ON SCHWARZ-PICK TYPE INEQUALITY FOR MAPPINGS SATISFYING POISSON DIFFERENTIAL INEQUALITY?
(鐘德光)
Department of Applied Statistics,Guangdong University of Finance,Guangzhou 510521,China
E-mail:huachengzhon@163.com
Fanning MENG(孟凡寧) Wenjun YUAN(袁文俊)?
School of Mathematics and Information Science,Guangzhou University,Guangzhou 510006,China
E-mail:mfnfdbx@163.com;wjyuan1957@126.com
Abstract Let f be a twice continuously differentiable self-mapping of a unit disk satisfying Poisson differential inequality|Δf(z)|≤B·|Df(z)|2 for some B>0 and f(0)=0.In this note,we show that f does not always satisfy the Schwarz-Pick type inequality where C(B)is a constant depending only on B.Moreover,a more general Schwarz-Pick type inequality for mapping that satisfies general Poisson differential inequality is established under certain conditions.
Key words Schwarz-Pick inequality;Poisson differential inequality;hyperbolically Lipschitz continuity
1 Introduction and Main Results
Let D be an open unit disk in the complex plane C and denote T=?D.For a domain ??C,let Cn(?)be the set of all complex-valued n-times of continuously differentiable functions from? into C.In particular,let C(?):=C0(?)be the set of all continuous functions in ?.
A real-valued function u,defined in an open subset ? of the complex plane C,is real harmonic if it is twice continuously differentiable in ? and satisfies Laplace’s equation
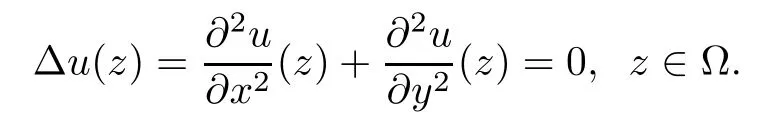
A complex-valued function ω=u+iv is harmonic if both u and v are real harmonic.We refer the readers to[7]for more properties of harmonic mappings in the plane.
Let P be the Poisson kernel,that is,the function
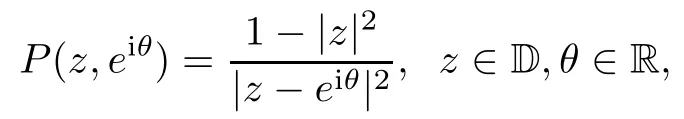
and let G be the Green function of the unit disk,that is,the function
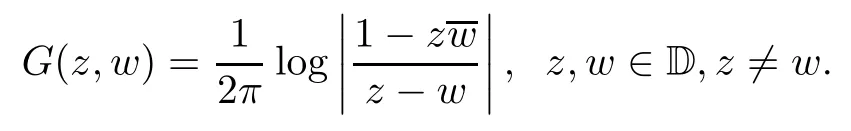
Let f:T→C be a bounded integrable function on the unit circle T and let g:D→C be continuous.The solution of Poisson’s equation Δω=g in D satisfying the boundary condition ω|T=f∈L1(T)is given by
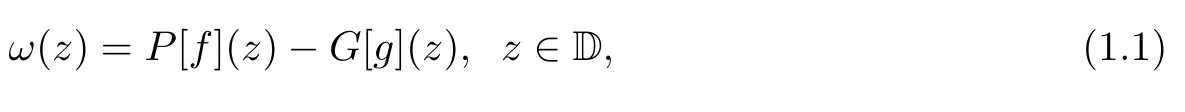
where
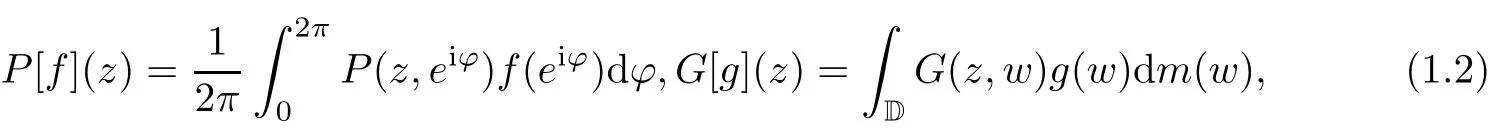
where dm denotes the Lebesgue measure in the plane.It was proved in[5]that for any g∈C(D),the function G:=G[g]satisfies the inequality
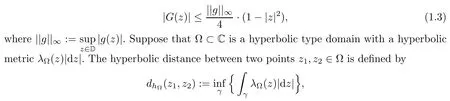
where the infimum is taken over all rectifiable curves γ in ? connected z1and z2.It is well known that when D=D,
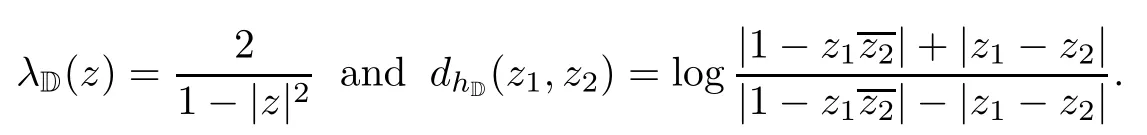
A function f from a hyperbolic type domain ? into a hyperbolic type domain ?′is said to be hyperbolically Lipschitz continuous if there exists a constant L>0 such that the inequality
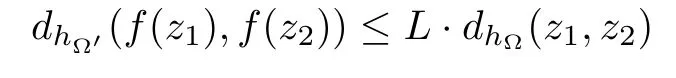
holds for any z1,z2∈?.
Suppose that ? and ?′are two simply connected domains of hyperbolic type in C with hyperbolic metrics λ?(z)|dz|and λ?′(w)|dw|,respectively.The classical Schwarz-Pick lemma states that if f is holomorphic from ? into ?′,then

