Computational study of inverse ferrite spinels
A EL Maazouzi,RMasrour,?,A Jabar,and M Hamedoun
1Laboratory of Materials,Processes,Environment and Quality,Cadi Ayyad University,National School of Applied Sciences,
Sidi Bouzid,Saf i63 46000,Morocco
2Instituteof Nanomaterialsand Nanotechnologies,MAScIR,Rabat,Morocco
(Received 6 February 2019;revised manuscript received 5 March 2019;published online4 April 2019)
Keywords:inverse ferritesspinels,Monte Carlo simulation,critical and Curie Weisstemperatures,magnetic
1.Introduction
Cubic ferrite has the formula M2+Fe3+O2-4,where M is a divalent atom(e.g.,Fe2+,Co2+,Zn2+,Ni2+,etc).The general chemical formula of inverse spinels family can be written in theform,wheretheparentheses represents the cations occupying tetrahedral A sites,whereasthe bracketsdenote the cations occupying octahedral B sitesin thespinel structure.Theparameter x isthedegreeof inversion def ined as the fraction of tetrahedral sites occupied by Fe3+cations.Ideal bulk M Fe2O4is a fully inverse spinel ferrite(x=1).The experimental determination of x isof vital importance because the physicochemical properties exhibited by the ferrites critically depend on this parameter.[1]Besides technological applications in spin-f iltering[2]and multiferroic devices,[3,4]several biomedical applications on targeting,diagnosis,and disease treatment have also been reported.In addition,thecations M and Fe in thelattice respectively occupy the tetrahedral(1/8,1/8,1/8)sites,Wyckoff position 8a,and octahedral(1/2,1/2,1/2)sites,Wyckoff position 16d.Therefore,the single positional parameter u plus the unit-cell parameter a are suff icient to determine the spinel structure.It