FROM LEIBNIZ SUPERALGEBRAS TO LIE-YAMAGUTI SUPERALGEBRAS
TANG Xin-xin,ZHANG Qing-cheng,WANG Chun-yue
(1.School of Mathematics and Statistics,Northeast Normal University,Changchun 130024,China)
(2.School of Media and Mathematics and Physics,Jilin Engineering Normal University,Changchun 130052,China)
Abstract:In this paper,we study the construction of Lie-Yamaguti superalgebras.By using left Leibniz superalgebras,we give the construction of left Leibniz superalgbebras,then give the construction of Lie-Yamaguti superalgebras from left Leibniz superalgebras.So we gain the construction of Lie-Yamaguti superalgebras,which generalizes the construction of Lie-Yamaguti algebras in the situation of superalgebras.
Keywords: Lie-Yamaguiti superlagebras;(left)Leibniz superlagebras;Akivis superalgebras;Lie supertriple systems;construction
1 Introduction
Lie algebras were studied for many years in mathematics and physics,such as in quantum field theory.As the noncommutative analogs of Lie algebras,Leibniz algebras were first introduced by Cuvier and Loday in[1]and[2].Researchers obtained many results about Leibniz algebras and we can find some of them in[3–6].There are two kinds of Leibniz algebras,left Leibniz algebras and right Leibniz algebras[7].For a given non-commutative algebra(A,·),if the left multiplication lx·y=x ·y,?x,y ∈ A is a derivation of A,then(A,·)is called a left Leibniz algebra[8].As non-associative algebras,left Leibniz algebras can construct Akivis algebras[9].Kinyon and Weinstein found that a left Leibniz algebra has a Lie-Yamaguti algebra structure by using an enveloping Lie algebra of Leibniz algebras.
Recently,Leibniz algebras are generalized to Leibniz superalgebras by Dzhumadil in[10].Then some important results were obtained such as[11]and[12].Like left Leibniz algebras and right Leibniz algebras,we can similarly obtain left Leibniz superalgebras and right Leibniz superalgebras.If(A,·)is a left Leibniz superalgebra,we can obtain a right Leibniz superalgebra(A,?)by defining x ? y=(?1)|x||y|y ·x.In this paper,we study the construction of left Leibniz superalgebras and Lie-Yamaguti superalgebras.
This paper is organized as follows.In Section 2,we recall the definition of Leibniz superalgebras and prove that every non-associative superalgebra has an Akivis superalgebra structure.Then we give examples and constructions of left Leibniz superalgebras.In Section 3,we define Lie-Yamaguti superalgebras and prove that every left Leibniz superalgebra has a Lie-Yamaguti superalgebra structure.
Throughout this paper,K denotes a field of characteristic zero;All vector spaces and algebras are over K;hg(A)denotes the set of homogeneous elements of the superalgebra A.
2 Leibniz Superalgebras
In this section,we introduce the definition of Leibniz superslgebras,and then give the constructions and examples of Leibniz superalgebras.
Definition 2.1[11](i)A(left)Leibniz superalgebra is a pair(A,·),in which A is a superspace,·:A×A→A an even bilinear map such that

for all x,y,z∈hg(A).
(ii)A(right)Leibniz superalgebra is a pair(A,·),in which A is a superspace,·:A×A →A an even bilinear map such that

for all x,y,z∈hg(A).
In this paper, “Leibniz superalgebras” means “l(fā)eft Leibniz superalgebras”.A super skew-symmetric Leibniz superalgebra is a Lie superalgebra.In this case,equations(2.1)and(2.2)become the Jacobi super-identity.If(A,·)is a left Leibniz superalgebra,we can obtain a right Leibniz superalgebra(A,?)by defining x ? y=(?1)|x||y|y ·x.
Definition 2.2 Let(A,·)be a superalgebra.
(i)The super-associator of A is an even trilinear map:A×A×A→A defined by

