Reduced delay in diagnosis of odontogenic keratocysts with malignant transformation: A case report
Xiao-Juan Luo, Ming-Liang Cheng, Chun-Ming Huang, Xiao-Ping Zhao
Xiao-Juan Luo, Ming-Liang Cheng, Chun-Ming Huang, Xiao-Ping Zhao, Center of Stomatology,Tongji Hospital, Tongji Medical College, Huazhong University of Science and Technology,Wuhan 430030, Hubei Province, China
Abstract
Key words: Odontogenic keratocysts; Malignant transformation; Primary intraosseous squamous cell carcinoma; Delay in diagnosis; Enucleation; Case report
INTRODUCTION
Odontogenic keratocysts (ODs) can transform into primary intraosseous squamous cell carcinoma (PIOSCC)[1]. However, this malignant transformation rarely occurs. To the best of our knowledge, approximately 30 cases have been reported[2].
The diagnosis of PIOSCC requires caution. An important reason is clinicians’unawareness of the malignant transformation of OD due to its rarity. In addition,similar symptoms of swelling, pain, chronic infection, and pus discharge occur between OD and PIOSCC. Imaging examinations may fail to distinguish one from the other given that the main feature of bony destruction is observed in both diseases,especially when PIOSCC is in its early stage[3,4]. Moreover, marsupialization of cystic lesions is favored by patients and clinicians. The time between patients’ attendance and the diagnosis of PIOSCC is considerably longer than that of squamous cell carcinoma in other oral and maxillofacial anatomical sites.
Information about the treatments and prognosis of PIOSCC is scarce. Although neck dissection remains in discussion, the radical excision of lesions with appropriate reconstruction and postoperative radio/chemotherapy is commonly performed[3,5-7].The two- and five-year survival rates in adults are approximately 62% and 38%,respectively; furthermore, patients with lymph node metastasis at first clinical attendance show a poor prognosis[4]. Timely diagnosis and proper treatment may benefit these patients’ prognosis.
In this article, we report a case of maxillary PIOSCC derived from the malignant transformation of OD with reduced delay in diagnosis and lymph node metastasis.We aim to remind clinicians of the underappreciated malignant transformation of OD,especially when patients present with a long history, massive cyst, chronic inflammation, recent persistent infections, aggravated pain, and numbness around the cystic lesion.
CASE PRESENTATION
Chief complaints
A 54-year-old woman was referred to Tongji Hospital in Wuhan, China with complaints of moderate pain, recurrent swelling, and pus discharge around her left maxillary lateral incisor for over 10 years.
History of past illness
The patient received interrupted anti-inflammatory therapy. The discomfort aggravated in the recent month, and no improvement was achieved by antibiotic treatment.
Personal and family history
The patient was generally in good health and had no history of alcohol, tobacco, or areca nut consumption.
Physical examination upon admission
Intraoral examination revealed a fistula at the palatine-side mucoperiosteum of the left maxillary lateral incisor, and intense pain was observed. No evident swelling was detected in the left maxilla. An abnormal looseness of maxillary tooth and enlarged lymph node were detected in the left neck.
Laboratory examinations
Routine laboratory tests revealed no remarkable abnormality, except for a slightly increased D–D dimer level (0.58 μg/mL FEU).
Imaging examinations
Cone beam computed tomography (CT) revealed massive bone destruction with a clear boundary from the left maxillary central incisor to the left secondary maxillary premolar and local bony destruction in the left first mandibular molar (Figure 1A-E).Other examination results, including those of magnetic resonance imaging (MRI)for neck and cranial and chest CT, were normal.
FINAL DIAGNOSIS
The patient was clinically diagnosed with OD. However, we were highly suspicious of squamous cell carcinoma due to the patient’s long history, recent aggravated pain,massive bony destruction, and lymph node enlargement. Such suspicion was confirmed by pathological findings 3 d after enucleation (Figure 2A-D).
TREATMENT
One week after the diagnosis, radical surgery (left subtotal maxillectomy with reconstruction with a free anterolateral thigh flap and left supraomohyoid neck dissection) was performed. Final pathological results confirmed squamous cell carcinoma in the left maxilla, and lymph node metastasis was observed. The patient received postoperative radiotherapy (local intensity-modulated radiotherapy, 3 Gy per day for 5 d a week for 4 wk) and synchronous chemotherapy (1 g cisplatin/d per week for 4 wk).
