Dependent,and Cumulative Effects on Cardiomyocyte Injury and Autophagy of 2.856 GHz and 1.5 GHz Microwave in Wistar Rats