for all x,y,z∈hg(A).
(ii)The super-Jacobian of A is an even trilinear map:A×A×A→A defined by
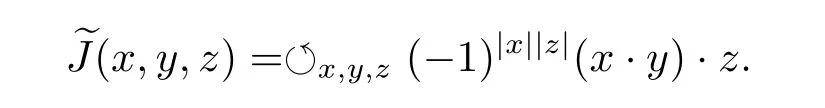
Remark 2.3 A not necessarily associative superalgebra is called a non-associative superalgebra.That is to say,(x,y,z)≠0 for some x,y,z ∈ hg(A).
Definition 2.4[13]An Akivis superalgebra is a triple(A,?,[?,?,?]),in which A is a superspace,? :A×A → A an even bilinear map,[?,?,?]:A×A×A → A an even trilinear map such that
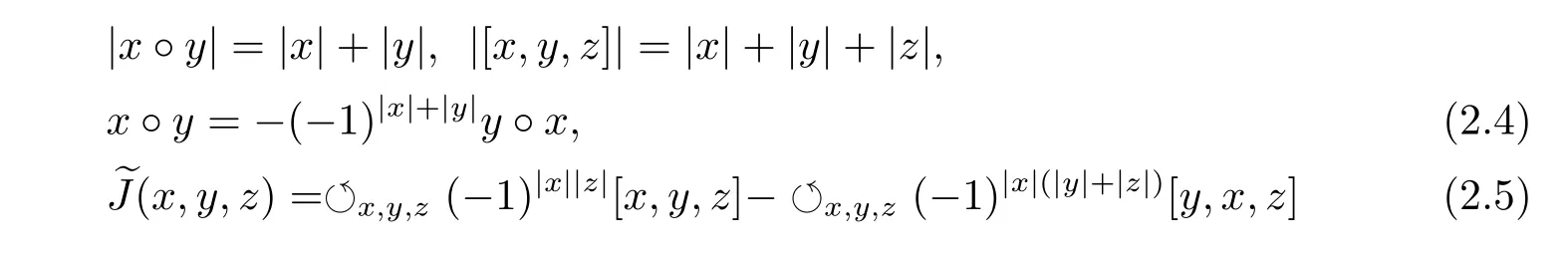
for all x,y,z∈hg(A).Equation(2.5)is called the Akivis super-identity.
Theorem 2.5 Every non-associative superalgebra(A,·)has an Akivis superalgebra(A,?,[?,?,?])structure with respect to the operation defined by

for all x,y,z∈hg(A).
Proof First,we proceed to verify that“?”is super skew-symmetric.

So we obtain equation(2.4).
Second,consider the Akivis super-identity.On one hand,
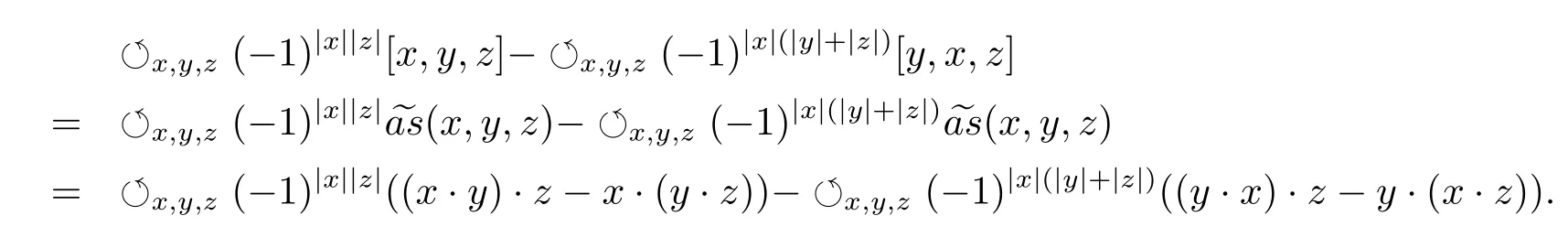
On the other hand,

That is
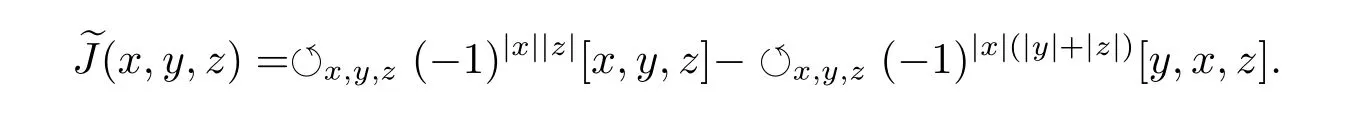
So we get equation(2.5).
An Akivis superalgebra derived from a given non-associative superalgebra A by Theorem 2.5 is said associated with A.We are interested in Akivis superalgebras associated with Leibniz superalgebras.
In terms of equation(2.3),equation(2.1)has the form