OUTCOME AND FOLLOW-UP
Postoperative follow-up for one year revealed no local recurrence or distant metastasis.
DISCUSSION
PIOSCC is classified into three types: (1) A solid cancer invades marrow spaces and incudes osseous reabsorption; (2) A squamous cell carcinoma derives from an odontogenic cyst; and (3) A squamous cell carcinoma derives from other benign epithelial odontogenic tumors[8]. According to previous reports, the diagnosis of PIOSCC must meet the following common criteria: (1) The intact oral mucosa without ulcer; (2) Verified absence of invasion from nearby malignancies, such as alveolar carcinoma and metastasis from distant organs; and (3) Confirmed transformation of the normal squamous epithelium to squamous cell carcinoma within cyst liningsviahistopathological examination[3,9-11]. In the current case, physical examination, MRI,and CT tests revealed the intact oral mucosa and a cystic lesion of the left maxilla,excluding the invasion and metastasis of other malignancies; histopathological examination provided evidence for the malignant transformation of OD-squamous epithelium. In conjunction with the patient’s medical history, recent aggressive behavior, and intraoperative findings, we considered that the patient suffered from PIOSCC deriving from OD.
Although information about biological characteristics of malignant OD is rare, the high recurrence rate and poor survival of PIOSCC may be partly attributed to its misdiagnosis as OD; subsequent curettage is conventionally performed, followed by enucleation combined with peripheral ostectomy and radical resection for localized and large or ill-defined lesions, respectively[12]. Apart from the similarity of clinical behavior and radiologic examination results between PIOSCC and OD, the acquired malignant transformation of OD as confirmed by pathology is another huge barrier to prescribing the proper