Safety evaluation of a polyherbal formulation containing hydroalcoholic extracts of Hippophae salicifolia, Nyctanthes arbor-tristis, Ocimum tenuiflorum, and Reinwardtia indica in rodents
Safety evaluation of a polyherbal formulation containing hydroalcoholic extracts of Hippophae salicifolia, Nyctanthes arbor-tristis, Ocimum tenuiflorum, and Reinwardtia indica in rodents
Dear Editor,
Herbal medicines have been used for prevention and treatment of human diseases and promotion of healthy living. These medicines, often self medicated and consumed as concentrated extracts, are not strictly regulated. Considering their popular use and increasing safety concerns, thorough evaluations of their efficacy and safety are warranted to protect consumers from potential adverse effects. Toxicity tests (acute, subacute and chronic) using animals are widely applied to evaulate adverse effects of a drug and thereby determine its "No Observed Adverse Effect Level" (NOAEL). Conducting such studies for herbal medicines will be valuable to determine potential toxic effects as well as safe dose ranges of herbal medicines just as pre-clinical and non-clinical toxicological studies are important for determining the therapeutic index of drugs.
We evaluated the acute and sub-acute toxicity of a polyherbal formulation containing hydro-alcoholic (70% ethanol) extracts of four medicinal plants, namely Nyctanthes arbor-tristis (75 mg from leaves), Ocimum tenuiflorum (50 mg from whole plant), Hippophae salicifolia (40 mg from seeds, fruits and leaves) and Reinwardtia indica (35 mg from roots) in rodents. The notable medicinal properties of these plants include the serotonergic properties of Nyctanthes arbor- tristis, whose leaves contain bioactive molecules including mannitol, glucose, essential oil, carotene, β-amyrin, β-sitosterol, hentriacontane, benzoic acid, triterpenoid (oleanolic acid, nyctanthic acid, friedeline, lupeol tannic acid, ascorbic acid, methyl salicylate) and iridoid glycosides (arborsides A, B, C)[1–2]. Ocimum tenuiflorum (family Lamiaceae) notably possesses cholinergic properties and contains eugenol, which has been reported to have acetylcholinesterase inhibitory activity[3–4]. Hippophae salicifolia (family Elaeagnaceae) is nutrient rich and possesses potent anti-oxidant properties[5]. Reinwardtia indica (family Linaceae) contains saponins, which could potentially help in the management of hyperglycemia[6–7].
We conducted acute and sub-acute oral dose toxicity studies of the test formulation in Swiss albino mice and albino Wistar rats, respectively. Single doses (10 to 5,000 mg/kg) were administered orally to mice. No treatment related deaths or clinical signs of toxicity were recorded at any of the doses at two weeks after drug administration and the lethal dose 50% of the test drug was greater than 5,000 mg/kg. For the sub-acute toxicity assessment, the doses employed ranged from 100 to 800 mg/kg·day (and vehicle as the control), which, in most cases, is acceptable as the limit dose for toxicity studies[8]. The formulation was administered orally to rats for either 14 or 28 days during which food intake and body weight were monitored. At the end of the treatment period, organ weights and haematological and biochemical parameters were measured along with a histopathologic examination. No treatment-emergent toxicities or mortality was observed. Additionally, no treatment related changes in the behaviour of the rats were observed. There was a small and insignificant reduction in body weight and food consumption of the rats in the treatment groups compared with the control group (Table 1), suggesting that sub chronic administration of the test formulation did not affect the normal growth of rats. Similarly, there were no significant changes in the weight of the organs (brain, liver, kidney, heart) following either 14 or 28 days of treatment at any of the doses compared to the controls.
Haematological parameters including haemoglobin, red blood cell count, white blood cell count, packed cell volume, mean corpuscular volume, mean corpuscular haemoglobin and mean corpuscular haemoglobin concentration were found to be all within the normal range in both the control and treatment groups (Table 2), withno significant differences between the treatment and control groups. There were also no significant treatment related effects on liver and kidney functions as determined by serum levels of cholesterol, creatinine, glucose, urea, protein, serum glutamic oxaloacetic transaminase, and serum glutamate pyruvate transaminase (Table 2). This was further confirmed by histological assessment of these organs. Additionally, there was no damage or defect in the architecture of the brain and heart in the treated or control rats. Further findings from the histological analyses of the treated rats are consistent with normal background lesions observed in clinically normal control rats. Based on these results, the NOAEL for the test formulation was established as 800 mg/kg for 28 days.