Moreover,equality occurs in(1.4)when f is conformal from ? onto ?′.In particular,if ?=?′=D,then inequality(1.4)becomes
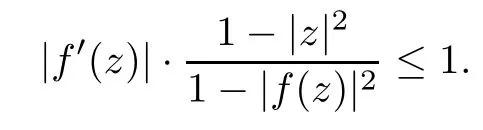
The Schwarz-Picklemma(1.4)has lots of generalizations.For example,Ahlfors[1]extended it to holomorphic mappings from a unit disk into a Riemann surface equipped with a Riemann metric whose Gaussian curvature is less than or equal to?1.In[19],Yau generalized it to holomorphic mappings between a complete K?hler manifold with Ricci curvature bounded from below by a constant and a Hermitian manifold with holomorphic bisectional curvature bounded from above by a negative constant.Osserman,in[16],obtained a general finite shrinking lemma from a geodesic disk of radius ρ1with respect to a metricwhich is circularly symmetric into a geodesic disk on a surface.We refer readers to the multipoint version[3]and the higher-order derivatives version[6,14]of the Schwarz-Pick lemma and references therein.
In this paper,we are particularly interested in the Schwarz-Pick type inequality for mappings satisfying Poisson differential inequality(1.9).Let f be a quasiconformal self-mapping of a unit disk satisfying the Poisson differential equation

where|Df(z)|=|fz(z)|+.In[12],Kalaj obtained the following result:
Lemma 1.1([12,Lemma 2.3]) Suppose that f is a K-quasiconformal self-mapping of D satisfying Poisson differential equation(1.5)and f(0)=0.Then there exists C(B,K)such that

