Gonadotrophin-releasing hormone agonist-induced pituitary adenoma apoplexy and casual finding of a parathyroid carcinoma:A case report and review of literature
Vanessa Trivi?o,Olga Fidalgo,Antía Juane,Jorge Pombo,Fernando Cordido
Vanessa Trivi?o,Olga Fidalgo,Antía Juane,Fernando Cordido,Department of Endocrinology,Complejo Hospitalario Universitario A Coru?a,A Coru?a 15006,Spain
Jorge Pombo,Department of pathological anatomy,Complejo Hospitalario Universitario A Coru?a,A Coru?a 15006,Spain
Abstract
Key words:Pituitary apoplexy;Pituitary adenoma;Primary hyperparathyroidism;MEN type 1;MEN type 4;Parathyroid carcinoma;Case report
INTRODUCTION
Gonadotropin-releasing hormone agonists(GnRHa),like triptorelin,are used to treat menorrhagia and uterine fibroids through pituitary down regulation.Pituitary Apoplexy(PA)is characterized by bleeding or impaired blood supply of the pituitary gland that usually occurs in the presence of a pituitary tumor[1].GnRHa will rarely induce PA in those who coincidentally have insidious pituitary adenoma[2,3],although most cases have not been diagnosed previously.PA represents one of the most serious,life- threatening endocrine emergencies that requires immediate management.It is a clinical syndrome associated with sudden headache,vomiting,visual impairment and meningismus caused by the rapid enlargement of a pituitary adenoma usually due to infarction of the tumor[4,5].
Recent data suggests that pituitary adenomas occur in almost 20% of the general population[3].The majority of these are non-functioning gonadotropinomas.Functioning Gonadotropins Adenomas(FGAs)are very rare and for premenopausal females tend to be universally associated with an elevated follicular-stimulating hormone(FSH),with varying levels of the luteinizing hormone(LH)[6].The most common clinical manifestations presented include menstrual irregularity,infertility,galactorrhea,and mass effects[7].A few patients were reported to have hormonal hypersecretion syndromes such as ovarian hyperstimulation,testicular enlargement,and precocious puberty[8].
The diagnosis can be very difficult in postmenopausal women because they exhibit elevated serum FSH in this period,making indistinguishable the FSH tumoral secretion,but in reproductive aged women can be difficult too because of de fluctuating levels of FSH during menstrual cycle[9].
Here we will discuss the case of the first female patient who has developed PA after receiving triptorelin for the treatment of menorrhagia and uterine fibroids through pituitary down regulation.We also discuss the casual finding of parathyroid carcinoma in the same patient.
CASE PRESENTATION
Chief complaints
A 46-year-old woman was transferred to our hospital from a secondary care hospital after complaints of headache and vomiting,with loss of consciousness 5 min after an injection of GnRH agonist.
History of present illness
Patient’s symptoms started 5 min after the injection of GnRH agonist prescribed by her gynecologist due to the presence of menorrhagia.
History of past illness
Hypertension under regular control.Left renal lithiasis treated with lithotripsy three times.Menarquia at the age of 10.Uterine myomas and long-standing menorrhagia,with secondary iron deficiency anemia.There was no history of migraine or any type of headache.
Physical examination
The patient’s temperature was 35.6 °C,heart rate was 56 bpm,respiratory rate was 16 breaths per minute,blood pressure was 200/85 mmHg and oxygen saturation in the room air was 98%.The clinical neurological examination revealed third right cranial nerve palsy,ptosis and movement limitation of the right eye,without any other pathological signs.Our first clinical consideration was a pituitary apoplexy.
Laboratory examinations
Blood hormonal analysis revealed a mild hyperprolactinemia(prolactin 68 ng/mL normal range 2.8-29.2 ng/mL).High FSH(76 mUI/mL).Insulin growth factor-1 and TSH level was normal;PTH was high 384 pg/mL.(normal range 14-72 pg/mL)serum calcium was high 12.9 mg/dL(normal range 8.5-10.1 mg/dL)with glomerular filtration rate mildly to moderately decreased.
Imaging examinations
An initial imaging evaluation with brain computed tomography scan,revealed an enlarged pituitary gland(3.5 cm)impinging upon the optic chiasm with bone involvement of the sella.The tumor invaded the cavernous sinuses.Following the contrast media administration,the lesion showed homogeneous enhancement with high density focus,suggesting hemorrhagic infarction of the tumor(Figure 1).
FINAL DIAGNOSIS
Due to the presence of pituitary gonadotroph macroadenoma and primary hyperparathyroidism,Multiple Endocrine Neoplasia type 1(MEN1)was suspected.
TREATMENT
Transsphenoidal endoscopic surgery was performed and adenomatous tissue with hemorrhagic foci was removed.Immunohistochemistry was positive for LH and FSH,the tissue did not express p53 and the cell proliferation index(MIB-1)was less than 3%(Figure 2).