treatment for patients with PIOSCC. Although the malignant lesion was diagnosed by enucleation in this case, biopsy and enucleation have been associated with the misdiagnosis of PIOSCC in previous reports[5,6]. More information is required to assess malignant tumors before the identification of the characteristics of malignant transformation of OD.
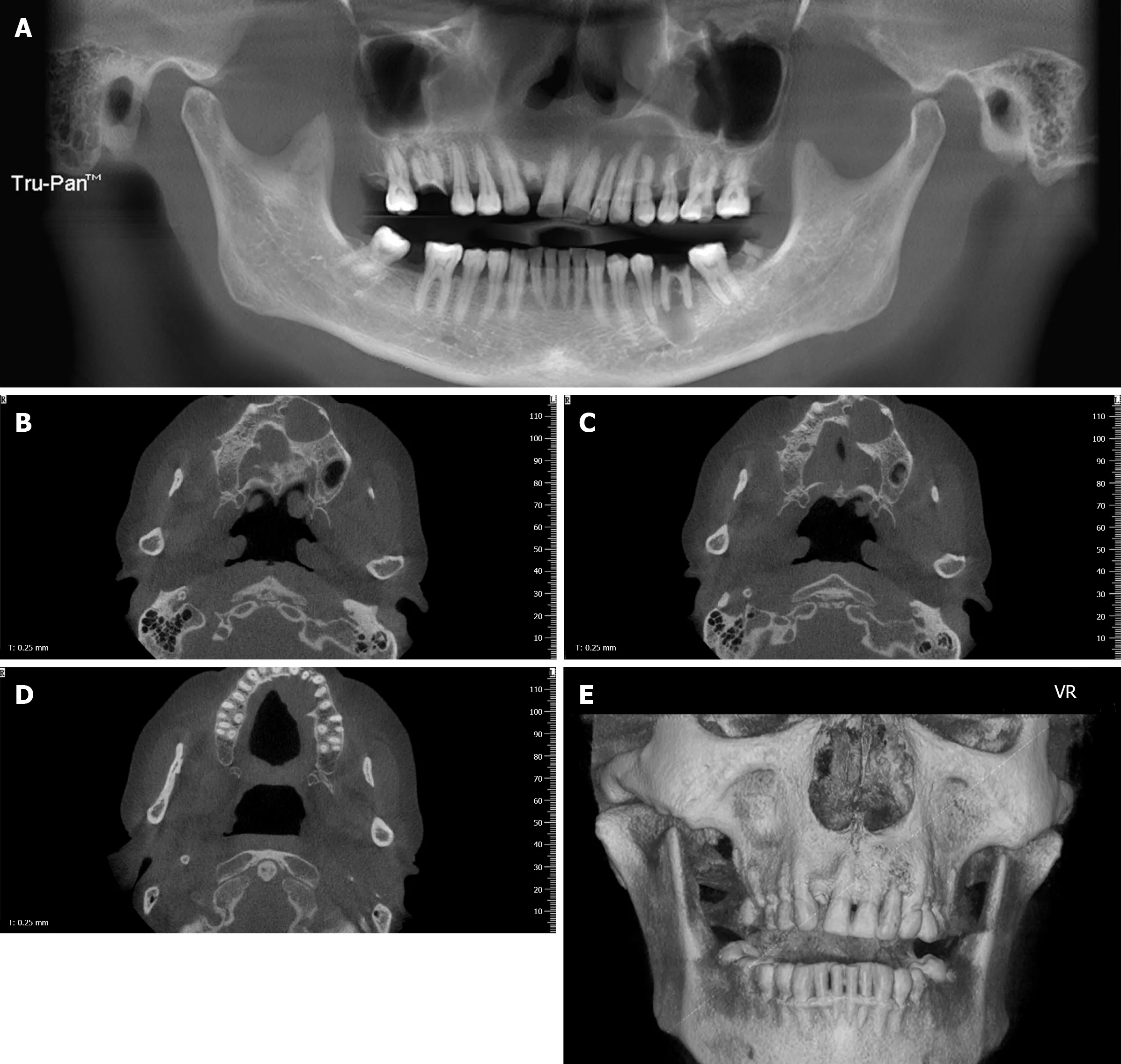
Figure 1 Images of cone beam computed tomography. A: Panoramic radiograph revealing a cystic lesion in the left maxilla and periapical radiolucency of inflammatory origin in the left first mandibular molar. The left maxillary lesion extended from the left maxillary central incisor to the left secondary maxillary premolar and showed no evident root resorption; B-D: An axial scan revealed buccal and palatal swelling of the cystic lesion with a clear boundary and a palatal cortex defect;E: Three-dimensional imaging revealed an intact labial maxillary bone.
A literature review suggests that a few cases of PIOSCC were diagnosedviasurgical biopsy because of a prejudged possibility of a malignant tumor, a few cases were unsuspectedly diagnosed by enucleation, and the remaining cases were diagnosed by radical resection of lesions due to relapse and aggravation after conservative treatment[13,14]. These prudent studies and our report demonstrate cases with a long medical history, persistent inflammation, huge mass, recent aggressive behavior, including numbness and lymph node enlargement. Several recurrences and continuous uncomfortableness are commonly observed in cases with delayed diagnosis. Although these symptoms are nonspecific, clinicians should be aware of the malignant transformation of OD and synthetically judge patients’ history, clinical behavior, and CT/MRI results. For cases without these characteristics, enucleation seems to the safe way to exclude early stage PIOSCC.
