Endoscopic-assisted lCG (EASl) technique for sentinel lymph node biopsy in breast cancer
Chi Wei Mok, Jun Xian Jeffrey Hing, Spoorthi Sudhakar Shetty, Su-Ming Tan
1Division of Breast Surgery, Department of Surgery, Changi General Hospital, Singapore 529889, Singapore.
2Singhealth Duke-NUS Breast Centre, Singapore 529889, Singapore.
Abstract Sentinel lymph node biopsy is currently the standard of care for axillary staging in early breast cancer patients with no clinical or radiological evidence of axillary lymph node involvement. Novel techniques studied in recent years include the use indocyanine green (ICG) fluorescence imaging, which was reported in a recent network meta-analysis to be comparable to standard dual modality in terms of false negative as well as detection rate.However, there have been no standardized operative methods leading to the underutilization of this modality in clinical practice. In addition, technical limitations such as the difficulty in tracing ICG flow in obese patients further restrict the use of ICG fluorescence in sentinel lymph node biopsy. In this article, we describe in detail the use of the endoscopic-assisted ICG technique in performing sentinel lymph node biopsy, which addresses limitations associated with conventional use of ICG fluorescence imaging. The technical novelty of this technique lies in the fact that it has not been previously described in the literature and it allows for the identification of sentinel lymph nodes with minimal incision and tissue disruption as well.
Keywords: Endoscope, endoscopic, endoscopic-assisted, EASI, indocyanine green, indocyanine green, fluorescence,novel technique, minimally invasive, minimal access
INTRODUCTION
The most widely used technique for sentinel lymph node (SLN) identification is the dual-modality method involving the injection of technetium-99m-labeled nanocolloid and blue dye into the peritumoral or periareolar region[1]. The dual technique has its shortcomings, including radiation exposure to healthcare professionals and patients, issues