is known that altering the occupancies of the M and Fe sites can giveriseto slight variationsof the spinel structure,which can affect thecorresponding natureand magnitudeof superexchange interactions,[5]namely,A–A,B–B,and A–B,of which the A–B interactions tend to be highly signif icant.
Different types of ferrite-based composites have been studied,including magnetic ferritescomposed of nonmagnetic oxides and polymers.[6–8]For practical applications,however,Fe3O4is the most promising candidate due to its high Curie temperature,TC=858 K,as compared to other half metals.These characteristicsof Fe3O4can be utilized in the developmentof tunneling magnetoresistancebased devicesthatwould operate at room temperature with high eff iciency.[9,10]Experimentally,the properties of ferrites are dependent on the synthesistechnique and synthesis conditions.[11]NiFe2O4has the inverse spinel structure in bulk form where divalent metal ions(Ni2+)occupy octahedral sites and mixed spinel structure in caseof nanoparticleswhere Ni2+ionscan occupy both tetrahedral and octahedral sites.[12]CuFe2O4is ferromagnetically ordered for a weak magnetic f ield and it has wide applications due to its high thermal stability.[13]Nickel ferrite NiFe2O4is a good example of inverse spinel ferrite and exhibitsferromagnetic naturewith a Curietemperatureof 858 K where half of the Fe3+ions occupy the tetrahedral sites and the remaining ions occupy the octahedral sites,it is used in repulsivesuspension for levitated railway systems,microwave absorber,magnetic liquids,magnetic refrigeration,and high density magnetic recording media.