Arthroscopic vs open ankle arthrodesis: A prospective case series with seven years follow-up
Federico Morelli, Giorgio Princi, Matteo Romano Cantagalli, Marco Rossini, Ludovico Caperna, Daniele Mazza,Andrea Ferretti
Federico Morelli, Giorgio Princi, Matteo Romano Cantagalli, Marco Rossini, Ludovico Caperna, Daniele Mazza, Andrea Ferretti, Department of Trauma and Orthopaedics, Sapienza University of Rome, Roma 00189, Italy
Abstract BACKGROUND The osteoarthritis of the ankle, although less common than other joints, is associated with severe functional limitation. Surgical options are ankle arthroscopic debridement, osteotomies, ankle arthrodesis and ankle arthroplasty. Ankle arthroplasty is increasingly used thanks to the new implants design, but ankle arthrodesis still represents the most used technique and it can be performed arthroscopically or with an open procedure.AIM To compare mid-term results of arthroscopic vs open ankle arthrodesis of patients affected by end-stage ankle arthritis.METHODS This study enrolled 23 patients, which underwent ankle arthrodesis. The patients were divided into 2 groups: group A (open procedure; n = 11) and group B (arthroscopic procedure, n = 12), the two groups were homogeneous with regard to age and body mass index (P = 0.347). The American Orthopaedic Foot and Ankle score (AOFAS), Freiburg Ankle score (FAS) and visual analogue scale for pain intensity were evaluated preoperatively, at six months and at final follow-up of 7.6 years in group A and 7.3 years in group B (P = 0.364).RESULTS Patients in the arthroscopic group showed better results at six-month follow-up compared to the open group at the AOFAS (group A, 62.2; group B, 78.5; P < 0.05) and the FAS (group A, 61.1; group B, 70.3; P = 0.015) scores. Pain relief was achieved in both groups at six-month follow-up (group A, 1.4; group B, 0.9; P = 0.162). Both open and arthroscopic groups showed improved clinical outcomes from baseline to final follow-up (P > 0.05). Hospital stay was shorter in group B than in group A (P = 0.001). More complications were reported in the open group than in the arthroscopic group (P = 0.459).CONCLUSION The arthroscopic and the open arthrodesis are valid and safe options for the treatment of ankle arthritis on the basis of clinical outcomes at 7 years follow-up. Moreover, the arthroscopic treatment shows faster improvement at six-month follow-up in comparison with the open group.
Key Words: Ankle; Osteoarthritis; Arthrodesis; Arthroscopy; Arthroplasty; Surgery
INTRODUCTION
End-stage ankle arthritis is a clinical condition associated with pain and severe function limitation. The ankle joint, even though subjected to more weight-bearing force per square centimeter and to injury than any other joint, is relatively less affected by osteoarthritis, up to nine times lower than knee and hip[1]. The most frequent cause of ankle arthritis is post-traumatic, which includes almost 80% of all osteoarthritis of this joint[2-4]; more rarely other clinical diseases as arthropathies, infections, tumors and neuropathic arthropathies are involved. Initial management of ankle arthritis consist of conservative options: first-line consist of weight management, exercise, braces, orthoses, and assistive devices, followed by adjunction of pharmacologic agents (non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug) and intra-articular injection (corticosteroid, hyaluronic acid,etc)[5]. In case of failure of conservative treatment, surgery is indicated. Possible surgical options are ankle arthroscopic debridement, osteotomies, ankle fusion and tibio-talar arthroplasty. Despite the development of new implant designs for ankle replacement that are improving its utilization and outcome, arthrodesis still represents the main surgical method to treat ankle arthritis, offering safe and stable results as regards in pain and function[6-9].
Ankle fusion is indicated for end-stage arthritis, residual joint destruction after infection, avascular talar necrosis, Charcot neuroarthropathy, and total ankle replacement failure[8]. For many years ankle arthrodesis has been considered a reliable procedure and for many authors it is still the reference standard for the treatment of end-stage ankle arthritis[10]. Success rate ranging from 80% to 100% has been reported for isolated tibio-talar fusion with patient satisfaction rates around 80%[11,12].