with radiotracer availability, dependency on availability of nuclear medicine units and allergic reactions to blue dye. New techniques have been developed to improve the clinical value of SLN biopsy with similar accuracy, but avoiding irradiation and risks of allergy[2]. Novel techniques studied in recent years include those using indocyanine green (ICG) fluorescence imaging,which was reported in a 2019 network meta-analysis by Moket al.[3], showed ICG to be superior to the blue dye technique alone and comparable to that of the standard dual-modality method. There was, however,technical difficulties with the use of ICG[4]especially in obese patients, thereby limiting the widespread use of this modality. In this article, we describe a minimally invasive technique which is effective in overcoming limitations and at the same time minimizes tissue dissection or disruption in the axilla.
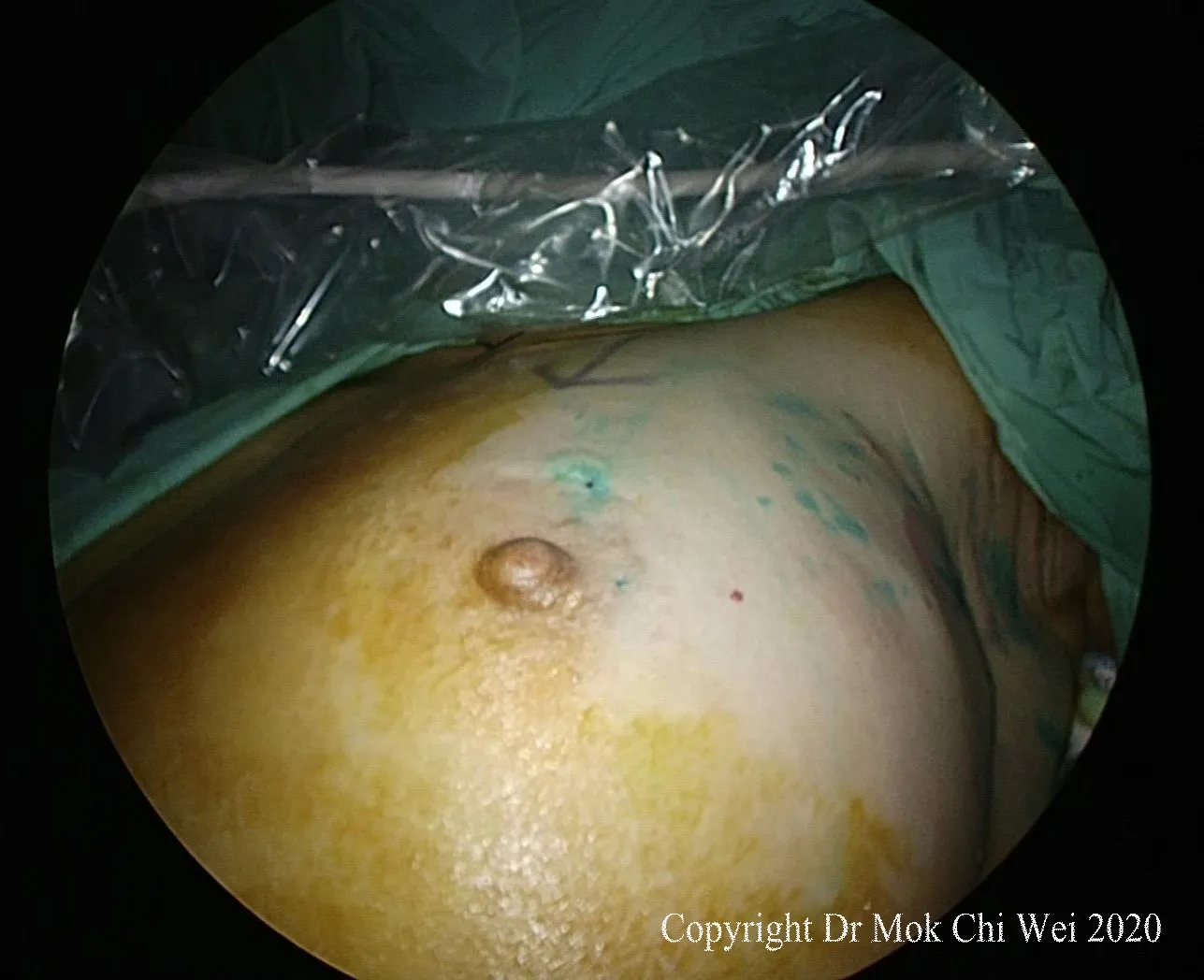
Figure 1. Injection of indocyanine green in the periareolar region
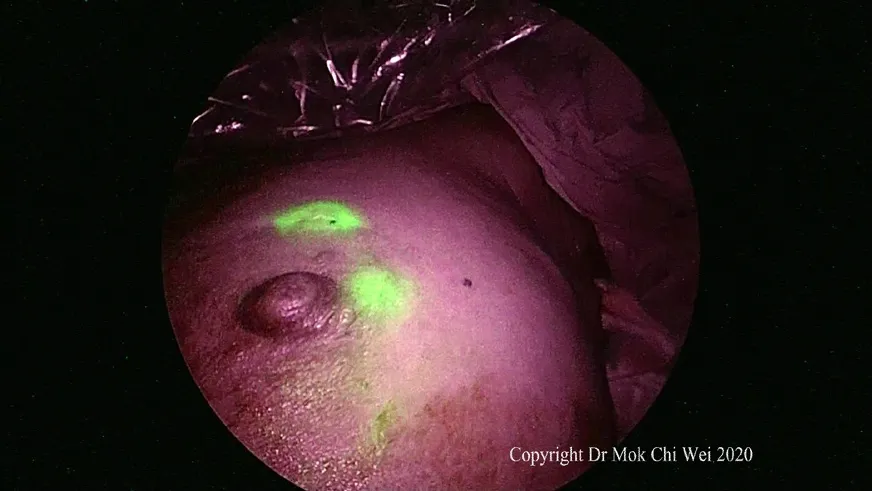
Figure 2. Visualization of indocyanine green under fluorescence imaging
TECHNIQUE
Detailed description of this technique as attached in Video 1.
ICG PREPARATION AND INJECTION
ICG VERDYE (Diagnostic Green, Bavaria) solution of 1.25 mg/0.5 mL (vial of 25 mg added to 10 mL of water for injection) was prepared, and 1 mL of ICG was injected intradermally over 12 o’clock and 9 or 3 o’clock (right and leた breast, respectively) with 0.5 mL per injection site aたer induction of general anesthesia[Figures 1 and 2]. Special care was taken to avoid contamination of surgical field with ICG to reduce artifacts under fluorescence imaging [Figure 3]. A 5-min waiting time was advised to allow for adequate lymphatic flow to the axilla. Lymphatic flow could be visualized under fluorescence imaging [Figures 4 and 5]to aid in determining the most optimal placement of the axillary incision. Alternatively, a direct axilla incision could be made within the axillary skin crease without prior identification of lymphatic flow.?