[14,15]In previouswork,[16]the CoFe2O4nanowire arrays become superparamagnetic at 600 K.High magnetostriction and strain-f ield derivative with low saturation f ield make(0 0 1)f iber textured CoFe2O4attractive for sonar detector and force sensor applications.[17]Theoretically,the formation condition and energy of possible intrinsic point defects have been investigated by the f irstprinciples calculations,and the effects of the intrinsic point defects on the electronic and magnetic properties of CoFe2O4have been analyzed.[18]The experimental and numerical results using Monte Carlo simulation of the reduced magneti-zation and coercivity cobalt ferrite/polyvinylpyrrolidone are in relatively good agreement with each other.[19] The firstprinciples,mean-field, and series expansions calculations have been used to study the electronic and magnetic structures of Fe3O4.[20] Green’s function theory has been used to study the magnetic properties of CuxNi1-xFe2O4 spinels.[21] The effect of Zn doping on magnetic properties of MnFe2O4 ferrite spinel has been studied by using high temperature series expansion combined with the Pad′e approximant and mean fieldtheory.[22]In the previous work,[23]silicene is an intriguing two-dimensional (2D) topological material which is closelyanalogous to graphene but with stronger spin–orbit coupling effect and natural compatibility with current silicon-based electronic industry. It could realize a ferromagnetic phase,super-counter-fluidity phase, and antiferromagnetic phase of polarized light that are of interest for studying spin-dependent photon-photon interactions.[24]The effect of spin transporton nonlinear excitations was investigated in a ferromagnetic nanowire with nonuniform magnetizations.[25]
