Empyema associated with vegetable foreign body aspiration
Ling Shen
Department of Respiratory Medicine, Hangzhou First People’s Hospital, Zhejiang University School of Medicine,Hangzhou 310000, China
Dear editor,
Empyema caused by foreign body aspiration in adults is extremely rare, and relevant cases have been rarely reported.[1-4]Certain types of foreign bodies, such as vegetables, are not visible on computed tomography(CT) scans, and this can lead to misdiagnosis. Herein,we described the successful treatment of an adult patient who presented with severe empyema following occult vegetable aspiration.
CASE
A 58-year-old male patient presented with a fivemonth history of dry cough, a two-week history of fever,and a one-week history of severe pain in the right side of the chest. He was a smoker, without a recent history of foreign travel or exposure to chemical fumes. He had no prior medical history and was not taking any medication.He was admitted to a local hospital two days after developing a fever and was administered sulperazone (2 g,every 12 hours). However, the symptoms of cough and fever persisted, and he later developed right chest pain.Therefore, he was transferred to our hospital.
On admission, the patient’s vital signs were recorded(temperature 39 °C, respiratory rate 22 breaths/minute,pulse rate 102 beats/minute, blood pressure 110/72 mmHg[1 mmHg=0.133 kPa]). Physical examination revealed diminished breath sounds on the right side of the chest without any murmur. The other systemic examination f indings were unremarkable.
A chest CT scan showed multiple encapsulated pleural effusions on the right side and consolidation in the right lower lobe (Figure 1). Laboratory test results revealed: white blood cell counts 11.5×109/L (with an 89.2% neutrophil ratio), C-reactive protein 92 mg/L (normal range 0-10 mg/L), and erythrocyte sedimentation rate 44 mm/hour (normal range 0-15 mm/hour).
After admission, the therapeutic thoracentesis was performed. The aspirated effusion appeared as cloudy and straw-colored fluid with a consistency similar to that of pus, and the total nucleated cell counts were 860×106/L. The levels of lactic dehydrogenase (LDH) and adenosine deaminase (ADA) were 7,590 U/L and 175 U/L,respectively, and both of them were markedly elevated. The concentration of glucose was extremely low (0.36 mmol/L).Evaluation of tumor markers in the effusion f luid indicated an elevated level of carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA, 35 μg/L, normal range <5 μg/L).
Based on these f indings, a diagnosis of empyema was considered. Samples of the pleural effusion, blood, and sputum were sent for aerobic and anaerobic cultures, and empirical treatment with meropenem (1 g per 8 hours)was initiated. Two days after admission, the patient was stabilized, and the symptoms were alleviated. The results of Gram staining and the blood and effusion culture tests were all negative. The concentrations of serum tumor markers, including CEA, carbohydrate antigen 199(CA199), and neuron-specif ic enolase (NSE), were within the normal range, whereas that of immunoglobulin E was 1,116×103U/L (normal range [1-110]×103U/L).
Bronchoscopy revealed a globular endobronchial lesion obstructing the right lower lobe bronchus (F igure 2A).Histopathology of the biopsied lesion specimens revealed an intense, acute inf lammation with granulation tissue reaction,inf lammatory exudates, and amorphous material. Th e patient underwent three endoscopic procedures to remove the granulation tissue. Eventually, a piece of pepper was found(Figure 2B). When asked about the foreign body aspiration,the patient stated that he often ate pepper, and he might have choked while eating pepper five months ago. However, he had never consulted a doctor for foreign body aspiration.The follow-up chest CT scan showed a signif icant resolution of the pneumonic process and a near-complete absorption of the pleural effusion after four weeks of treatment with antibiotics.
DISCUSSION
Cases of airway foreign bodies (AFBs) are relatively rare in adults; the prevalence of AFBs has been estimated as 0.25% of bronchoscopies.[5]Most patients with AFBs have significant risk factors, including neurological and neuromuscular diseases, drug and alcohol abuse, or a history of head trauma. Swallowing difficulties and other gastrointestinal tract disorders also increase the risk of AFBs. However, the patient described herein did not have these risk factors and he had not undergone any obvious aspiration procedure; thus, pneumonia and empyema were suspected before an accurate diagnosis was made.