Since the first description by Schneider[13] in 1983, arthroscopic ankle arthrodesis has seen increase in popularity and utilization because of numerous advantages. Several studies in literature in fact, show reduced postoperative pain and a lower use of painkiller drugs[14,15], as well as decreased morbidity, duration of hospitalization, lower infection rate and more rapid return to daily activities[16,17], preserving a better fusion rate and time to union[18]. Moreover, with arthroscopic procedure the indication for arthrodesis can be extended to patients with high wound complications risk such as diabetes or skin problems.
The purpose of the present study was to compare two cohorts of patients who were managed with either an open or an arthroscopic arthrodesis for the treatment of endstage ankle arthritis: clinical outcome, morbidity and length of hospital stay are reported for both groups.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
This is a comparative case series. Between June 2008 and January 2012, forty patients (40 ankles) with end-stage ankle arthritis that needed ankle fusion surgery, were selected for this prospective study. Institutional review board approval was granted, and informed consent was obtained from all study participants.
Decision on which surgical procedure to be utilized was based on the grade of varus or valgus malalignment of the involved ankle. Therefore patients were divided in two groups: In group A (open procedure), were included patients with end-stage ankle arthritis with severe varus or valgus deformity (≥ 10°); in group B (arthroscopic procedure) those with minor ankle malalignment (< 10°).
Exclusion criteria were the following: diabetes mellitus, Charcot neuroarthropathy, osteomyelitis, previous total ankle arthroplasty, subtalar arthritis requiring fusion at same time of the tibio-talar procedure, neurological diseases.
Following the aforementioned criteria, we enrolled 23 patients (23 ankle) for this study, 11 patients in group A and 12 patients in group B. No significant difference were found between the two groups regarding average age (respectively 67.0 ± 2.6 and 64.6 ± 1.9), body mass index (BMI, 23.6 ± 1.0 and 23.8 ± 1.0), sex (open group shows 8 male/3 female and arthroscopic group 5 male/7 female) and dominant side (8/3 and 9/3). Details of all demographic data are shown in Table 1.
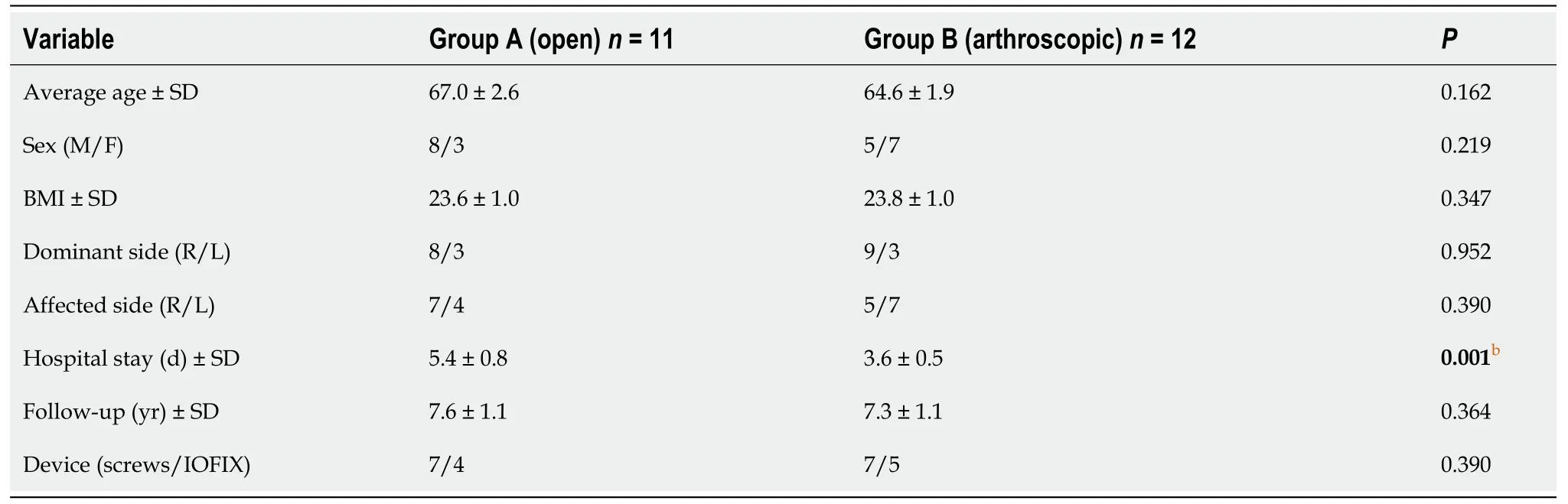
Table 1 Demographic data
Seventeen patients were excluded from further analysis: 7 patients with incomplete clinical follow-up, 7 patients performed triple arthrodesis, 3 patients affected by diabetes mellitus.