Because the operations of the Akivis superalgebra(A,?,[?,?,?])defined by the(left)Leibniz superalgebra(A,·)satisfy the super skew-symmetrization and equation(2.4),the Akivis super-identity(2.5)has the form
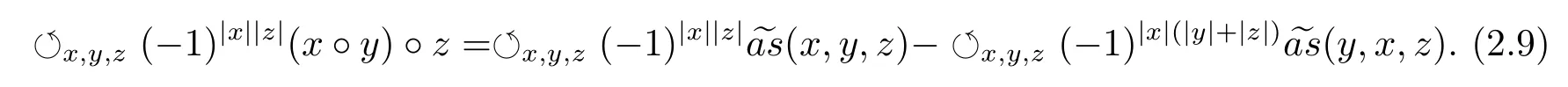
By equations(2.8)and(2.1),we have?(?1)|x||y|(y,x,z)=(x·y)·z?(x,y,z).So equaiton(2.9)becomes

Lemma 2.6 Let(A,·)be a Leibniz superalgebra,and consider on(A,·)the operation[x,y]:=x·y?(?1)|x||y|y·x for all x,y∈ hg(A).Then
(i)

(ii)
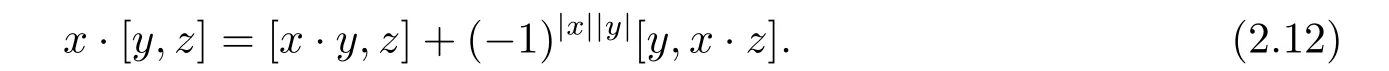
Proof(i)Equation(2.1)implies that

Likewise,interchanging x and y,we have
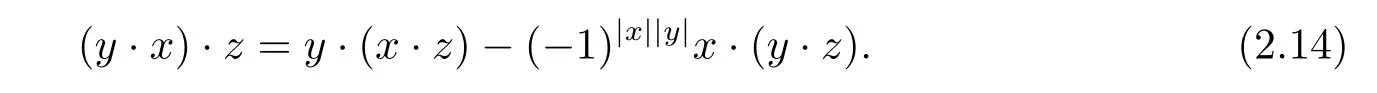
Then,consider
(ii)By calculating directly,we have

Lemma 2.7 Let(A,·)be a Leibniz superalgebra,(A,?,[?,?,?])be an Akivis superalgebra associated with Leibniz superalgebra(A,˙).Then

ProofWe get the result from equation(2.10).
An superalgebra(A,·)is called Lie-super-admissible if its commutator superalgebra(A,?)is a Lie superalgebra.We can obtain following lemma immediatly from Lemma 2.7.
Lemma 2.8 A Leibniz superalgebra(A,·)is Lie-super-admissible if and only if

for all x,y,z∈hg(A).
We now give an example of 3-dimensional Leibniz superalgebra and some methods to construct Leibniz superalgebras.We can find following definitions and similar constructions in[14].
Example 2.9 Let A=Aˉ0⊕Aˉ1be a 3-dimensional superspace.Aˉ0=span{e1,e3},Aˉ1=span{e2}.The nonzero product is given by e2·e3=e2,e3·e1=e1,e2·e2= ?e2,e3·e3=e1.Then(A,·)is a left Leibniz superalgebra.
Proposition 2.10 Let(A,?)be an associative superalgebra.Consider the linear map D:A→A which satis fies