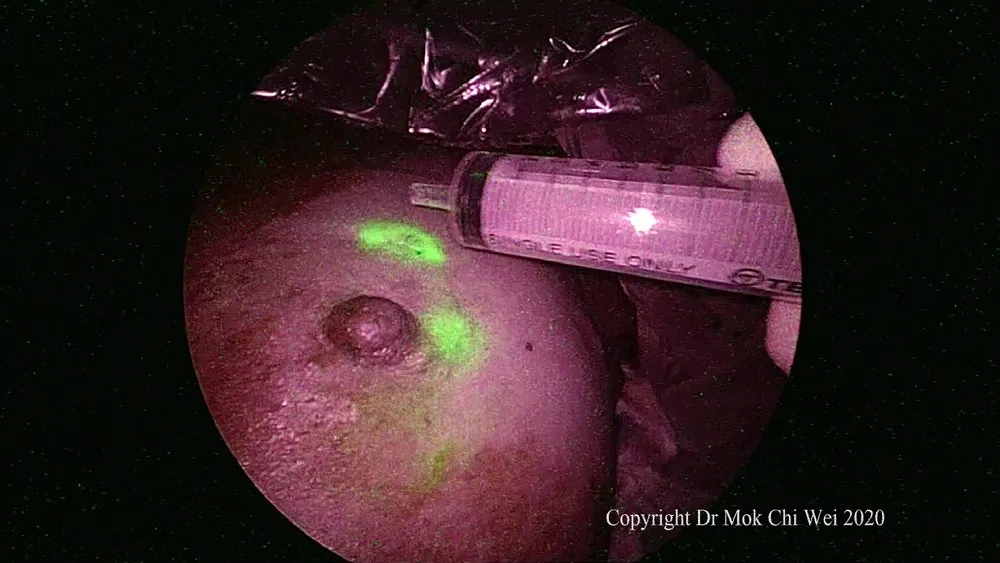
Figure 3. Gentle tap at the injection site to stimulate lymphatic flow. An empty syringe was used to avoid contamination of the surgical field
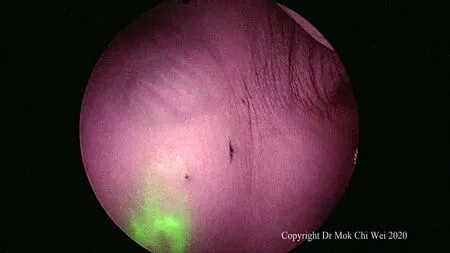
Figure 4. Lymphatic flow can be visualized and lymph fluid observed flowing towards the axilla, via overlay mode

Figure 5. Lymphatic flow can be visualized and lymph fluid observed flowing towards the axilla, via pure fluorescence mode
ENDOSCOPIC-ASSISTED ICG TECHNIQUE AND IDENTIFICATION OF SENTINEL LYMPH NODES
The endoscopic-assisted ICG (EASI) technique involved the use of an optical trocar (Endopath Xcel?Bladeless Trocar, Johnson & Johnson, USA), a 5- or 10-mm 0° or 30° endoscope and ICG system (Olympus Visera Elite II, Olympus, Tokyo, Japan) in performing the SLN biopsy. A 5- or 10-mm stab incision(depending on the endoscope used) was placed along the axillary skin crease. In our institution, blue dye was used concomitantly with ICG as a second modality. Direct optical entry was performed with slow and controlled movement while looking for lymphatic flow, either blue or green (under fluorescence imaging)[Figure 6]. Direction of entry was then guided by lymphatic flow until the first SLN was identified.