All patients had a minimum follow-up of 5 years and mean FU of 7.4 years.
Analyzing the etiology of the ankle arthritis, the two groups showed comparable data. The main cause was post-traumatic, that include 72.7% (8 patients) and 83.3% (10 patients) of the cases respectively in group A and in group B. In the open group, we found out a similar percentage of idiopathic arthritis compared to the arthroscopic group (group A, 9.0%, 1 patient; group B, 8.5%, 1 patient); two patients of group A were affected by Rheumatoid arthritis (18.1%) counter to 1 in the arthroscopic group (8.5%).
Surgical procedures
In the open group the approach entailed a longitudinal lateral incision combined with an ancillary antero-medial incision to obtain a good congruence of bone surfaces. The lateral dissection included osteotomy and removal of the cortical portion of the distal fibula, with subsequent placement of the remaining lateral aspect of the distal fibula and onlay graft before wound closure. All of the residual cartilage and subchondral bone was removed from the distal tibia, talar dome, lateral talus and medial gutter. The deformity was corrected with planar cuts to place the foot and the ankle in a neutral fusion position. The subchondral plate was preserved unless the deformity required planal resection, after which the subchondral plate was fenestrated and drilled, and fish scaled with a curved osteotome. The desired position of fusion was then ensured by means of direct visualization and fluoroscopy, after which the fusion was stabilized in 7 cases with 2 or 3 large diameter (≥ 6.5 mm) cannulated screws, interfragmentary compression screws reinforced with the before mentioned fibular onlay graft. In 4 cases the IOFIX (Extremity Medical, New Jersey, United States) system was used.
Arthroscopic procedure was performed with anteromedial and anterolateral portals using noninvasive distraction. Adequate inflow was achieved with use of a 2.9 mm arthroscope within a 4.0 mm fenestrated cannula or a 4.0 mm arthroscope with a 5.5 mm fenestrated cannula and a pump with 30 mmHg of inflow pressure at the surgeon's discretion. After removal of articular cartilage, the subchondral bone was prepared with a 2 mm drill and osteotome or high-speed burr. Osseous contours were preserved, and fusion sites were stabilized with two or three compression screws (7cases) or with the IOFIX system (4 cases).
Postoperative protocol
The same postoperative protocol was used for both groups. After surgery, patients were managed with ankle immobilization in a below-the-knee plaster cast without weight-bearing for the first six weeks. Progressive weight-bearing was allowed from seventh to twelfth week, when the cast was removed. Anti-thrombotic prophylaxis protocol was performed for 6 wk with enoxaparin 4000 UI/die.
Outcomes evaluation
Clinical evaluation was obtained using the American Orthopaedic Foot and Ankle score (AOFAS)[19], Freiburg Ankle score (FAS)[20] and visual analogue scale (VAS) for pain evaluation that were collected pre-operatively, at six months and at final follow-up.
Demographic data were collected preoperatively. Secondary outcome measures also included length of the hospital stay and radiographic evaluation. Antero-posterior, lateral radiographs and Saltzman view were made at baseline, monthly until bone healing at the arthrodesis site was achieved, at sixth-month and at final follow-up[21-23] (Figures 1 and 2).
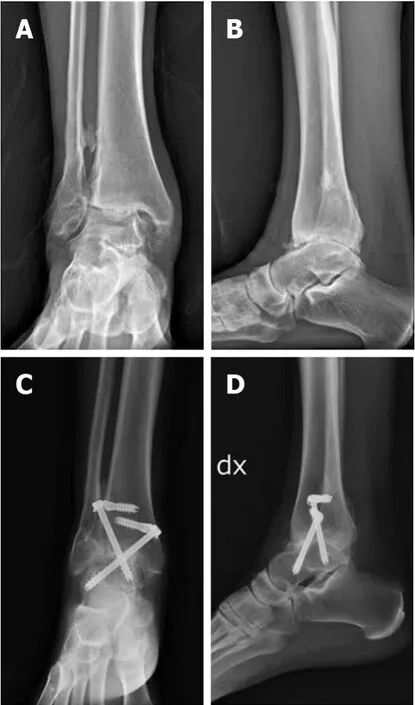
Figure 1 X-rays (IOFIX system).