Define an even bilinear map[?,?]D:A×A → A,such that
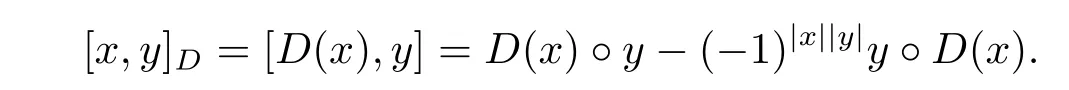
Then(A,[?,?]D)is a left Leibniz superalgebra.
Proof We only need to verify that(A,[?,?]D)is a left Leibniz superalgebra.Calculate directly,
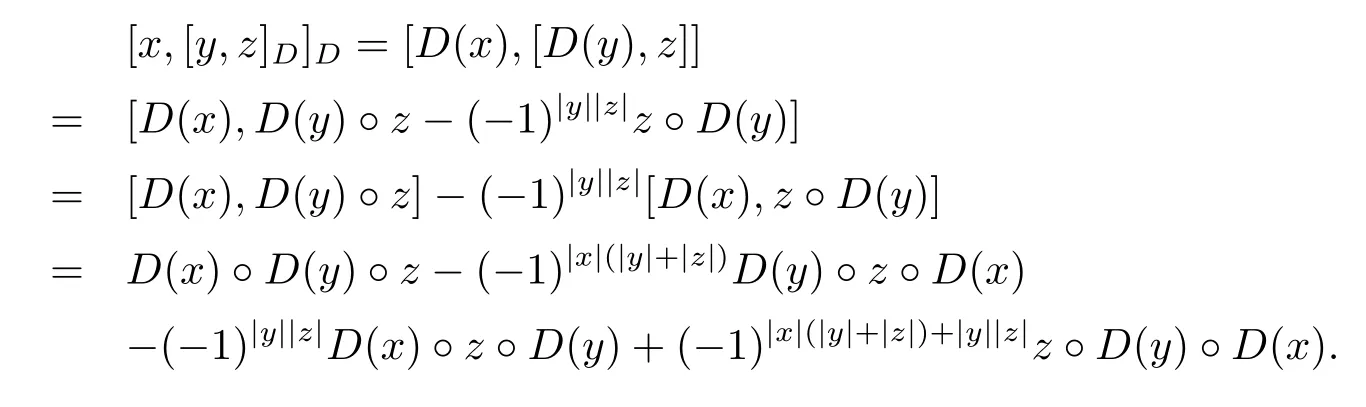
and


So we get[x,[y,z]D]D=[[x,y]D,z]D+(?1)|x||y|[y,[x,z]D]D.Therefore(A,[?,?]D)is a left Leibniz superalgebra.
Definition 2.11[14]A superdialgebra is a triple(A,?,?),in which A is a superspace,?,?:A×A→A two bilinear maps such that
(1)x?(y?z)=(x?y)?z;
(2)x?(y?z)=(x?y)?z=x?(y?z);
(3)x?(y?z)=(x?y)?z=(x?y)?z for all x,y,z∈hg(A).
Proposition 2.12 Let(A,?,?),be a superdialgebra.Define an even bilinear map[?,?]:A × A → A such that[x,y]=(?1)|x||y|y ? x ? x ? y.Then(A,[?,?])is a left Leibniz superalgebra.
Proof Calculate directly,

and

So we get[x,[y,z]]=[[x,y],z]+(?1)|x||y|[y,[x,z]].Therefore(A,[?,?])is a left Leibniz superalgebra.
Definition 2.13[14]A dendriform superalgebra is a triple(A,<,>),in which A is a superspace,<,>:A×A→A two even bilinear maps such that
(1)(x<y)<z=x<(y<z)+x<(y>z);
(2)x>(y>z)=(x<y)>z+(x>y)>z;
(3)(x>y)<z=x>(y<z)for all x,y,z∈hg(A).
Proposition 2.14 Let(A,<,>)be a dendriform superalgebra.Define two even bilinear maps?,[?,?]:A×A → A such that x?y=x< y+y> x,[x,y]=(?1)|x||y|y?x?x?y.Then(A,[?,?])is a left Leibniz superalgebra.
ProofCalculate directly,

and
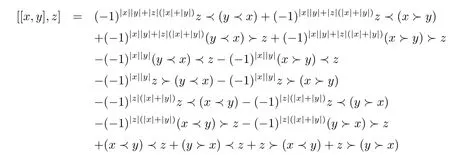
and

So we get

Therefore(A,[?,?])is a left Leibniz superalgebra.
Definition 2.15[14]A Rota-Baxter superalgebra is a triple(A,·,R),in which A is a superspace,(A,·)a superalgebra,R:A → A an even bilinear map satistying Rota-Baxter super-identity

for all x,y ∈ hg(A).R:A → A is called a Rota-Baxter super-operator of weight λ.If(A,·)is an associative superalgebra,then we call(A,·,R)associative Rota-Baxter superalgebra.
Proposition 2.16 Let(A,·,R)be an associative Rota-Baxter superalgebra with weight 0.Define two even bilinear maps?,[?,?]:A×A → A such that