CONCLUSION
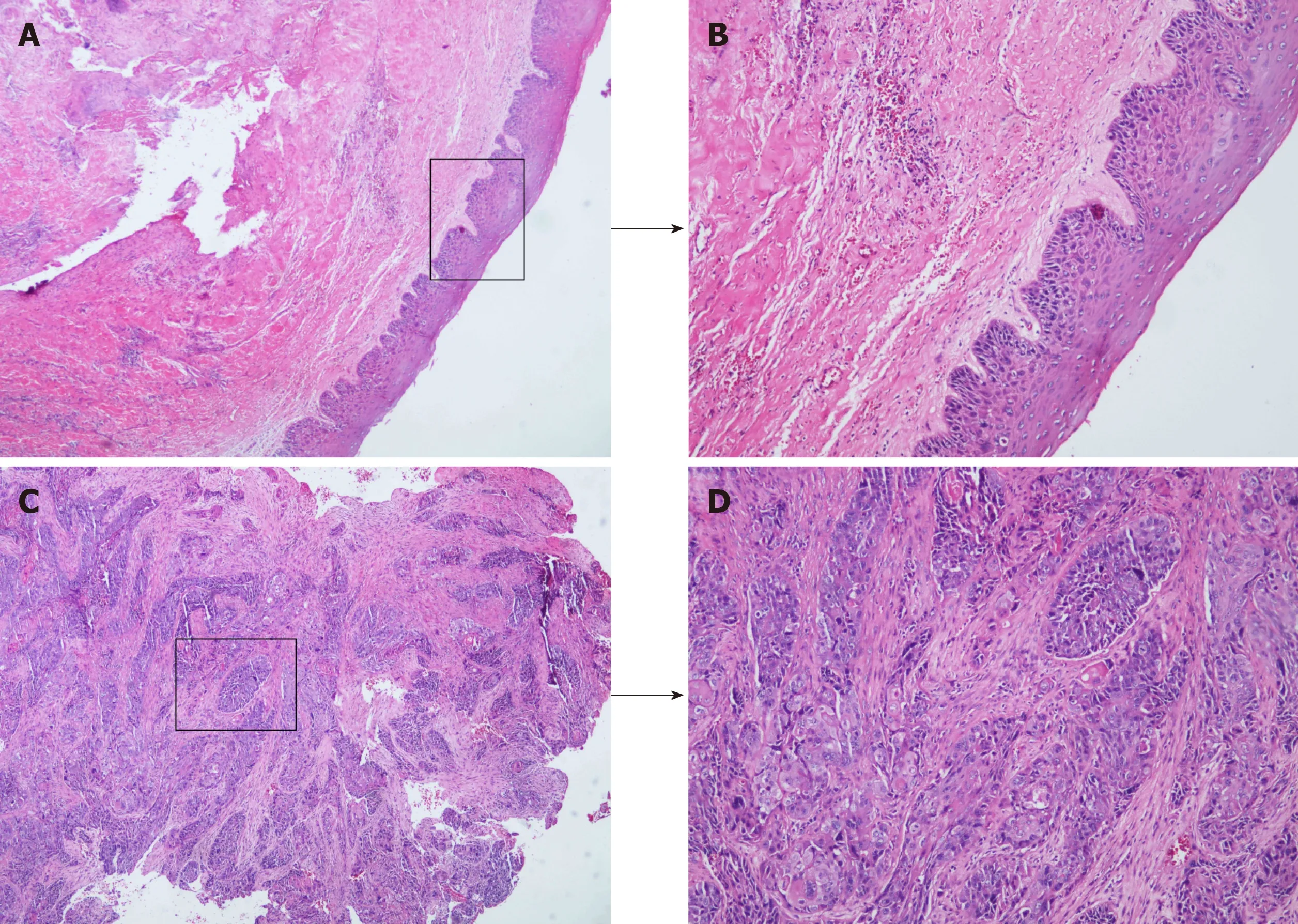
Figure 2 Malignant transformation of odontogenic keratocysts. A: Histopathological examination revealed an intact structure of cyst lining (× 40) B: Inflammatory cell infiltration in the submucosa (× 100); C: Destruction of cyst lining and invasion of massive squamous cell carcinoma (× 40); D: Moderately differentiated squamous cell carcinoma (distinct foci of squamous cell carcinoma, × 100).
This article presents a case with reduced delay in the diagnosis of PIOSCC in the maxilla. Our case suggests that for the timely diagnosis and treatment of PIOSCC,clinicians should be aware of the malignant transformation of OD, especially when patients present a cystic lesion with a long history, chronic inflammation, recent aggravated behaviors including pain and lymph node enlargement.
 World Journal of Clinical Cases2020年11期
World Journal of Clinical Cases2020年11期
- World Journal of Clinical Cases的其它文章
- Macrophage activation syndrome as an initial presentation of systemic lupus erythematosus
- Optical coherence tomography guided treatment avoids stenting in an antiphospholipid syndrome patient: A case report
- Uterine incision dehiscence 3 mo after cesarean section causing massive bleeding: A case report
- Ataxia-telangiectasia complicated with Hodgkin's lymphoma: A case report
- Gastric pyloric gland adenoma resembling a submucosal tumor: A case report
- Endoscopic pedicle flap grafting in the treatment of esophageal fistulas: A case report