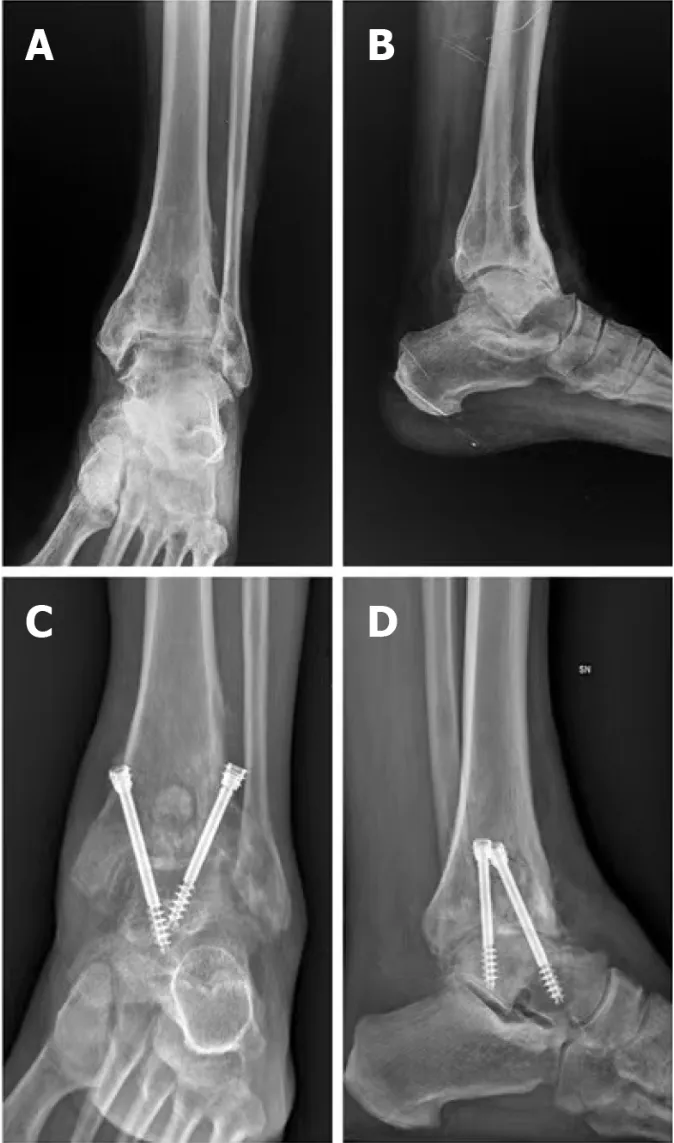
Figure 2 X-rays (screw fixation).
To eliminate interobserver variability, all radiographic measurements were completed by a single independent radiographic reviewer who was blinded to the treatment. The alignment was measured using the ruler application in the Centricity Enterprise Web V2.1 PACS viewing system (GE Healthcare, Chalfont St. Giles, Buckinghamshire, United Kingdom).
Statistical analysis
The data were analysed by using IBM SPSS Statistics for Windows, version 23.0 (IBM Corp., Armonk, N.Y., United States). All the data was first analysed for normality of distribution using the Kolmogorov–Smirnov test. Continuous variables were expressed as mean ± SD, categorical variables displayed as frequencies and the appropriate parametric (studentttest) or non-parametric test (Mann–Whitney U test or χ2test) was used to assess the significance of the differences between groups. All of the intergroup comparisons were two-sided and statistical significance was set atP< 0.05.
RESULTS
The study sample consisted of twenty three patients allocated in two groups: group A (open procedure group;n= 11) and group B (arthroscopic procedure group;n= 12). The groups were homogeneous with regard to age, BMI, dominant side and fixation device (P> 0.05) (Table 1).
Clinical outcomes intergroup comparison at baseline, at six months and final followup are reported in Table 2.