Postoperative evolution was good,with progressive recovery of right cranial nerve III palsy,ptosis and movement of the right eye.Subsequent testing found hypothyroidism and hypoadrenalism,for which the patient was treated with replacement drugs.Prolactin and FSH level decreased to normal range and LH was suppressed.An elevated value of PTH was found,469 pg/mL with serum calcium 13.9 mg/dL.
A parathyroid ultrasound was performed.In the caudal portion of the right thyroid lobe a solid hypoechoic nodule(14 mm x 13 mm x 16 mm),with small hyperechoic images inside it suggesting microcalcifications was found.
A parathyroid sestamibi scan was negative.
OUTCOME AND FOLLOW-UP
After clinical suspicion,a genetic test of MEN1 was requested since it can change the type of parathyroid surgery to be performed.Genetic counseling was provided to thepatient,upon which she provided written authorization for MEN1 testing.Genomic DNA obtained was screened for 2-10 coding exons of the MEN1 gene by bidirectional sequence analysis and the result was negative.
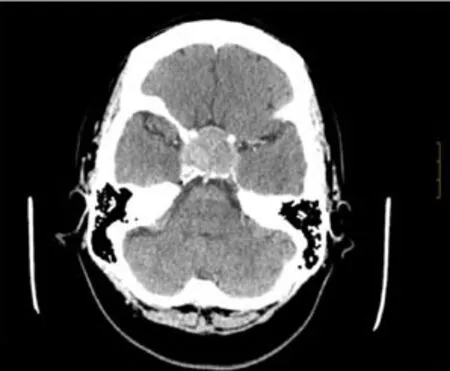
Figure 1 Axial brain computed tomography scan with contrast media administration.
A right lower parathyroidectomy was performed and the pathologic study showed the presence of an encapsulated parathyroid carcinoma of 1.5 cm,with capsular and vascular invasion(Figure 3).A MEN type 4(MEN4)genetic test was performed that was negative.
DISCUSSION
Pituitary apoplexy may result from spontaneous hemorrhage into a pituitary adenoma;after head trauma with skull base fracture;in association with hypertension,diabetes mellitus,sickle cell anemia,or acute hypovolemic shock.Until now precipitating factors include major surgery,pregnancy,gamma knife irradiation,anticoagulant therapy,coagulopathy secondary to liver failure and administration of thyrotropin releasing hormone,bromocriptine,cabergoline or gonadotrophin releasing hormone agonist[1].
FGAs are adenomas expressing and secreting biologically active gonadotropins and causing distinct clinical manifestations,in premenopausal females mainly menstrual irregularities(oligo/amenorrhea,spotting-menorrhagia)and the ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome[7].The vast majority of the immunohistochemically confirmed gonadotroph adenomas are hormonally silent(in surgical series accounted for 64% of all clinically nonfunctioning pituitary adenomas),and the FGAs are very rare with a prevalence unknown.These tumors most frequently produce FSH and less frequently produce both FSH and LH[6].The published literature includes only small case-series or individual case reports[10].
In the present case,triptorelin was administered to control menorrhagia due to the presence of uterine fibroids.To our knowledge,this is the first case of pituitary apoplexy after the use of triptorelin for pituitary down-regulation in conjunction with uterine fibroids.The exact mechanism by which GnRH agonists precipitate pituitary apoplexy in patients with pituitary adenomas is unknown[11].However,multiple factors that increase the risk or are directly associated with the cause of the bleeding have been implicated,in any case the temporal relationship with the administration of the drug strongly suggests a causal relationship.Guerraet al[12].suggest a biphasic phenomenon,because in the series of cases presented the symptoms of the patients began in the first 24 h after the administration of the drug and in others up to 10 d later.Therefore,an acute and subacute mechanism is suggested[12].
The acute pathophysiologic events due to cell degranulation and cell shrinking,in association with the abnormal capillaries,would explain the apoplexy that occur hours after giving GnRHa[13].The subacute mechanism would explain the events occurring more than a week after the medication was given,when GnRH-induced cell growth and protein synthesis can have an effect on intrasellar pressure,causing generalized ischemia and consequent bleeding[12,14].
The principle initial acute symptom is a headache that can be moderate to severe,possibly attributed to irritation or stretching of dura mater in the sella supplied by branches of the trigeminal nerve.Other clinical features commonly seen are nauseaand vomiting and can be extremely severe.Visual symptoms occur after headache,including ptosis,ophthalmoplegia,decreased visual acuity,loss of visual field,and anisocoria,consistent with the imaging finding of extrasellar extension[1,5].Prompt and proper intervention is crucial for patients with pituitary apoplexy,especially in presence of consciousness change or cranial nerve palsy.Randeva showed that visual acuity could be remarkably improved by transsphenoidal surgery.In patients operated on within 8 d,recovery was complete,but the rate dropped to only 46% after this cut-out point.Fortunately,our case patient completely recovered,although necessarily receiving transsphenoidal surgery[1].