The sequelae of aspiration may be immediate or delayed. Some studies have reported delays in diagnoses of AFBs, ranging from several days to 10 years.[6-8]In a study by Dong et al,[7]more than half of the cases had diagnostic delays of more than one month. These patients were usually hospitalized because of complications of long-term retention of AFBs, such as recurrent pneumonia. In a large sample study of AFBs conducted in adults, the most frequently reported complications were granulation formation(76.5%), obstructive pneumonia (22.0%), bleeding (14.5%),atelectasis (10.0%), and endobronchial stenotic scarring(8.0%).[7]Radiographic findings of atelectasis, pneumonia,air trapping, and an irregular radiopaque shadow are indicative of an AFB. However, 10%-20% of patients with special cases of AFBs, such as those with aspiration of vegetable matter, had normal radiographs.[9-11]In our case,the aspirated pepper was not detected on chest CT due to its small size and low density.
Although rare, post-obstructive pneumonitis, as a consequence of AFBs, with secondary empyema has been reported.[1-4]The mechanisms of non-iatrogenic AFB-induced empyema are poorly understood; one main mechanism is post-obstructive pneumonia caused by foreign body aspiration. Vegetable foreign bodies,such as pepper and peanuts, are most likely to cause granulation. We presumed that the aspiration of the pepper by our patient induced an inf lammatory response,followed by the formation of gran ulation tissue that lasted 4-5 months. Although ADA and CEA are often elevated in patients with empyema, it is necessary to distinguish it from tuberculosis-related pleural effusion(TBPE) and malignant pleural effusions (MP E).According to Saraya et al,[12]a pleural LDH to ADA ratio greater than 15.5 is indicative of parapneumonic effusion(PPE) or empyema rather than TBPE or MPE. The ratio of pleural LDH to ADA in our case was approximately 43, and we preferred a diagnosis of empyema over TBPE.
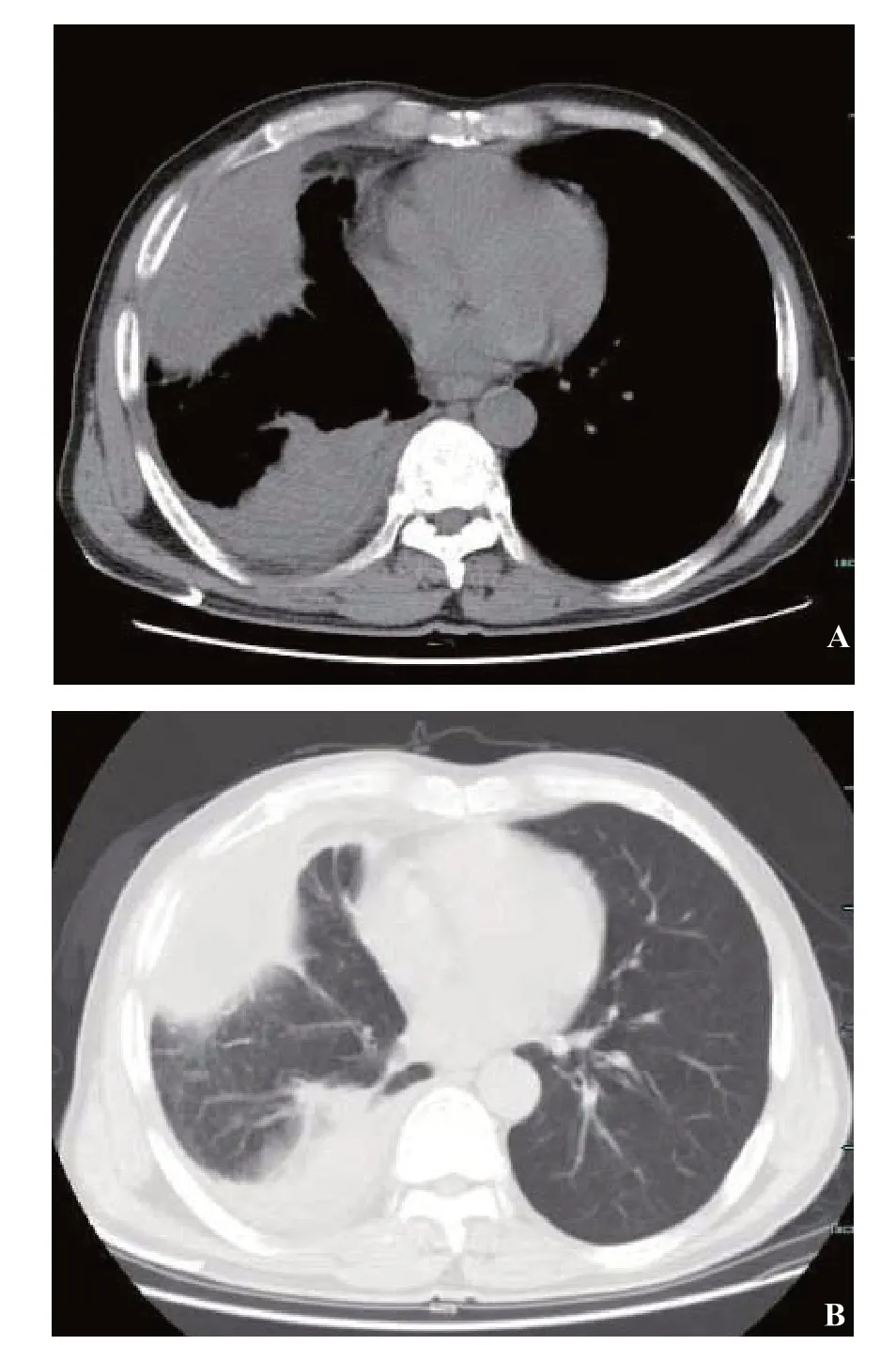
Figure 1. Chest computed tomography (CT) image acquired after admission. Mediastinal window (A) and lung window (B) demonstrating the encapsulated pleural effusion and right lower lobe consolidation with an obstructing lesion in the right lower lobe bronchus.