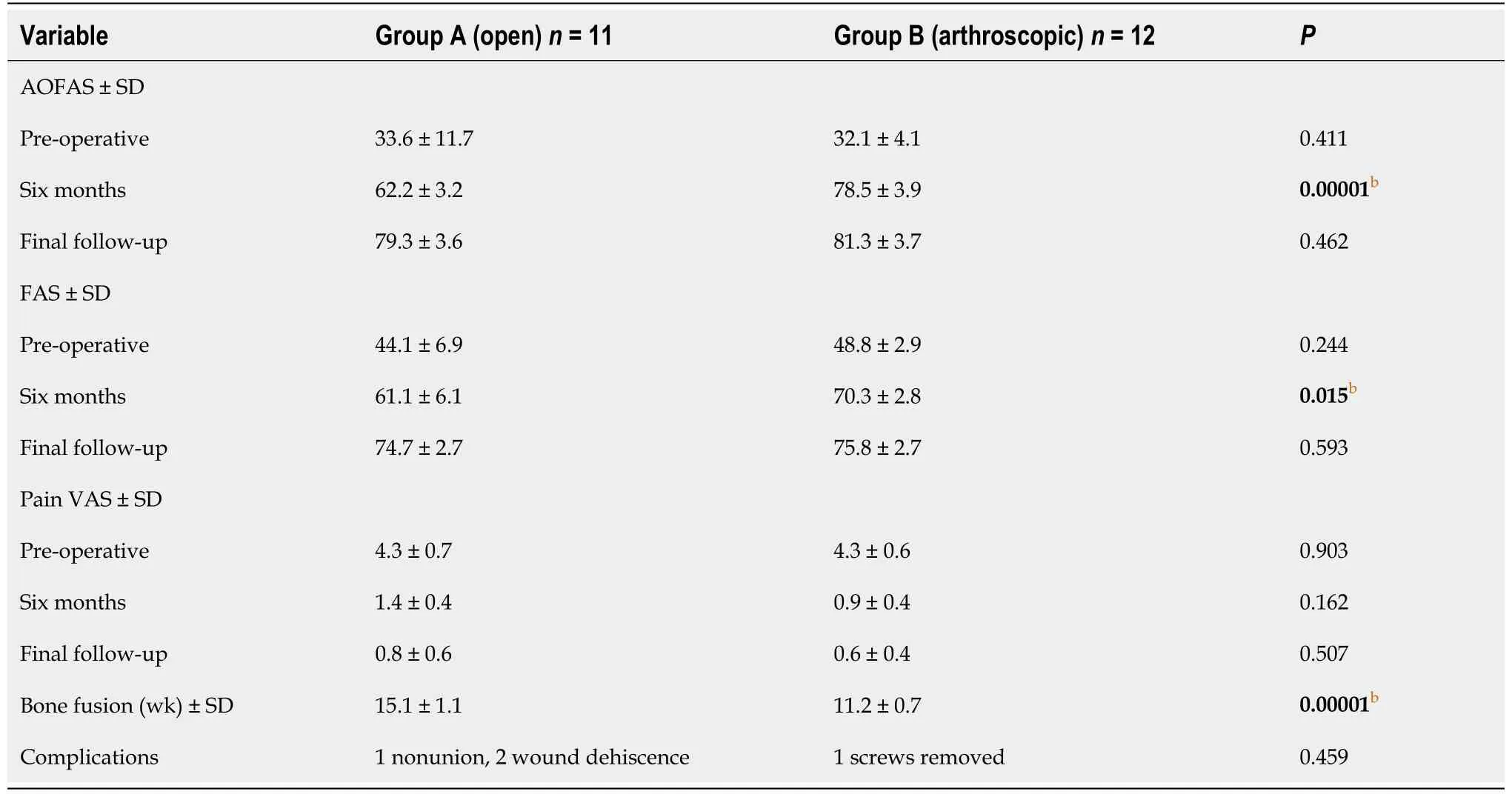
Table 2 Clinical outcomes
Average preoperative AOFAS was 33.6 in group A and 32.1 in group B (P= 0.411); at six-month follow-up results showed significant differences between the two groups, the mean score was 62.2 in group A and 78.5 in group B (P= 0.00001); at final follow up, AOFAS average score was 79.3 in the open group and 81.3 in the arthroscopic group (P= 0.462).
The FAS increased in group A from 44.1 at baseline to 61.1 at six months, and to 74.7 at final follow-up; in group B it increased from 48.8 at baseline, to 70.3 at six months, and to 75.8 at final follow-up. Results were statistically significant at six-month followup (P= 0.015), no statistical significance was found neither at baseline (P= 0.244) nor at final follow-up (P= 0.593).
The preoperative VAS score was 4.3 in group A and 4.3 in group B (P= 0.903); Pain relief was achieved in both groups at six-month follow-up, VAS score was 1.4 in the open group and 0.9 in the arthroscopic group (P= 0.162). The average score at final follow was 0.8 in group A and 0.6 in group B (P= 0.507).