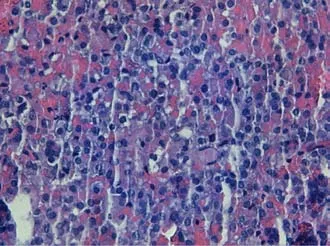
Figure 2 Microscopic findings of the pituitary adenoma.
During the follow up of the pituitary adenoma,hypercalcemia with high PTH and a parathyroid adenoma was detected.This data suggest MEN1,because she had two of the three main endocrine features of MEN 1[15,16,17].
In an analysis of 324 patients with MEN1,pituitary adenomas were found in 136 patients,and of these 85 were lactotroph,12 somatotroph,6 corticotroph,13 cosecreting(5 PRL + GH;2 PRL + FSH;4 PRL +ACTH,1 PRL + alfa-subunit,and 1 GH + alfa-subunit)and 20 nonsecreting.when 15 of the 20 nonsecreting adenomas were examined by immunocytochemistry,two stained for LH and FSH,suggesting that they were gonadotroph adenomas[18].Adenomas categorized as nonfunctioning have also been reported in other series of patients with MEN1[15],and it is well recognized that most clinically nonfunctioning adenomas are composed of cells with variable gonadotropic differentiation.
Primary hyperparathyroidism with parathyroid carcinoma was found in the present case.One of the most common endocrine diseases is primary hyperparathyroidism.It usually results from a single parathyroid adenoma,and less frequently tumors can develop in multiple parathyroid glands.Parathyroid carcinoma(PC)is a rare cause of hyperparathyroidism[19,20,21].In a retrospective study of two European cohorts of patients with primary hyperparathyroidism,the frequency of PC ranged from 0.3 to 2.1 percent.Around half of PC cases are diagnosed at an average age of 50 years with no sex or race predilection.Most of the patients present clinical and biochemical manifestations of severe hyperparathyroidism,including severe hypercalcemia,elevated parathyroid hormone level,as well as renal complications like the ones we are counting in this case[22].A palpable neck mass is present in 30%-76% of patients.However,the diagnosis of PC is rarely made preoperatively[23].There is no evidence that PC arises from pre-existing benign parathyroid lesions.PC can occur sporadically and,in 15% of cases,in association with familial isolated primary hyperparathyroidism and hyperparathyroidism-jaw tumor syndrome[24,25].This is not the case for other syndromes like multiple endocrine neoplasia(MEN1,MEN2A)where the occurrence of PC is very rare;only one case was reported in a series of 348 cases of MEN1(0.28 percent)from the Mayo Clinic from 1977 to 2013[26,27].
The genetic study of MEN1 was performed due to the presence of pituitary gonadotroph macroadenoma in addition to hyperparathyroidism,although in patients with MEN1,there are tumors in three or all four parathyroid glands[16].Beside the affectation with MEN1 it is recommended to change the type of operation to perform.Minimally invasive parathyroidectomy is not recommended,because it does not support the routine identification of all four parathyroid glands.Subtotal parathyroidectomy with transcervical near-total thymectomy is the most common initial neck operation performed[16,28].The genetic test for MEN1 was negative in our patient.Approximately 5%-10% of patients with MEN1 do not have mutations of the MEN1 gene,and these patients may have mutations involving other genes.One ofthese genes is the CDNK1B and was identified to be involved by investigations of a recessive MEN-like syndrome in a naturally occuring rat model,referred to as MEN4[29,30],where the most common phenotypic features are parathyroid and pituitary adenomas[31,32].In our patient the presence of this mutation was negative too.

Figure 3 Microscopic findings of the parathyroid carcinoma.
CONCLUSION
Pituitary adenoma apoplexy could be due to the administration of gonadotrophinreleasing hormone agonist.The presence of both pituitary adenoma and parathyroid carcinoma is infrequent and can be related to multiple endocrine neoplasia syndrome,or mutations that have not been discovered or are sporadic.
 World Journal of Clinical Cases2019年20期
World Journal of Clinical Cases2019年20期
- World Journal of Clinical Cases的其它文章
- Rh-incompatible hemolytic disease of the newborn in Hefei
- Ureteral Ewing’s sarcoma in an elderly woman:A case report
- Anaplastic lymphoma kinase-negative anaplastic large cell lymphoma masquerading as Behcet's disease:A case report and review of literature
- Synchronous quadruple primary malignancies of the cervix,endometrium,ovary,and stomach in a single patient:A case report and review of literature
- Sister Mary Joseph’s nodule in endometrial carcinoma:A case report
- Alternative technique to save ischemic bowel segment in management of neonatal short bowel syndrome:A case report