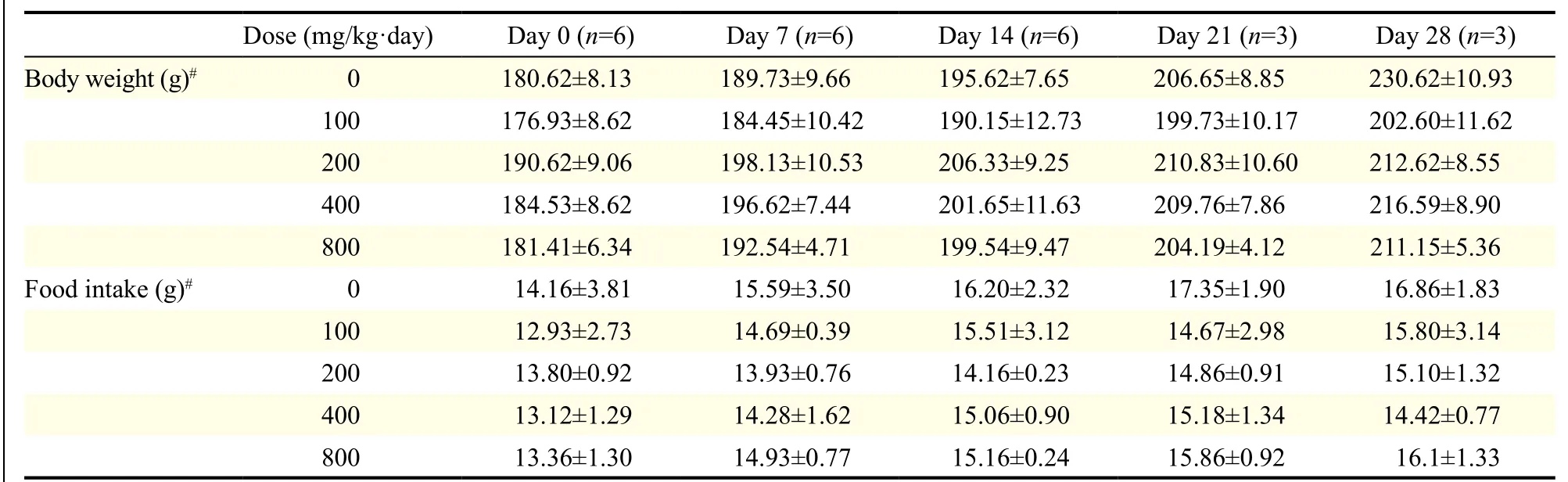
Table 1 Effect of the test formulation on the body weight and food intake of rats in the sub-acute toxicity study
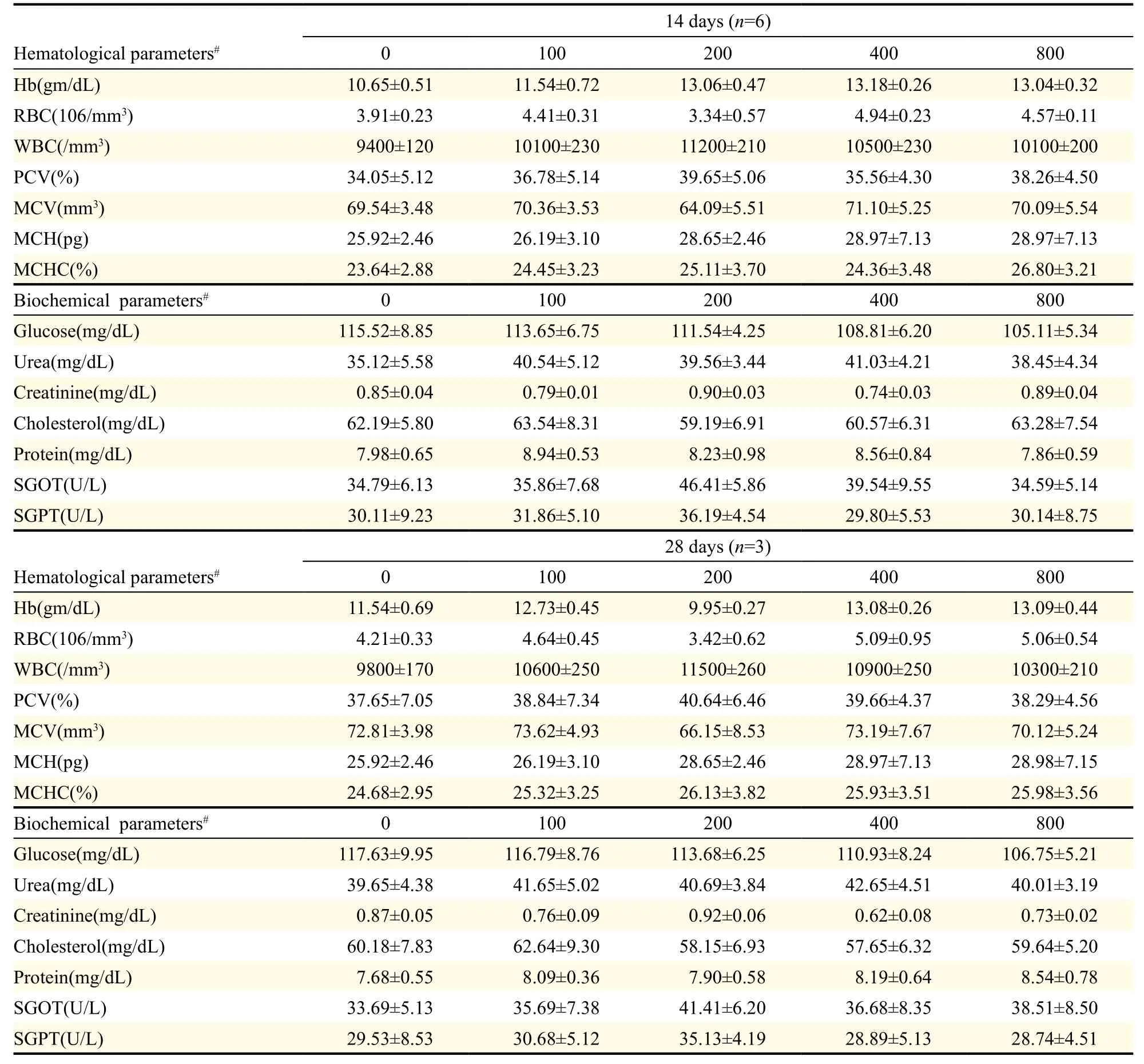
Table 2 Effect of the test formulation on haematological and biochemical parameters of rats in the sub-acute toxicity study
In conclusion, no adverse effects of the polyherbal formulation following acute (up to 5,000 mg/kg) and sub acute (up to the maximum tested dose of 800 mg/kg/day for 28 days) oral administration in rodents were observed, which thereby demonstrates a favourable safety profile of the test formulation. This study provides valuable data on the toxicity profile of hydro alcoholic extracts of the medicinal plants Nyctanthes arbor- tristis, Ocimum tenuiflorum, Hippophae salicifolia and Reinwardtia indica, with results supporting their safe longer term use in combination.
Yours Sincerely,
Rinki Kumari, Aruna Agrawal and G.P. Dubey
Institute of Medical Sciences, Banaras Hindu University Varanasi - 221005, India
K. Ilango
Interdisciplinary School of Indian System of Medicine SRM University, Kattankulathur
Kancheepuram Dist - 603203, India
Praveen K Singh, G.P.I. Singh
Adesh University, Barnala Road
Bathinda - 151109, India
?Correspoding author: Mrs. Rinki Kumari Institute of Medical Sciences, Banaras Hindu University
Varanasi - 221005, India
Tel: 0091-9359441275
E-mail: rinkiv3@gmail.com
References
[1] Das S, Sasmal D, Basu SP. Evaluation of CNS depressant activity of different plant parts of nyctanthes arbortristis linn[J]. Indian J Pharm Sci, 2008,70(6):803-806.
[2] Agrawal J, Pal A. Nyctanthes arbor-tristis Linn–a critical ethnopharmacological review[J]. J Ethnopharmacol, 2013; 146(3):645-658.
[3] Joshi H, Parle M. Cholinergic basis of memory improving effect of Ocimum tenuiflorum linn. Indian J Pharm Sci, 2006,68(3):364.