Then(A,[?,?])is a left Leibniz superalgebra.
ProofCalculate directly,

and

and
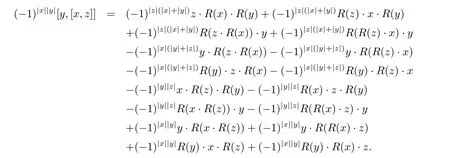
By Rota Baxter super-identity,we can get
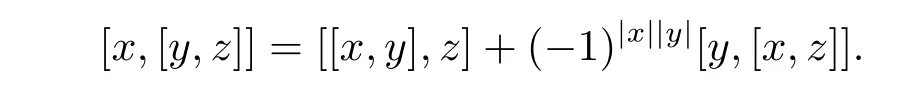
Therefore(A,[?,?])is a left Leibniz superalgebra.
3 Leibniz Superalgebras,Lie Supertriple Systems,Lie-Yamaguti Superalgebras
Definition 3.1 A Lie-Yamaguti superalgebra(LYSA)is a triple(A,[?,?],{?,?,?}),in which A is a superspace,[?,?]:A × A → A an even bilinear map and{?,?,?}:A×A×A→A an even trilinear map such that
(LYS01)|[x,y]|=|x|+|y|;
(LYS02)|{x,y,z}|=|x|+|y|+|z|;
(LYS1)d[x,y]+(?1)|x||y|[y,x]=0;
(LYS2){x,y,z}+(?1)|x||y|{y,x,z}=0;
(LYS5){x,y,[u,v]}=[{x,y,u},v]+(?1)|u|(|x|+|y|)[u,{x,y,v}];
(LYS6)
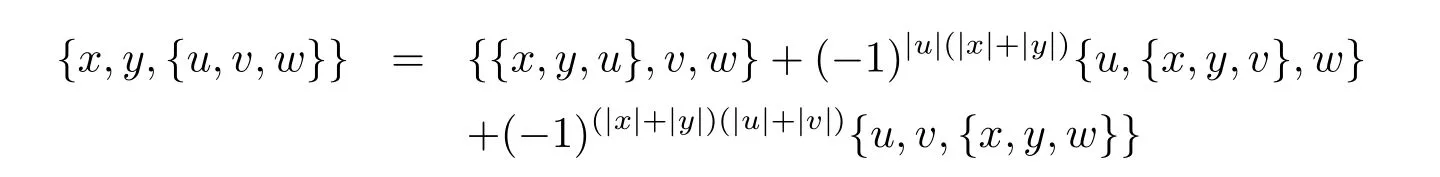
for all x,y,z,u,v,w∈hg(A),where?x,y,zdenotes the sum over cyclic permutation of x,y,z.
Definition 3.2[15]A Lie supertriple system is a pair(A,{?,?,?})such that
(1){x,y,z}=(?1)|x||y|{y,x,z};
(3)

for all x,y,z,u,v,w∈hg(A).
If[x,y]=0 for all x,y∈hg(A),then Lie-Yamaguti superalgebras become Lie supertriple systems.So Lie-Yamaguti superalgebras can be seen as general Lie supertriple systems.
Let lxdenote the left multiplication operator on(A,·)which given by lxy=x ·y for all x,y ∈ hg(A).Then equation(2.1)means that lxare super-derivations of(A,·).By Lemma 2.6(ii),we can get following proposition.
Proposition 3.3 Let(A,·)be Leibniz superlagebra,(A,?,[?,?,?])be its associate Akivis algebra.Then the operators lxare derivations of(A,?,[?,?,?])for all x ∈ A.
We can obtain a Lie-Yamaguti superalgebra structure from Leibniz superalgebra as following theorem.
Theorem 3.4 Every(left)Leibniz superalgebra(A,·)has a Lie-Yamaguti superalgebra structure(A,[?,?],{?,?,?})with respect to the operation defined by