The patients which underwent open surgery stayed in the hospital for an average of 5.4 d, whereas patients treated arthroscopically for 3.6 d (P= 0.001).
Statistical significance was found in bone fusion time, ten patients out of eleven in group A achieved satisfactory consolidation in 15.1 wk at X-ray evaluation with a union rate of 90.9%. All patients in group B (100%) showed good consolidation at 11.2 wk (P= 0.00001).
One patient in group A underwent revision surgery for symptomatic nonunion within twenty-four months from first surgery. In one patient of group B screws were removed three years after surgery due to pain and discomfort. We reported two cases of wound dehiscence in the open group that were successfully treated with medical therapy.
DISCUSSION
Ankle arthrodesis is considered a safe option for surgical management of end-stage ankle arthritis with good clinical results even compared with total ankle arthroplasty[5]. To authors’ knowledge there were few clinical studies comparing mid-term results between arthroscopic ankle arthrodesis (AAA) and open ankle arthrodesis (OAA); our average follow-up of 7.4 years can be considered a long-term follow-up compared with literature.
Clinical results reported by other authors are good both for AAA and OAA with slightly better results for OAA although often not statistically significant[9]. Many authors considered it as relative contraindication for arthroscopic ankle arthrodesis a large coronal plane deformity)[15,24]. Townshendet al[25], however, achieved technical success for coronal plane deformities up to 30° with arthroscopy and up to 36° for open arthrodesis. They also evaluated the results of open and arthroscopic ankle arthrodesis in a comparative case series with two years follow-up. They reported significantly greater improvement in the ankle osteoarthritis scale at one and two years and shorter hospital stay in the arthroscopic group. Those data are partially congruent to our results. We found better clinical results for arthroscopic procedure at six months, but similar results at final follow-up between two groups.
Wooet al[26] demonstrated that patients who underwent arthroscopic ankle arthrodesis reported a higher SF-36 score on physical functioning at 6 mo and higher AOFAS at 24-mo, the analysis of VAS scores demonstrated significant less pain during the perioperative period compared with the open group and no significant difference among the two groups at 6 and 24 mo. In this study, it is shown an improvement at 6 mo at the AOFAS (P= 0.00001) and at the FAS (P= 0.015) and at final follow-up at the AOFAS (P= 0.462) and at the FAS (P= 0.593); the VAS showed that pain relief was achieved in both groups at six-month (P= 0.162) and at final follow-up (P= 0.507).
A systematic review by Parket al[27] reported that the mean AOFAS score was statistically significant greater in the arthroscopic group at 6 and 12 mo, and a greater improvement in the AOS scores at 1 and 2 years in the arthroscopic group with statistical significance. The SF-36 mental component summary the scores at 1 and 2 years were without a statistical difference greater in the arthroscopic group, The SF-36 physical component summary scores were higher in the arthroscopic group at 1 and 2 years, but the difference was only statistically significant at 1 year.
This study showed that complication rates were overall higher in the group A (27%; 1 revision and 2 wound dehiscence) than in the group B (8%; 1 screws removed) in accordance with the systematic review by Parket al[27] in which the most common reoperation was screw removal (open group, 5.1%; arthroscopic group, 9.5%) and the second most common was re-arthrodesis (open group, 2.5%; arthroscopic group, 4%). Another study by Wooet al[26] did not reported postoperative complications in the arthroscopic group, but complication rate was 20% in the open group, 16% of these required revision surgery. Quayleet al[18] identified that open ankle arthrodesis and a low BMI were the strongest predictors of developing a complication.
Ogilvie-Harriset al[15] reported prospectively collected data on nineteen arthroscopic arthrodesis and demonstrated an average length of stay of only one day. Zvijacet al[28] reported an average duration of hospitalization of 3 d for open arthrodesis and 1 d for arthroscopic procedure. Similarly, in our results the arthroscopic group showed shorter hospitalization time (P= 0.001).