This lemma can be viewed as a kind of Schwarz-Picktype inequality for the K-quasiconformal self-mapping of D satisfying Poisson differential inequality(1.5).Now,let F(D,B)={f:D→D:f(0)=0,|Δf|≤B·|Df|2,f∈C2}.We can derive,by using the Schwarz lemma for harmonic mapping[9],the Schwarz-Pick type inequality

for the class F(D,0).In[12],Kalaj asked if the quasiconformality assumption is important for Lemma 1.1.In other words,does(1.7)hold for some constant C=C(B)instead of π/2 for the class F(D,B)?We summarize this as follows:
Question 1.2Is the Schwarz-Pick type inequality

always valid for mappings in the class F(D,B)?
The first aim of this paper is to give a negative answer to the question.We have
Theorem 1.3The mappings in the class F(D,B)do not always enjoy Schwarz-Pick type inequality(1.8).
Although the answer to Question 1.2 is negative,one can establish a Schwarz-Pick type inequality(1.8)for twice continuously differentiable self-mappings of a unit disk satisfying Poisson differential inequality(1.8)under certain conditions.For example,in[15],a Schwarz-Pick type inequality(1.8)for(K,K′)–quasiconformal self-mappings of a unit disk satisfying the Poisson differential inequality(1.8)was obtained.However,those mappings discussed in Lemma 1.1 and[15,Lemma 2.1]require quasiconformality.Here,we establish one kind of inequality(1.8)for those mappings satisfying(1.5)under certain conditions(with no requirement of quasiconformality).Actually,our result also works with twice continuously differentiable selfmappings of a unit disk satisfying the following more general Poisson differential inequality:

It is noted that both harmonic mappings and holomorphic mappings are contained in the class of functions satisfying inequality(1.9).We refer the reader to the research works on those mappings for two dimensions[4,8]and higher dimensions[11].Next,we will state our result on Schwarz-Pick type inequality(1.8)for twice continuously differentiable self-mappings of a unit disk satisfying the general Poisson differential inequality(1.9)under certain conditions.Throughout the rest of this paper,L(a,b,K)always refers to the constant in Lemma 2.5.According to[8],one can give the explicit expression of L(a,b,K)when the values of a,b are small enough.
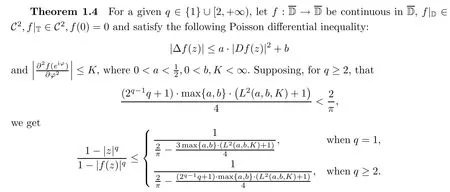
Under which conditions,the subject of a harmonic self-mapping of the unit disk that has Lipschitz continuity with respect to a given metric has attracted the attention of many researchers;see the papers[17,20]and the references cited therein.A direct and interesting corollary of Theorem 1.4 is the property of hyperbolically Lipschitz continuity for those mappings mentioned in Theorem 1.4.
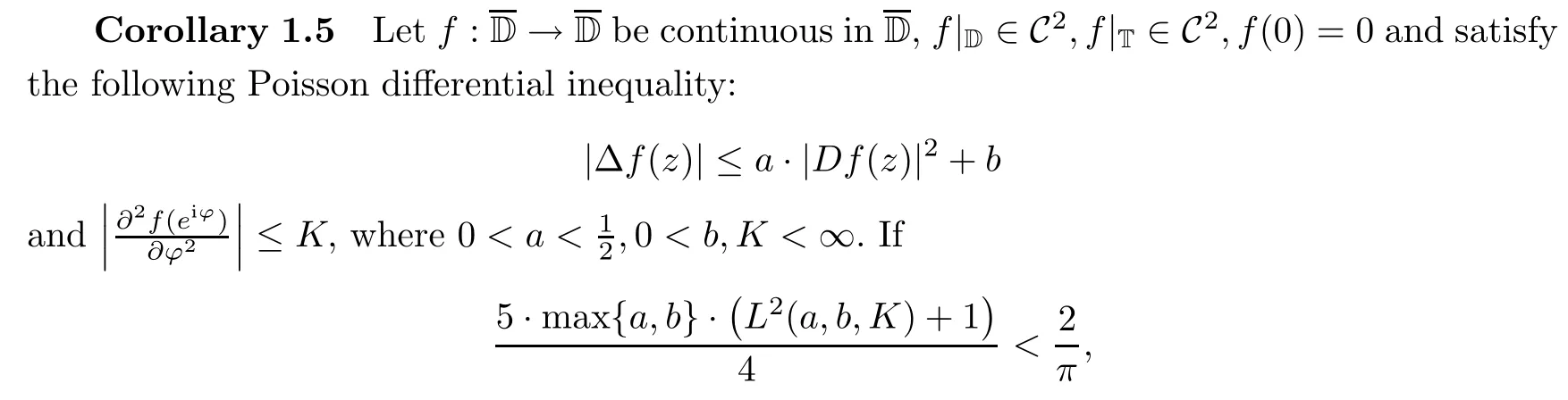
then f is a hyperbolically Lipschitz continuity;that is,the inequality
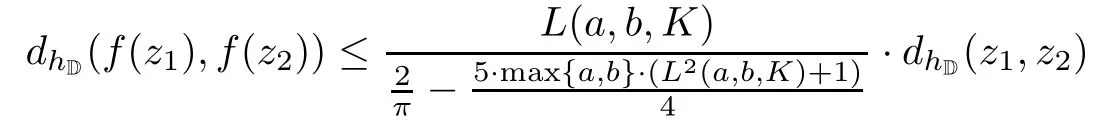
holds for any z1,z2∈D.
The organization of the rest of this paper is as follows:in Section 2 we make some preparations which will be used in the proof of Theorems 1.2 and 1.3.The proof of Theorem 1.2 will be presented in Section 3.The proof of Theorem 1.3 is given in Section 4.The last section is devoted to the proof of Corollary 1.4.
2 Some Preparations
In[13],Kalaj and Zhu obtained a Schwarz-Pick type inequality for the harmonic selfmapping f of D with f(0)=0.It is read as follows:
Lemma 2.1([13,Proposition 3.6]) If f is a harmonic self-mapping of D with f(0)=0,then the inequality