ProofEquations(3.2),(2.1)and(2.8)imply

Moreover,we have
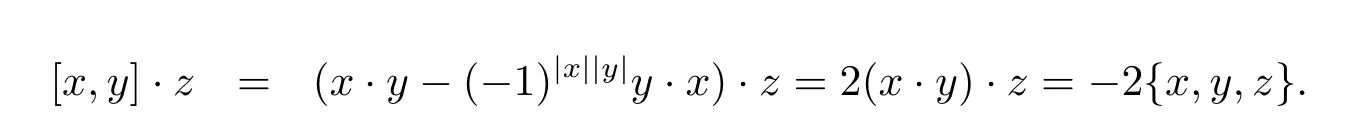
So we get

Thus equations(3.2),(3.3)and(3.4)are different expressions of the operation “{?,?,?}”.Now we proceed to verify equations(LYS1)–(LYS6).For(LYS1),

So we get(LYS1).For(LYS2),

So we get(LYS2).For(LYS3),(2.10)and(3.3)imply

So we get(LYS3)by transposition.For(LYS4),

So we get(LYS4).For(LYS5),

So we get(LYS5).For(LYS6),

So we get(LYS6).Therefore(A,[?,?],{?,?,?})is a Lie-Yamaguti superalgebra.
Remark 3.5 By Proposition 2.10,Proposition 2.12,Proposition 2.14 and Proposition 2.16,we can get left Leibniz superalgebras from associative superalgebras,superdialgebras,dendriform superalgebras and associative Rota-Baxter superalgebras.Then using Theorem 3.4,we will obtain corresponding Lie-Yamaguti superalgebras from above superalgebras[16].Then we give an 3-dimensional example of Lie-Yamaguti superalgebra by Theorem 3.4.
Example 3.6 Let A=Aˉ0⊕Aˉ1be a 3-dimensional superspace.Aˉ0=span{e1,e3},Aˉ1=span{e2}.The nonzero product is given by e2·e3=e2,e3·e1=e1,e2·e2= ?e2,e3·e3=e1.Then(A,·)is a left Leibniz superalgebra.By Theorem 2.8,when we define the binary operation and the ternary operation by(3.1)and(3.2),we get a Lie-Yamaguti superalgebra(A,[?,?],{?,?,?})with nonzero product
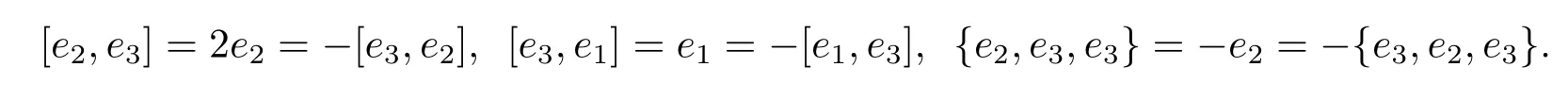
The following proposition is a direct conclusion of Theorem 3.4.
Proposition 3.7 Let(A,·)be Leibniz superlagebra,(A,?,[?,?,?])be its associate Akivis algebra.Define{x,y,z}=(?1)|x||y|[y,x,z]+[x,y,z]for all x,y,z ∈ hg(A),then(A,?,{?,?,?})is a Lie-Yamaguti superalgebra.
In Leibniz superlagebra(A,·)and its associate Akivis algebra(A,?,[?,?,?]),consider even ternaty operation

for all x,y,z∈hg(L).We have
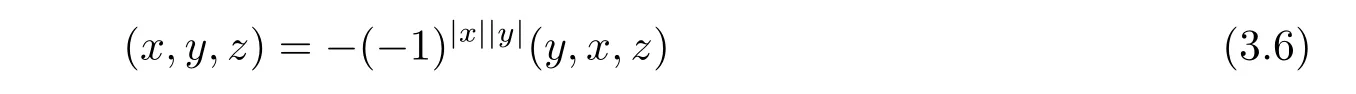
and the Akivis super-identity(2.5)is written as

A superalgebra(A,(?,?,?))called a supertriple system if the even trilinear operation satis fies(3.6)and(3.7).By Theorem 2.5,any non-associative algebra has a supertriple system structure defined by(3.5),and we call it the associate supertriple system.