In the present work,we have used the Monte Carlo simulation to study the magnetic properties of inverse 3(a),and 4(a),respectively.The obtained values are given in Table 2.The CurieWeiss temperaturesθCWare deduced from the inverse of magnetic susceptibilities for the four inverse ferrite spinels from Figs.1(a),2(a),3(a),and 4(a),respectively(see Table 1).The obtained values of TCandθCWare near to those obtained by experiment results[28,29]and the molecular-f ield approximation.[30]
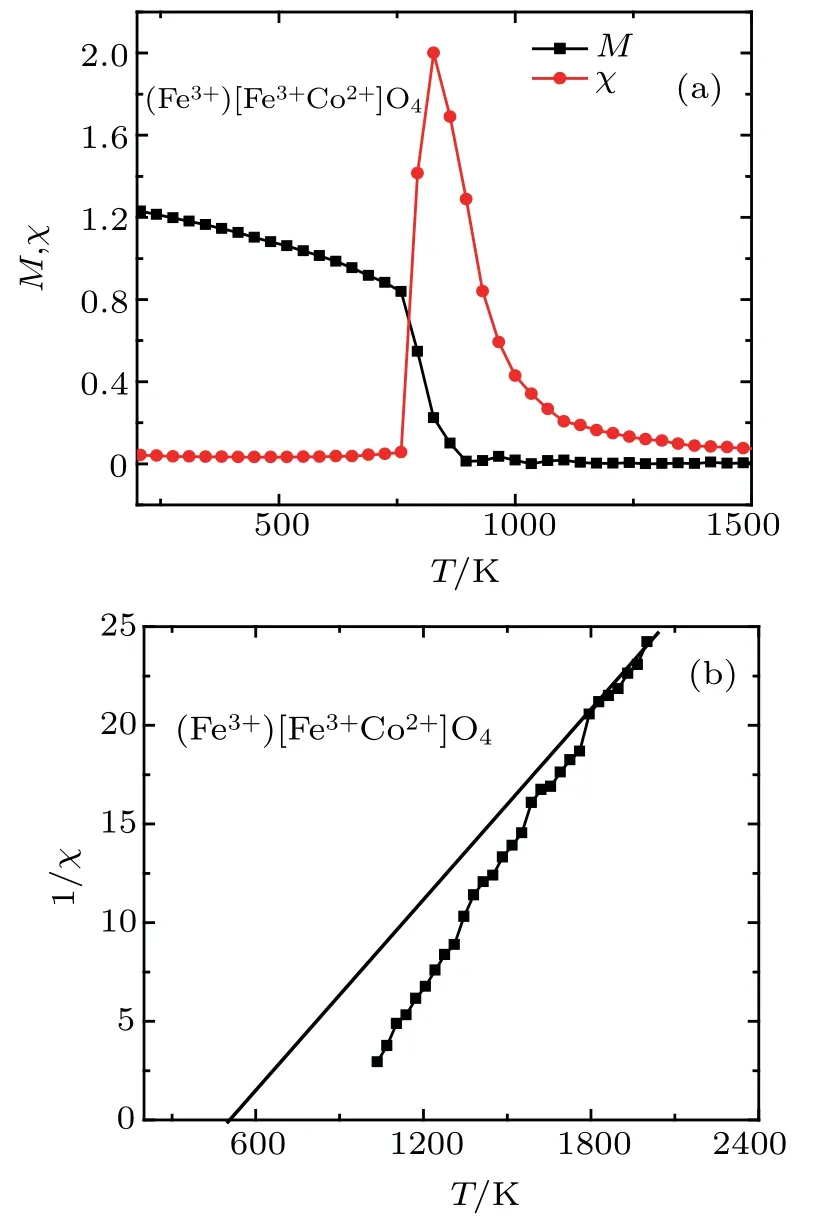
Fig. 1. (a) The thermal magnetization and magnetic susceptibility and(b) inverse magnetic susceptibility of(Fe3+) Fe3+Co2+ O2-4 spinels.The straight line in panel (b) is used to deduce the Curie Weiss temperature
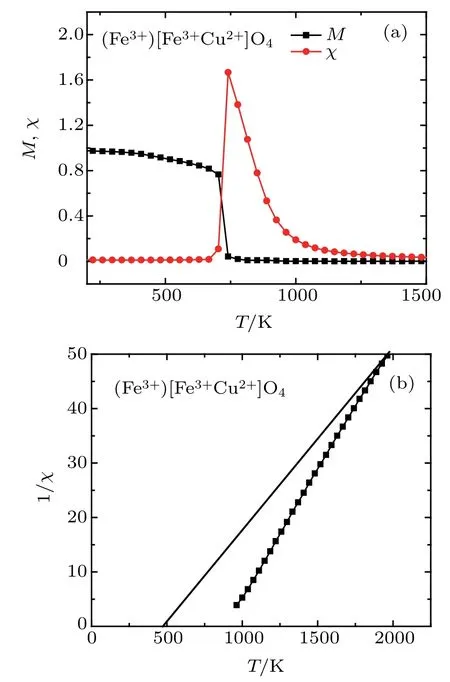
Fig. 2. (a) The thermal magnetization and magnetic susceptibility and(b) inverse magnetic susceptibility of(Fe3+)Fe3+Cu2+ O2-4 spinels.The straight line in panel (b) is used to deduce the Curie Weiss temperature.
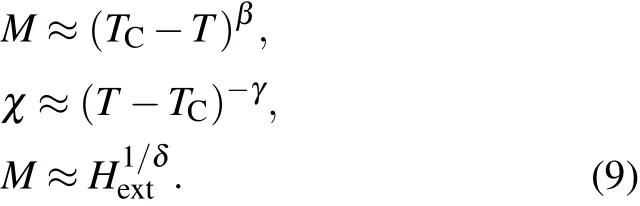
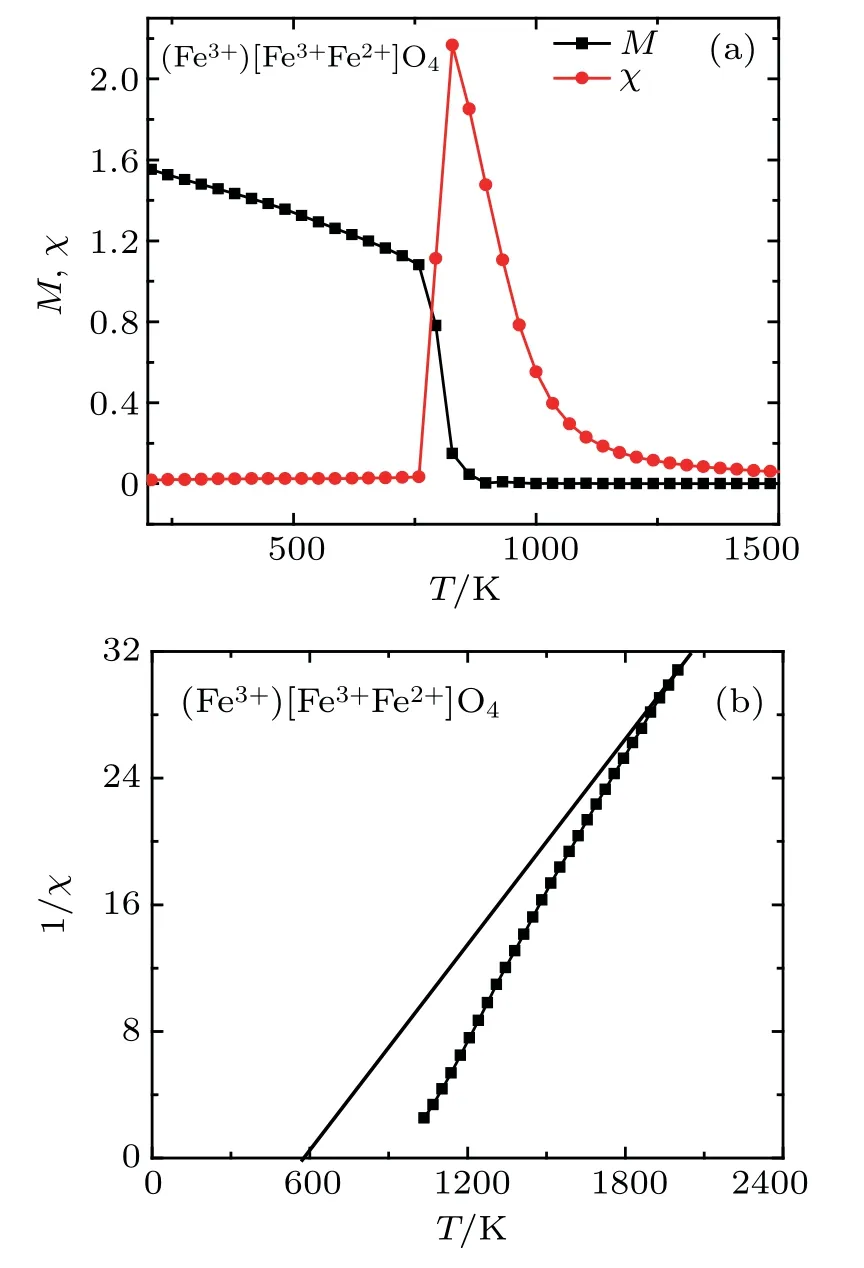
4 spinels.The straight line in panel(b)isused to deduce the CurieWeiss temperature.
Fig.3.(a)The thermalmagnetization andmagnetic susceptibility and(b)inversemagnetic susceptibility of(Fe3+)Fe3+Fe2+O2-
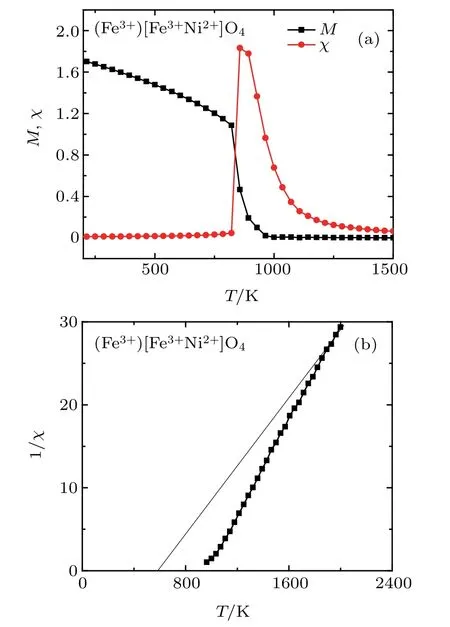
Fig.4.(a)The thermalmagnetization andmagnetic susceptibility and(b)inversemagnetic susceptibility of(Fe3+)Fe3+Ni2+O2-
4spinels.enlarged low f ield region.
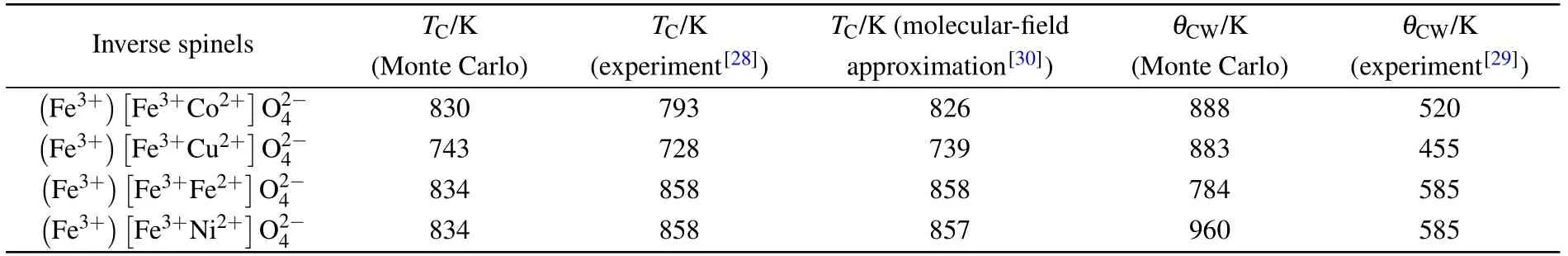
Tab le2.The criticaland CurieWeiss temperaturesobtained by Monte Carlo simulations,experiments(Ref.[25]for T C and Ref.[29]forθCW),andmolecular-f ield approximation[30]for the spinels.