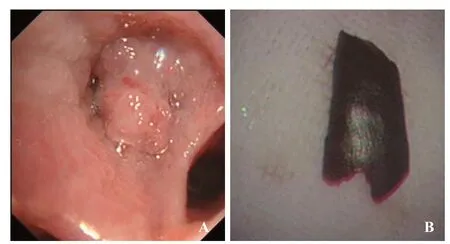
Figure 2. Bronchoscopic images. A: an irregular mass obstructing the right lower lobe bronchus; B: the aspirated pepper removed from the bronchus.
Treatment typically involves the removal of the aspirated foreign body by f lexible or rigid bronchoscopy.In most cases, foreign bodies are easily detected and removed by bronchoscopy. However, in a few cases of AFBs lodged in the distal bronchus, the granulation formation may be misdiagnosed as a tumor[13]or aspergilloma.[14]Some cases of AFB have been diagnosed and removed through surgery.[11]In our case, the first two bronchoscopies did not detect the bronchial foreign body. This indicates that in cases of suspected bronchial foreign bodies, the removal of granulation tissue is necessary to expose them in the deeper tissues.
CONCLUSIONS
Empyema secondary to foreign body aspiration in adults is uncommon. Prolonged misdiagnosis can lead to serious complications. Our case was successfully diagnosed and treated using fiberoptic bronchoscopy.For refractory pneumonia and empyema, foreign body aspiration should be considered even if there is no obvious history of aspiration. A detailed medical history should be obtained and a bronchoscopy should be performed as soon as possible.
Funding:This work was supported by a grant from Health Commission of Zhejiang Province (2020361927).
Ethical approval:Not needed.
Conflicts of interests:The author declares that he has no competing interests.
Contributors:LS wrote the f irst draft of this paper, and approved the f inal version.
 World journal of emergency medicine2021年2期
World journal of emergency medicine2021年2期
- World journal of emergency medicine的其它文章
- World Journal of Emergency Medicine
- Overlapping public health crises during the coronavirus disease pandemic
- Comparison of intraosseous access and central venous catheterization in Chinese adult emergency patients: A prospective, multicenter, and randomized study
- A red herring: An unusual case of pneumothorax
- A case of a successful post-transcatheter aortic valve replacement His bundle pacing
- Detection of adrenal mass during an educational point-of-care ultrasound in the emergency department