holds for every z∈D and q>0.In particular,we have,for q=2,that

Next,we will establish a Schwarz-Pick type inequality(2.1)of the harmonic self-mapping of a unit disk with the removed of the assumption that f(0)=0.The result is as follows:
Lemma 2.2Let f be a harmonic self-mapping of D satisfying|f(0)|<2/π.Then for any q≥1,the inequality

holds for every z∈D.
ProofApparently,inequality(2.3)is true when z=0.Hence,we assume that z/=0.By a generalized Schwarz type inequality for harmonic self-mapping[10,18]of the unit disk,we get
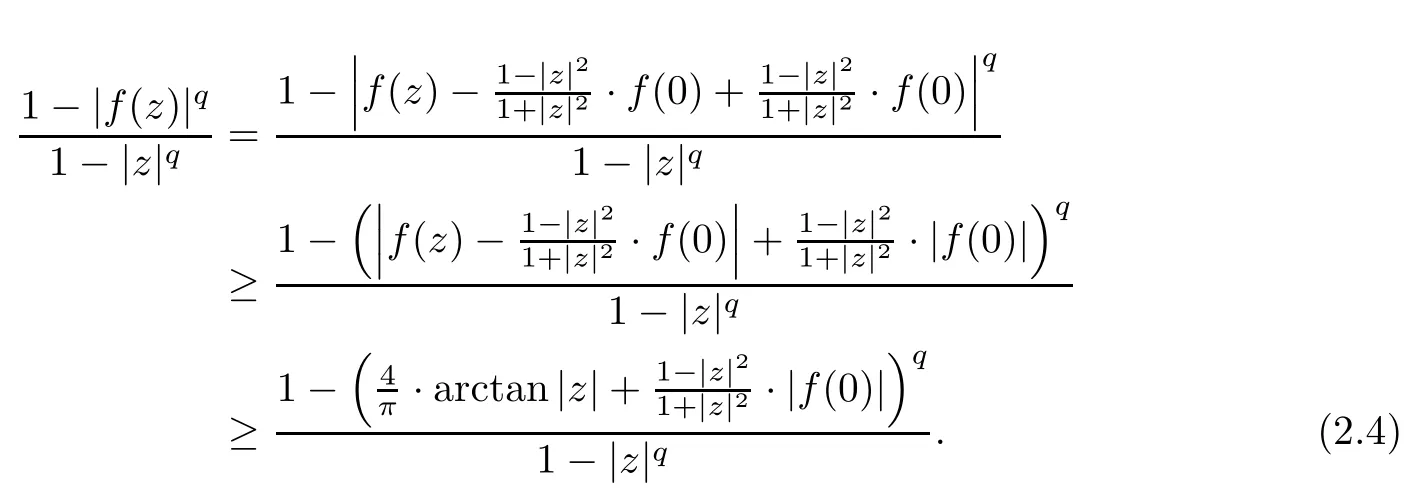
Next,we will use L’Hospital’s rules for monotonicity[2]to decide the monotonicity of the function
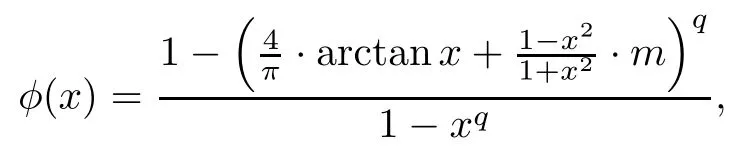
where x∈(0,1),m∈[0,2/π).To do this,we introduce the function
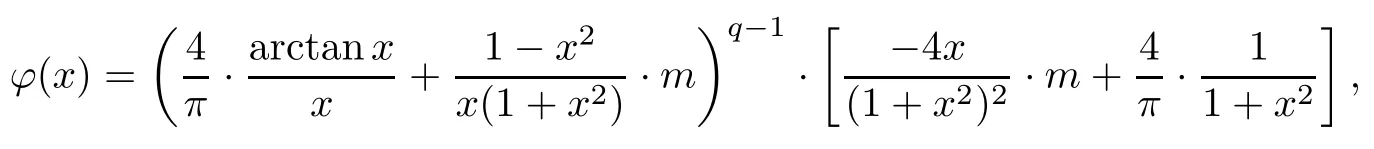
where x∈(0,1),m∈[0,2/π).Then we have

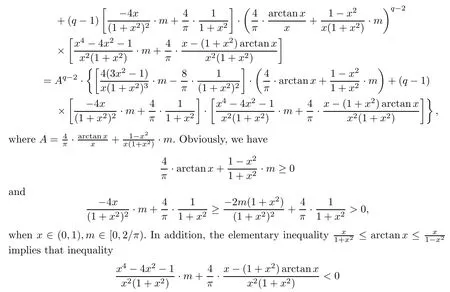
holds for any x∈(0,1),m∈[0,2/π).Finally,we verify that
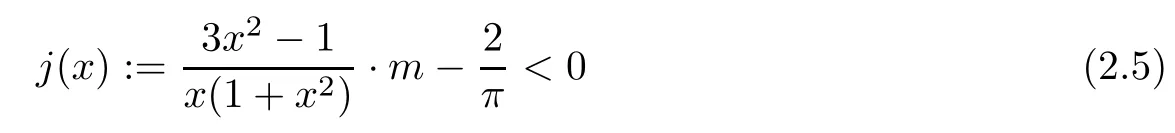
for any x∈(0,1),m∈[0,2/π).Since