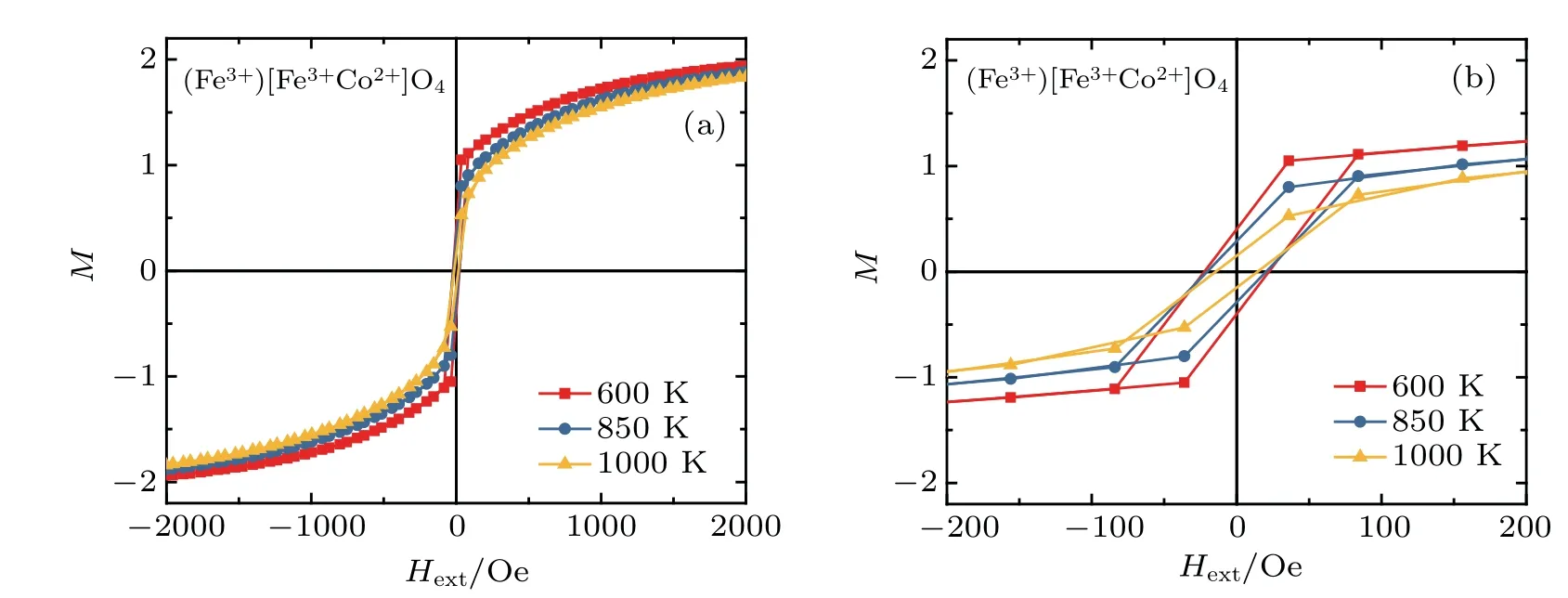
Fig.5.(a)Magnetic M(H ext)loop of(Fe3+)Fe3+Co2+O2-4 for different temperatures T=600K,850 K,and 1000 K,and(b)the
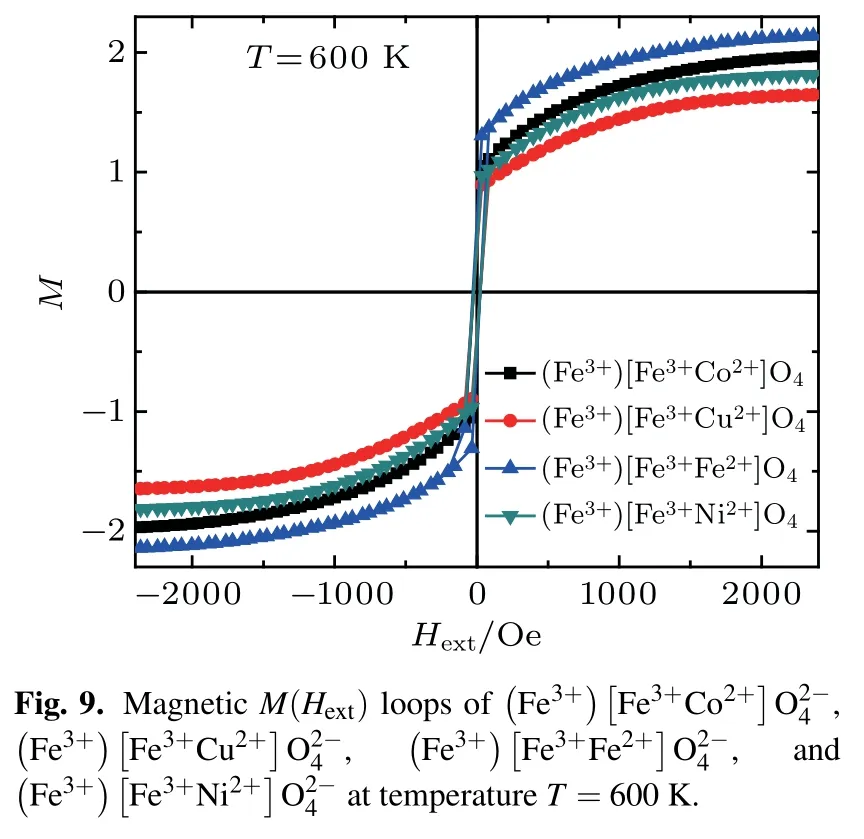
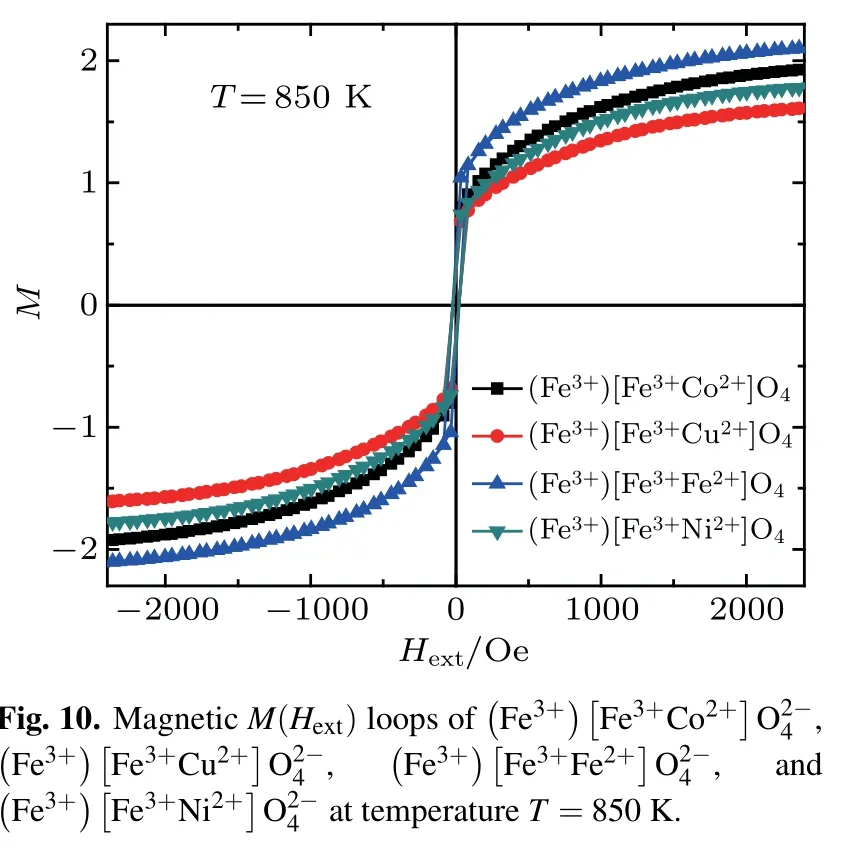
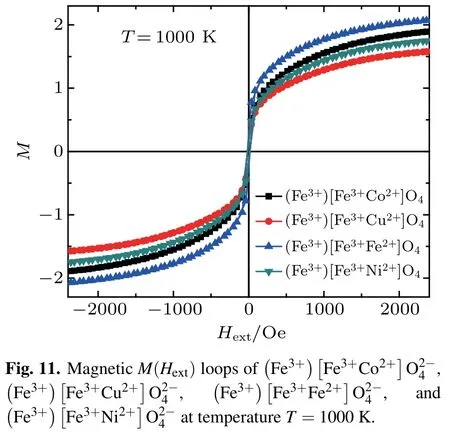
Themagnetic M(Hext)loopsof,, andspinels are shown in Figs.7–10,respectively,for several values of temperatures T=600 K,850 K,and 1000 K.From these curves,we deduce that the magnetic coercive f ield,remanentmagnetization,and saturationmagnetization decreasewith increasing temperature(see Figs.5(b),6(b),7(b),and 8(b)).This