[4] Dohi S, Terasaki M, Makino M. Acetylcholinesterase inhibitory activity and chemical composition of commercial essential oils[J]. J Agric Food Chem, 2009, 57(10):4313-4318.
[5] Pant M, Lal A, Rani A. Hippophae salicifolia d don- a plant with multifarious benefits[J]. Int J Pharm Pharm Sci, 2014,6(11):37-40.
[6] Abha S, Swati V, Shukla RK. Preliminary phytochemical screening, antibacterial and nitric oxide radical scavenging activities of reinwardtia indica leaves extract[J]. Int J PharmTech Res, 2013;5:1670-1678.
[7] Elekofehinti OO. Saponins: Anti-diabetic principles from medicinal plants - A review[J]. Pathophysiology, 2015,22(2):95-103.
[8] International Conference on Harmonisation. ICH M3(R2) -Guidance on non-clinical safety studies for the conduct of human clinical trials and marketing authorization for pharmaceuticals[J]. Int Conf Harmon, 2009,3(4):25.
8 April 2015, Revised 28 July 2015, Accepted 9 December 2015, Epub 28 April 2016
R99, Documnet code: B
The authors report no conflicts of interest.
 THE JOURNAL OF BIOMEDICAL RESEARCH2016年3期
THE JOURNAL OF BIOMEDICAL RESEARCH2016年3期
- THE JOURNAL OF BIOMEDICAL RESEARCH的其它文章
- Choriocarcinoma-associated pulmonary thromboembolism and pulmonary hypertension: a case report
- Effects of microalgal polyunsaturated fatty acid oil on body weight and lipid accumulation in the liver of C57BL/6 mice fed a high fat diet
- Caspase-1 inhibition attenuates activation of BV2 microglia induced by LPS-treated RAW264.7 macrophages
- Novel monoclonal antibody against beta 1 integrin enhances cisplatin efficacy in human lung adenocarcinoma cells
- Human lgG Fc promotes expression, secretion and immunogenicity of enterovirus 71 VP1 protein
- Effect of vitamin D3 on production of progesterone in porcine granulosa cells by regulation of steroidogenic enzymes