ProofLet k(y)=(y+ε)q?yq,y∈[0,1).Then we have k′(y)=q[(y+ε)q?1?yq?1]≥0.Hence,k is monotonic increasing when 0≤y<1,0≤ε<1,q>1,which implies that
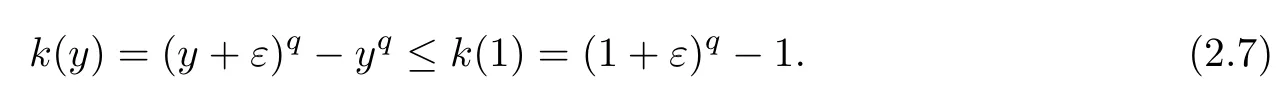
Let λ(ε)=(1+ε)q?2q?1qε?1.Then,λ′(ε)=q[(1+ε)q?1?2q?1]≤0.Therefore,λ(ε)≤λ(0)=0;namely,for any 0≤ε<1,it holds that(1+ε)q?1≤2q?1qε.Combining this inequality with(2.7),we get the desired inequality. □
Lemma 2.4For any t∈[0,1),we have

ProofConsidering the function φ(t)=·arctant,t∈[0,1)we get
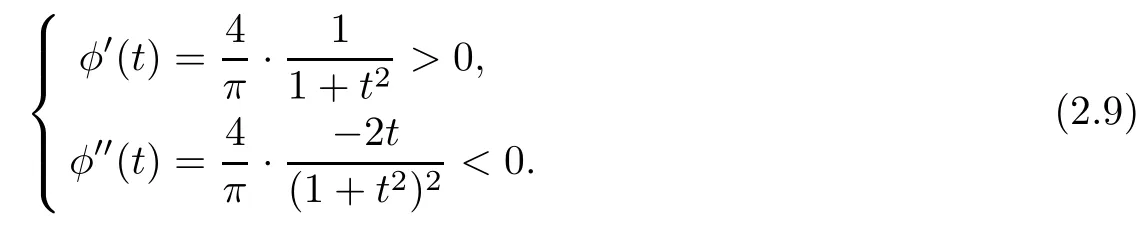
This shows that φ is monotonically increasing and concave in[0,1),which implies that the tangent of φ at the point(1,1)lies above the image of φ.Hence,the desired inequality(2.8)follows. □
The following result,obtained by Heinz-Bernstein[4,8],is crucial for us to get a Schwarz-Pick type inequality for mappings satisfying the Poisson differential inequality(1.9)under certain conditions:
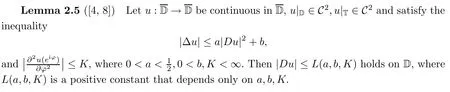
3 Proof of Theorem 1.2

This finishes the proof.
4 Proof of Theorem 1.3
By Lemma 2.5,there is constant L(a,b,K)>0 such that|Df|≤L(a,b,K)holds for any z∈D.Now,let

where h(z)=l(z)(|Df(z)|2+1)and||l||∞≤max{a,b};one can simply define l(z):=Δf(z)·(|Df(z)|2+1)?1,z∈D.By assumption,we have h∈C(D).Hence,we get that||h||∞≤max{a,b}·(L2(a,b,K)+1),by Lemma 2.5.Now,using formula(1.1),we have