behavior is similar in magnetic propertiesofmultilayer BaTiO3/NiFe2O4thin f ilms prepared by solution deposition technique in Ref.[31].The wellsaturated hysteresis loopsare recorded in the range from 0.2 T to-0.2 T(Figs.5–8)and their shapes resemble the ferrimagnetic behavior typical for cobalt(ornickel,copper-iron)ferritebasedmaterials.
Figures 9–11 present the magnetic M(Hext)loop of (andfor temperatures T=600 K,850 K,and 1000 K,respectively.The saturationmagnetization and themagnetic coercive f ield decrease as the number of electrons in the valence shell of themagnetic atom(3d)increase,such asgiven in the periodic table.For a weak externalmagnetic f ield,the four systems present the ferromagnetical order and the superparamagnetic order for a higher externalmagnetic f ield such as given in Ref.[13].enlarged low f ield region.enlarged low f ield region.
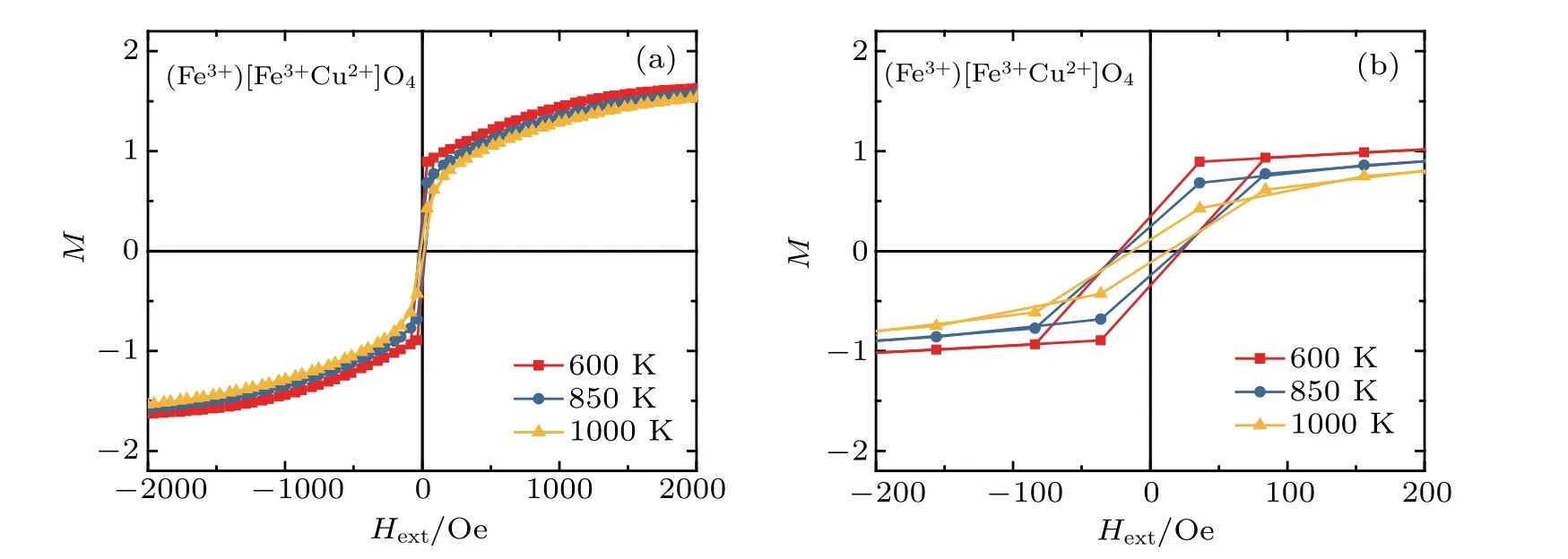
Fig.6.(a)Magnetic M(H ext)loop of(Fe3+)Fe3+Cu2+O2-4 for different temperatures T=600K,850 K,and 1000 K,and(b)the
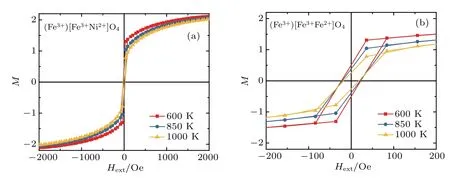
Fig.7.(a)Magnetic M(H ext)loop of(Fe3+)Fe3+Fe2+O2-4 for temperatures T=600 K,850 K,and 1000K,and(b)the enlarged low f ield region.