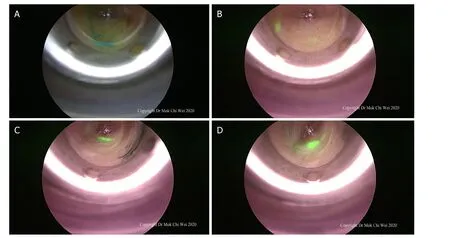
Figure 6. A-D: after a stab incision was made, direct optical entry using a bladeless trocar was performed and lymphatic flow was observed (either blue dye or indocyanine green) until the first sentinel lymph node was visualized under endoscopic guidance
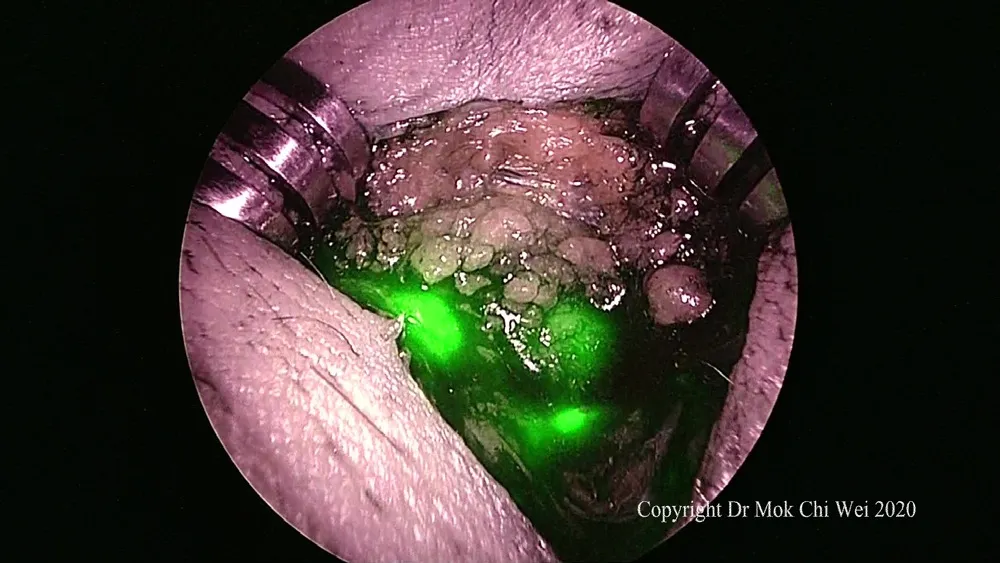
Figure 7. After identification of the first sentinel lymph node, the stab incision was extended to allow for a focused dissection as well as retrieval of the first sentinel lymph node. Subsequent sentinel lymph node were retrieved as well if any and sent for intraoperative frozen section analysis
RETRIEVAL OF SENTINEL LYMPH NODES
Once the first SLN was identified, the camera was thenremoved. With the optical trocar still in place,minimal extension of the skin incision to 1.5 or 2 cm was then performed to allow retrieval of the SLN. A focused and directed dissection towards the SLN as guided by the optical trocar resulted in minimal tissue/lymphatic disruption or damage [Figures 7 and 8]. Aたer retrieval of the first SLN, fluorescence imaging was then used to trace the lymphatic flow beyond the first SLN and detect further SLNs, if any [Figures 9 and 10].In cases where dual modality was used, the second technique could be used to detect SLNs that were not ICG-avid. Nodes were sent for intraoperative frozen section analysis and axillary dissection performed as deemed necessary if the frozen section analysis returned positive for metastatic carcinoma.

Figure 8. Sentinel lymph node retrieved showing indocyanine green under fluorescence imaging

Figure 9. A, B: axilla examined under direct vision/palpation as well as indocyanine green fluorescence imaging. In Figure 9B, as the axilla showed an area of indocyanine green fluorescence without any clinically palpable nodes, the area was excised to ensure that it was just lymphatic flow (false positive) rather than sentinel nodes
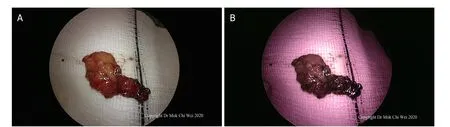
Figure 10. A, B: after excision, the tissue was examined under white light as well as fluorescence mode, confirming that there were no further sentinel lymph nodes and that the area of fluorescence shown in Figure 9B was indeed a false positive observation
CONCLUSION
The EASI technique for SLN biopsy is an innovative approach to utilize ICG in SLN biopsy with the potential to overcome the difficulty of visualizing ICG flow especially in obese patients as well as resulting in minimal tissue/lymphatic disruption.
DECLARATIONS
Authors’ contributions
Conception and design of the study: Mok CW, Hing JXJ, Shetty SS
Draたing of manuscript: Mok CW
Revision and preparation of final manuscript: Mok CW, Hing JXJ, Shetty SS, Tan SM
Availability of data and materials
Not applicable.
Financial support and sponsorship
None.
Conflicts of interest
All authors declared that there are no conflicts of interest.
Ethical approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Written informed consent for publication was obtained as appropriate.
Copyright
? The Author(s) 2020.
- Mini-invasive Surgery的其它文章
- Cause of recurrent laryngeal nerve paralysis following esophageal cancer surgery and preventive surgical technique along the left recurrent laryngeal nerve
- Mediastinoscopic esophagectomy with lymph node dissection using a bilateral transcervical and transhiatal pneumomediastinal approach
- Current management of gastroesophageal reflux disease in the obese population - a review of the literature
- MlS Al - artificial intelligence application in minimally invasive surgery
- From TATA to single port robotic (SPr) taTME:approaches to distal rectal cancer
- Uniportal video assisted thoracoscopic left upper bronchial sleeve lobectomy in a pediatric patient