Time of consolidation of the arthrodesis is a key factor for the success of this surgical technique. Myersonet al[16] and other authors reported that traditional open arthrodesis requires approximately 14 wk to achieve satisfactory consolidation[9,18,26,27,29]. On the other hand, regarding arthroscopic procedure, there was no consensus on the fusion timing; Collmanet al[30] reported that arthroscopic procedures required an average 47 days to achieve bone fusion, while Glicket al[31] reported an average time to fusion of 9 wk. A systematic review and meta-analysis by Honnenahalli Chandrappaet al[32] showed that the fusion rate was significantly lower in the open group than in the arthroscopic group. Moreover, it has been shown by Collmanet al[30] and Winsonet al[33] that arthroscopic ankle arthrodesis achieves high union rates, facilitates short time to union, and permits rapid patient mobility. In this study, the open group required approximately 15 wk to achieve satisfactory consolidation of the fusion at X-ray evaluation with a rate of 90.9% and the arthroscopic group required approximately 11 wk, with a fusion rate of 100%. The pre-operative hindfoot alignment and the shorter time to fusion in the arthroscopic group, could explain the better clinical results compared with open procedure. In this study, the improvement in clinical outcomes was greater and more rapid in the arthroscopic group than in the open treatment group, with maximum improvement achieved at six months followup. The arthroscopic arthrodesis is less invasive than open procedure and there is less soft-tissue disruption associated which may reduce the degree of permanent functional impairment of joints and soft tissues adjacent to the arthrodesis site. Furthermore, It appears to allow more rapid activation of the bone-healing cascade, leading to more rapid bone healing and fast functional improvements[25].
The present study is limited by a lack of randomization, a large number of patients lost at final follow-up, and a small sample. Patients were not consecutive, and, in the early period, an open technique was preferred for some of the more difficult cases at the center at which the arthroscopic procedures were performed. Secondly, we did not evaluate the postoperative alignment, furthermore there was no intermediate followup between six-month and final follow up.
The main finding of the present study was that ankle arthrodesis is a safe and effective procedure to treat end-stage arthritis with long-term good clinical outcomes, but arthroscopic procedures had a more rapid improvement, with maximum achieved by six months.
CONCLUSION
In this comparative case series, it has been shown that both open and arthroscopic ankle arthrodesis were associated with good clinical outcomes at a long term followup on the basis of validated outcome measures. The arthroscopic treatment group showed a more rapid improvement of clinical scores at six months in comparison with the open group, beyond that a shorter hospital stay and a better union rate.
ARTICLE HIGHLIGHTS
Research background
Ankle arthrodesis is a commonly used treatment for end stage ankle arthrosis. There are two different surgical approaches: open arthrodesis and arthroscopic arthrodesis.
Research motivation
To compare the results of arthroscopic arthrodesis vs open arthrodesis and evaluate the different efficacy of these surgical approaches.
Research objectives
The aim of the study was to analyze the medium and long term results of the two surgical treatments using the clinical evaluation scales for the ankle.
Research methods
Patients treated with open and arthroscopic technique were divided into two groups.To evaluate the surgical treatments we used The American Orthopaedic Foot and Ankle score (AOFAS), Freiburg Ankle score (FAS) and visual analogue scale for pain intensity. This study enrolled 23 patients which were evaluated preoperatively, at six months and at final follow-up (7 years).
Research results
Arthroscopic treatment shows better results at six months with the AOFAS and FAS.The decrease of pain at six months is present in both groups. At the final follow up both treatments show good clinical results. To be noted is the data relating to hospital stay, which appears to be lower for arthroscopic treatment.
Research conclusions
There are no differences between open and arthroscopic treatments at clinical results at a medium to long term follow-up, and in both cases it was possible to achieve excellent results.
Research perspectives
In perspective, despite being a medium-long term follow up, it is possible to reevaluate the same court of patients at a greater distance to verify the stability of these results.
 World Journal of Orthopedics2021年12期
World Journal of Orthopedics2021年12期
- World Journal of Orthopedics的其它文章
- Intraosseous device for arthrodesis in foot and ankle surgery:Review of the literature and biomechanical properties
- Decision aids can decrease decisional conflict in patients with hip or knee osteoarthritis: Randomized controlled trial
- Surgical treatment outcome of painful traumatic neuroma of the infrapatellar branch of the saphenous nerve during total knee arthroplasty
- Rates of readmission and reoperation after operative management of midshaft clavicle fractures in adolescents
- Role of biomechanical assessment in rotator cuff tear repair:Arthroscopic vs mini-open approach
- Assessing the accuracy of arthroscopic and open measurements of the size of rotator cuff tears: A simulation-based study