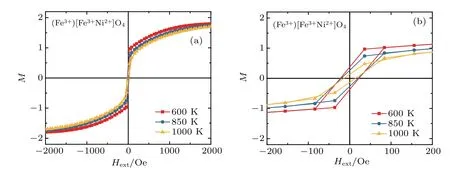
Fig.8.(a)Magnetic M(H ext)loop of(Fe3+)Fe3+Ni2+O2-4 for different temperatures T=600 K,850 K,and 1000 K,and(b)the
Wehavecalculatedthecriticalexponentsβ,γ,andδassociatedwiththemagnetization,magneticsusceptibility,and externalmagneticfieldusingEq.(7).Theobtainedvaluesof β,γ,andδaregiveninTable3.Theobtainedvaluesare comparablewiththosegivenby3DIsingmodel(β=0.22,γ=1.24,andδ=4.78).[31–37]
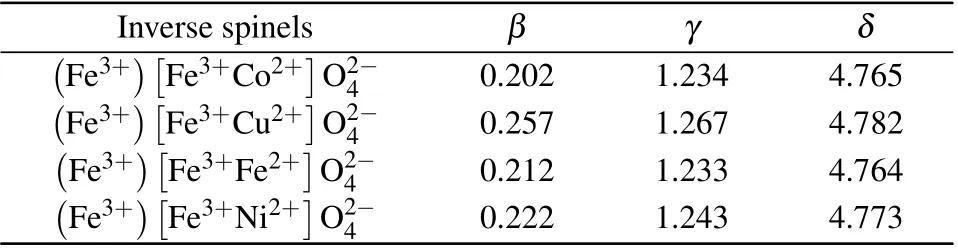
Table3.Thecriticalexponentsβ,γ,andδassociatedwiththemagnetization,magneticsusceptibility,andexternalmagneticfieldofthe spinels.
5.Conclusion
The magnetic properties of inverse ferrite(Fe3+)Fe3+Co2+O2-4, (Fe3+)Fe3+Cu2+O2-4,(Fe3+)Fe3+Fe2+O2-4,and(Fe3+)Fe3+Ni2+O2-4spinels areinvestigated.ThecriticaltemperaturesandtheCurieWeiss temperaturesarefoundusingMonteCarlosimulation.The obtainedvaluesofTCandθCWareneartothoseobtainedby experiments.Themagneticcoercivefiled,remanentmagnetization,andsaturationmagnetizationdecreasewithincreasing temperature.Thecriticalexponentsβ,γ,andδarededuced.Theobtainedvaluesarecomparablewiththosegivenby3D Isingmodel.[31–37]
- Chinese Physics B的其它文章
- Effectsof chem icalpressure on dilutedmagnetic sem iconductor(Ba,K)(Zn,M n)2As2*
- Particle–hole f luctuationsand possible superconductivity in dopedα-RuCl3*
- Surface stabilized cubic phaseof CsPb I3 and CsPbBr3 atroom tem perature*
- Raman scattering study ofmagnetic layered M PS3 crystals(M=M n,Fe,Ni)*
- Low tem perature Pmmm and C2/m phases in Sr2CuO3+δ high temperature superconductor*
- Crystallographic andmagnetic propertiesof van derWaals layered FePS3 crystal*