where f|T:=k.For the case of q=1,by using formula(4.2)and Lemma 2.4,we get
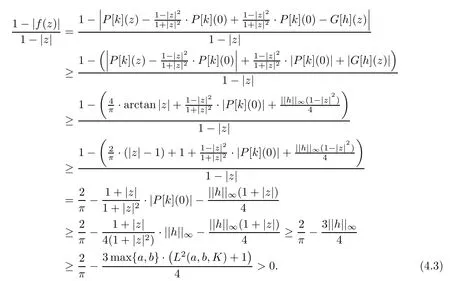
For the case of q≥2,since f(0)=0 and
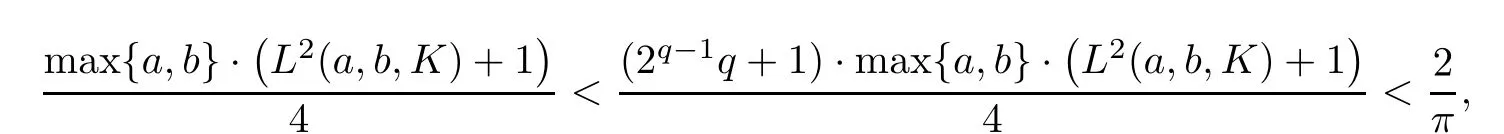
we get(by using estimate(1.3))that
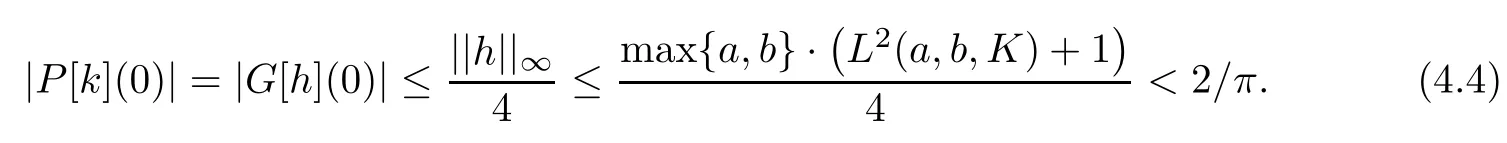
Hence,P[k]is a harmonic self-mapping of D satisfying|P[k](0)|<2/π.By virtue of Lemma 2.2,we get that
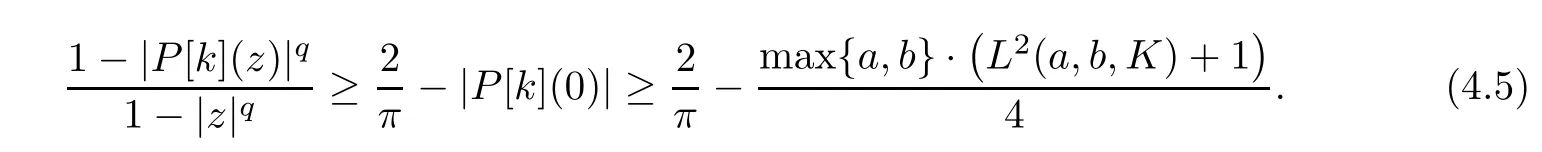
Now,using(4.5)and Lemma 2.3,we get that
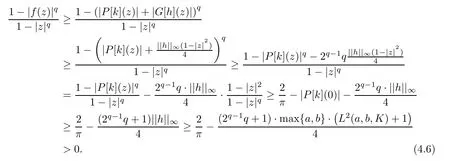
Hence,the proof of Theorem 1.3 is complete.
5 Proof of Corollary 1.4
This completes the proof.
AcknowledgementsThe second and third authors would like to express their hearty thanks to the Chern Institute of Mathematics,which provided them with a very comfortable research environment.Also,the authors would like to express their sincere thanks to the referees for their great efforts in improving this paper.
 Acta Mathematica Scientia(English Series)2021年3期
Acta Mathematica Scientia(English Series)2021年3期
- Acta Mathematica Scientia(English Series)的其它文章
- ANALYSIS OF THE GENOMIC DISTANCE BETWEEN BAT CORONAVIRUS RATG13 AND SARS-COV-2 REVEALS MULTIPLE ORIGINS OF COVID-19?
- DYNAMICS ANALYSIS OF A DELAYED HIV INFECTION MODEL WITH CTL IMMUNE RESPONSE AND ANTIBODY IMMUNE RESPONSE?
- BILINEAR SPECTRAL MULTIPLIERS ON HEISENBERG GROUPS?
- EXISTENCE AND UNIQUENESS OF THE GLOBAL L1 SOLUTION OF THE EULER EQUATIONS FOR CHAPLYGIN GAS?
- UNIQUENESS OF THE INVERSE TRANSMISSION SCATTERING WITH A CONDUCTIVE BOUNDARY CONDITION?
- THE FIELD ALGEBRA IN HOPF SPIN MODELS DETERMINED BY A HOPF ?-SUBALGEBRA AND ITS SYMMETRIC STRUCTURE?
